Amitriptyline hydrochloride
Synonym(s):10,11-Dihydro-N,N-dimethyl-5H-dibenzo[a,d]cycloheptane-Δ5γ-propylamine hydrochloride;3-(10,11-Dihydro-5H-dibenzo[a,d]cyclohepten-5-ylidene)-N,N-dimethyl-1-propanamine;Amitriptyline hydrochloride;AMT
- CAS NO.:549-18-8
- Empirical Formula: C20H24ClN
- Molecular Weight: 313.86
- MDL number: MFCD00012537
- EINECS: 208-964-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:07:02
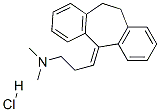
What is Amitriptyline hydrochloride ?
Description
Amitriptyline (hydrochloride) (CRM) (Item No. 19031) is a certified reference material categorized as a tricyclic antidepressant. This product is intended for analytical forensic applications. This product is also available as a general research tool .
Chemical properties
White to Off-White Solid
Originator
Elavil HCl Merck Sharp and,Dohme,US,1961
The Uses of Amitriptyline hydrochloride
Amitriptyline hydrochloride is a tricyclic antidepressant drug. Amitriptyline hydrochloride inhibits the norepinephrine and serotonin transporters but has a high affinity for α1-adrenergic, serotonin and muscarinic acetylcholine receptors.
The Uses of Amitriptyline hydrochloride
vasoconstrictor
The Uses of Amitriptyline hydrochloride
Amitriptyline hydrochloride has been used:
- as an antidepressant to study its effects on social behavior and memory in transgenic for acid sphingomyelinase (t-ASM) mice
- as a tricyclic antidepressant to analyze its effects on glucocorticoid receptor function in whole human blood
- as an anti-depressant to study its effects on scratching and locomotion behavior in chloroquine-induced mouse
What are the applications of Application
Amitriptyline Hydrochloride is an antidepressant with anticholinergic and sedative properties
Definition
ChEBI: Amitriptyline hydrochloride is an organic tricyclic compound.
Manufacturing Process
Phthalic anhydride is reacted with phenylacetic acid to form 3-
benzylidenephthalide which is then hydrogenated to 2-phenethylbenzoic acid.
Conversion to the acid chloride followed by intramolecular dehydrochlorination
yields the ketone, 5H-dibenzo[a,d]cyclohepten-5-one. The ketone undergoes a
Grignard reaction with 3-(dimethylamino)propyl chloride to give 5-(γ-
dimethylaminopropylidene)-5H-dibenzo[a,d]cycloheptene.
Then, as described in US Patent 3,205,264, a solution of 5-(γ-
dimethylaminopropylidene)-5H-dibenzo[a,d]cycloheptene (42 grams; 0.153
mol) in 105 ml of ethanol is hydrogenated over Raney nickel (1.5 grams) at
65°C under an initial hydrogen pressure of 450 lb. After 1 mol of hydrogen is
absorbed (3.5 hours), the reaction mixture is filtered to remove the catalyst
and is acidified with 80 ml of 2.5 N hydrochloric acid (0.2 mol). The acidic
solution is concentrated to dryness under vacuum and is flushed three times
with 100 ml of benzene to remove residual water. The solid residue then is
dried under vacuum at 40°C to yield 44.9 grams (94% of theory) of the
product, MP 187-189.5°C, equivalent weight 307, ultraviolet absorption A%
2380432. Recrystallization from isopropyl alcohol and ether affords the product
in high purity.
In practice it is usually used as hydrochloride.
brand name
Elavil (AstraZeneca); Endep (Roche).
Therapeutic Function
Antidepressant
General Description
Amitriptyline, 3-(10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenzo[a,d]cyclohepten-5-ylidene)-N,N-dimethyl-1-propanamine hydrochloride,5-(3-dimethylaminopropylidene)-10,11-dihydro-5Hdibenzo[a,d]cycloheptene hydrochloride (Elavil), is one ofthe most anticholinergic and sedative of the TCAs. Becauseit lacks the ring-electron–enriching nitrogen atom ofimipramine, metabolic inactivation mainly proceeds not at theanalogous 2-position but at the benzylic 10-position (i.e.,toluene-like metabolism predominates). Because of the 5-exocyclic double bond, E- and Z-hydroxy isomers are producedby oxidation metabolism. Conjugation produces excretablemetabolites. As is typical of the dimethyl compounds,N-demethylation occurs, and nortriptyline is produced, whichhas a less anticholinergic, less sedative, and more stimulantaction than amitriptyline. Nortriptyline is a SNERI; thecomposite action of drug and metabolite is nonselective.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Tricyclic antidepressant; inhibits the norepinephrine and serotonin transporters with Kis of 100 nM and 14.7 nM, respectively; high in vitro affinity for α1-adrenoceptors, serotonin and muscarinic acetylcholine receptors.
Clinical Use
Tricyclic antidepressant:
Depression, used especially where sedation is
required
Neuropathic pain (unlicensed)
Migraine prophylaxis (unlicensed)
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion, intraperitoneal, intravenous, and subcutaneous routes. Human systemic effects by ingestion: convulsions, respiratory depression, changes in sleep, hallucinations, muscle contractions, somnolence, blood pressure decrease, coma, cyanosis, dyspnea, and ataxia. An experimental teratogen. Other experimental reproductive effects. Mutation data reported. Used in the treatment of depression. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of HCl and NOx. See also ELAVIL.
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
Amitriptyline has been used for behavioral conditions such as separation anxiety or generalized anxiety in dogs, and excessive grooming, spraying and anxiety in cats. Amitriptyline may be useful for adjunctive treatment of pruritus, or chronic pain of neuropathic origin in dogs and cats. In cats, it potentially could be useful for adjunctive treatment of lower urinary tract disease. Amitriptyline has been tried to reduce feather plucking in birds.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Alcohol: increased sedative effect.
Analgesics: increased risk of CNS toxicity with
tramadol; possibly increased risk of side effects with
nefopam; possibly increased sedative effects with
opioids.
Anti-arrhythmics: increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias with amiodarone - avoid; increased
risk of ventricular arrhythmias with disopyramide,
flecainide or propafenone; avoid with dronedarone.
Antibacterials: increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias with moxifloxacin and delamanid -
avoid with moxifloxacin.
Anticoagulants: may alter anticoagulant effect of
coumarins.
Antidepressants: possibly increased serotonergic
effects with duloxetine; enhanced CNS excitation
and hypertension with MAOIs and moclobemide;
concentration possibly increased with SSRIs; risk
of ventricular arrhythmias with citalopram and
escitalopram - avoid; possible increased risk of
convulsions with vortioxetine; concentration reduced
by St John’s wort.
Antiepileptics: convulsive threshold lowered;
concentration reduced by carbamazepine,
phenobarbital and possibly fosphenytoin, phenytoin
and primidone.
Antimalarials: avoid with artemether/lumefantrine
and piperaquine with artenimol.
Antipsychotics: increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias especially with droperidol, fluphenazine,
haloperidol, pimozide, sulpiride and zuclopenthixol
- avoid; increased antimuscarinic effects with
clozapine and phenothiazines; concentration
increased by antipsychotics.
Antivirals: increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias
with saquinavir - avoid; concentration possibly
increased with ritonavir.
Atomoxetine: increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias and possibly convulsions.
Beta-blockers: increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias with sotalol.
Clonidine: tricyclics antagonise hypotensive
effect; increased risk of hypertension on clonidine
withdrawal.
Cytotoxics: increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias
with arsenic trioxide.
Dapoxetine: possibly increased risk of serotonergic
effects - avoid. Dopaminergics: avoid with entacapone; CNS
toxicity reported with selegiline and rasagiline.
Pentamidine: increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias.
Sympathomimetics: increased risk of hypertension
and arrhythmias with adrenaline and noradrenaline;
metabolism possibly inhibited by methylphenidate.
Metabolism
Amitriptyline undergoes extensive first-pass metabolism and is demethylated in the liver by the cytochrome P450 isoenzymes CYP3A4, CYP2C9, and CYP2D6 to its primary active metabolite, nortriptyline. Other paths of metabolism of amitriptyline include hydroxylation (possibly to active metabolites) by CYP2D6 and N-oxidation; nortriptyline follows similar paths. Amitriptyline is excreted in the urine, mainly in the form of its metabolites, either free or in conjugated form.
storage
Room temperature (desiccate)
Properties of Amitriptyline hydrochloride
| Melting point: | 196-197°C |
| Flash point: | 11 °C |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | H2O: soluble |
| form | powder |
| pka | 9.4(at 25℃) |
| color | white to off-white |
| PH | 4.5~6.0 (10g/l, 25℃) |
| Water Solubility | almost transparency |
| Merck | 14,487 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 549-18-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Amitriptyline hydrochloride (549-18-8) |
Safety information for Amitriptyline hydrochloride
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H301:Acute toxicity,oral H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Amitriptyline hydrochloride
Amitriptyline hydrochloride manufacturer
HRV Global Life Sciences
Rivashaa Agrotech Biopharma Pvt. Ltd.
Ralington Pharma
S D Fine Chem Limited
Gemini Exports
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 549-18-8 Amitriptyline hydrochloride 98%View Details
549-18-8 Amitriptyline hydrochloride 98%View Details
549-18-8 -
 549-18-8 98%View Details
549-18-8 98%View Details
549-18-8 -
![5-[3-(Dimethylamino)propylidene]dibenzosuberane hydrochloride CAS 549-18-8](https://img.chemicalbook.in//Content/image/CP5.jpg) 5-[3-(Dimethylamino)propylidene]dibenzosuberane hydrochloride CAS 549-18-8View Details
5-[3-(Dimethylamino)propylidene]dibenzosuberane hydrochloride CAS 549-18-8View Details
549-18-8 -
 Amitriptyline Hydrochloride CAS 549-18-8View Details
Amitriptyline Hydrochloride CAS 549-18-8View Details
549-18-8 -
 Amitriptyline hydrochloride 99%View Details
Amitriptyline hydrochloride 99%View Details
549-18-8 -
 549-18-8 Amitriptyline hydrochloride 98%View Details
549-18-8 Amitriptyline hydrochloride 98%View Details
549-18-8 -
 Amitriptyline hydrochloride >98% (HPLC) CAS 549-18-8View Details
Amitriptyline hydrochloride >98% (HPLC) CAS 549-18-8View Details
549-18-8 -
 Amitriptyline hydrochloride CAS 549-18-8View Details
Amitriptyline hydrochloride CAS 549-18-8View Details
549-18-8