Triflusal
Synonym(s):α,α,α-trifluoro-2,4-cresotic acid acetate;2-(Acetyloxy)-4-(trifluoromethyl)benzoic acid;acetyl-4-trifluoromethylsalicylic acid;Drisgen;Triflusal
- CAS NO.:322-79-2
- Empirical Formula: C10H7F3O4
- Molecular Weight: 248.16
- MDL number: MFCD00866793
- EINECS: 206-297-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-12 17:04:03
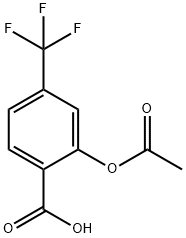
What is Triflusal?
Absorption
Absorbed in the small intestine with a bioavailability range from 83% to 100%. There is no significant difference between the absorption of the oral solution and capsule formulation. Triflusal displays a Cmax of 11.6 mcg/ml and a tmax of 0.88 h. The major metabolite of triflusal presents different pharmacokinetic properties by showing a Cmax and tmax of 92.7 mcg/ml and 4.96 h, respectively.
Toxicity
There is the possibility of producing major systemic hemorrhages.[L1168]
Description
Triflusal is an antiplatelet agent structurally related to the salicylates, but it is not derived from ASA. Triflusal and its metabolite (3-hydroxy-4-triuoro-methylbenzoic acid or HTB) produce specic inhibition of platelet arachidonic acid metabolism (McNeely and Goa, 1998). A single 12-month open-label trial of Triflusal in 73 VaD patients (López-Pousa et al., 1997) showed fewer declines in MMSE scores in the active group compared with untreated subjects. More recently, Triflusal was used in patients with amnesic MCI; 257 patients were randomized to receive 900 mg of Triflusal or placebo for 18 months. Triflusal therapy was associated with a signicantly lower rate of conversion to dementia (Gómez-Isla et al., 2008).
Chemical properties
White to Off-White Solid
The Uses of Triflusal
An analog of Aspirin; inhibits platelet aggregation. Antithrombotic.
The Uses of Triflusal
Antithrombotic;Cyclooxygenase inhibitor
Background
Triflusal is a 2-acetoxy-4-trifluoromethylbenzoic acid and it is an aspirin chemically-related molecule but not a derivative. The benefits of this agent are the lack of action over the arachidonic acid pathway, the driven production of nitric oxide and the increase of cyclic nucleotide concentration on endothelial cells. The latest translates into the expansion of peripheral blood vessels. It is very important as a secondary prevention of ischemic stroke by offering a lower risk of bleeding. It was developed by J. Uriach and Company and even though it is commercialized in different countries it is not approved by the FDA, EMA or HealthCanada.
Indications
Triflusal is indicated as prophylaxis of thromboembolic disorders. It has been registered in Spain and in other countries of Europe, South America and South Korea for the prevention of Stroke and myocardial infarction.
What are the applications of Application
Triflusal is An aspirin analog
Definition
ChEBI: 2-acetyloxy-4-(trifluoromethyl)benzoic acid is a member of salicylates, a carboxylic ester and a member of benzoic acids.
Mechanism of action
2-hydroxy-4-trifluoromethylbenzoic acid (HTB), the deacetylated metabolite of triflusal, retains significant antiplatelet activity. Triflusal is rapidly absorbed and metabolized. The area under the concentration–time curve for triflusal is 20.26 mg/L/hour after a 900-mg dose, whereas that for HTB is 42.27 mg/L/hour. Much of the pharmacokinetic data for triflusal activity is associated with HTB. The inhibition of COX, as measured by reduced production of thromboxane B2, is 25% after 2 hours and 85% after 7 days with triflusal, whereas the effects of aspirin on thromboxane B2 is more than 90% reduction after 2 hours and is maintained at this level after 7 days. It would appear that the presence of a 4-trifluoromethyl group also greatly enhances triflusal's ability to inhibit the activation of nuclear factor κB, which in turn regulates the expression of the mRNA of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 needed for platelet aggregation. In addition, triflusal increases nitric oxide synthesis in neutrophils, which results in an increased vasodilatory potential. Finally, an additional site of action for triflusal/HTB is the inhibition of cAMP phosphodiesterase, leading to increased levels of cAMP. Elevated cAMP levels decrease platelet aggregation through decreased mobilization of calcium. Aspirin and salicylic acid do not significantly increase cAMP levels.
Pharmacokinetics
Triflusal is an antithrombotic anticoagulant. It irreversibly inhibits the production of thromboxane-B2 in platelets by acetylating cycloxygenase-1. Triflusal affects many other targets such as NF kappa B, which is a gene expression regulatory factor for cycloxygenase-a and cytokines. Numerous studies comparing the efficacy and safety profile (i.e. systemic hemorrhage) between triflusal and acetylsalsylic acid has shown either no significant difference or a better effacy and safety profile for triflusal. Triflusal has been shown to protect cerebral tissue due to its inhibition of lipid peroxidation resulting from anoxia-reoxygenation.
Clinical Use
Triflusal (2-acetoxy-4-trifluoromethyl benzoic acid) is an antiplatelet drug that despite its structural similarity to aspirin exhibits quite different pharmacological and pharmacokinetic properties.
Metabolism
In the liver, triflusal undergoes deacetylation, forming its main metabolite 2-OH-4-trifluoromethyl benzoic acid (HTB). This major metabolite seems to have marked antiplatelet properties in vitro.
Properties of Triflusal
| Melting point: | 120-122° (upon slow heating); 110-112° (upon quick heating) |
| Boiling point: | 316.0±42.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.433±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO: >30mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| pka | 2.97±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | white to off-white |
| λmax | 297nm(H2O)(lit.) |
| Merck | 14,9688 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 322-79-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Triflusal
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H317:Sensitisation, Skin H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P333+P313:IF SKIN irritation or rash occurs: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Triflusal
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 322-79-2 Triflusal 98%View Details
322-79-2 Triflusal 98%View Details
322-79-2 -
 Triflusal CAS 322-79-2View Details
Triflusal CAS 322-79-2View Details
322-79-2 -
 Triflusal 98.00% CAS 322-79-2View Details
Triflusal 98.00% CAS 322-79-2View Details
322-79-2 -
 Triflusal CAS 322-79-2View Details
Triflusal CAS 322-79-2View Details
322-79-2 -
 Triflusal CAS 322-79-2View Details
Triflusal CAS 322-79-2View Details
322-79-2 -
 Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
110-86-1 -
 Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
84-74-2 -
 Thiourea 99% ARView Details
Thiourea 99% ARView Details
62-56-6
