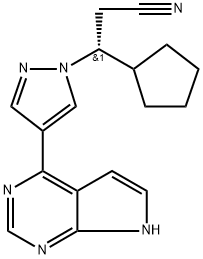
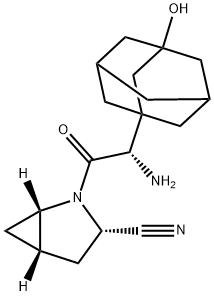
Saxagliptin
- CAS NO.:361442-04-8
- Empirical Formula: C18H25N3O2
- Molecular Weight: 315.41
- MDL number: MFCD12756398
- EINECS: 1308068-626-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-10-14 17:29:00
What is Saxagliptin?
Absorption
Following a 5 mg single oral dose of saxagliptin to healthy subjects, the mean plasma AUC values for saxagliptin and its active metabolite were 78 ng?h/mL and 214 ng?h/mL, respectively. The corresponding plasma Cmax values were 24 ng/mL and 47 ng/mL, respectively. Saxagliptin did not accumulate following repeated doses. The median time to maximum concentration (Tmax) following the 5 mg once daily dose was 2 hours for saxagliptin and 4 hours for its active metabolite. Bioavailability, 2.5 - 50 mg dose = 67%
Toxicity
Adverse reactions reported in ≥5% of patients treated with saxagliptin and more commonly than in patients treated with placebo are: upper respiratory tract infection, urinary tract infection, and headache.
Chemical properties
White Solid
The Uses of Saxagliptin
Saxagliptin is a potent and selective reversible inhibitor of dipeptidyl peptidase-4, which is being developed for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. It is absorbed rapidly after oral administration an d has a pharmacokinetic profile compatible with once daily dosing.
The Uses of Saxagliptin
Saxagliptin is a potent and selective reversible inhibitor of dipeptidyl peptidase-4, which is being developed for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. It is absorbed rapidly after oral administration and has a pharmacokinetic profile compatible with once daily dosing.
Background
Saxagliptin (rINN) is an orally active hypoglycemic (anti-diabetic drug) of the new dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor class of drugs. FDA approved on July 31, 2009.
Indications
Treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus to improve glycemic control in combination with other agents or as monotherapy.
What are the applications of Application
Saxagliptin is a potent and selective reversible inhibitor of dipeptidyl peptidase-4
Definition
ChEBI: A monocarboxylic acid amide obtained by formal condensation of the carboxy group of (2S)-amino(3-hydroxyadamantan-1-yl)acetic acid with the amino group of (1S,3S,5S)-2-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hex ne-3-carbonitrile. Used in its monohydrate form for the treatment of Type II diabetes.
Pharmacokinetics
Post-administration of saxagliptin, GLP-1 and GIP levels rise up to 2- to 3- fold. Because it is very selective of DPP-4 inhibition, there are fewer systemic side effects. Saxagliptin inhibits DPP-4 enzyme activity for a 24-hour period. It also decreased glucagon concentrations and increased glucose-dependent insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells. The half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) is 0.5 nmol/L. Saxagliptin did not prolong the QTc interval to a clinically significant degree.
Clinical Use
Saxagliptin, previously identified as BMS-477118, is an oral hypoglycemic of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor class developed by Bristol-Myers Squibb for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. DPP-IV is the primary enzyme responsible for degradation of incretins, such as glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), which is a hormone responsible for the glucose-dependent stimulation of insulin in humans. Inhibitors of DPP-IV serve as effective glucose regulators by increasing the endogenous concentration of GLP-1.
Synthesis
The initial discovery route to saxagliptin was a 15-step, convergent synthesis focused on the production and use of compounds 109
and 113 (Schemes a and b). While the strategy of early
drug delivery involved rapid synthesis to support preclinical
activities and Phase I clinical trials, as saxagliptin entered Phase
II, a greater emphasis was placed on defining and demonstrating
a commercially viable synthetic process. Scheme a describes a
more expedient route to the preparation of adamantylamino acid
109. Commercially available 1-adamantoic acid (106) was first
converted to the corresponding acid halide through the use of
thionyl chloride prior to a Grignard addition reaction utilizing
iodomethane and magnesium metal to furnish ketone 107. This
ketone was then subjected to oxidizing conditions involving potassium
permanganate to provide the hydroxylated ketoacid 108.
The amino acid 109 was furnished through the use of phenylalanine
dehydrogenase in near-quantitative yield in 99% enantioselectivity.
The synthesis of 113 began with commercially available ethyl
N-tert-butoxycarbonylpyroglutamate (110) (Scheme b). Selective
reduction of the amide carbonyl within 110 through the use
of lithium triethylborohydride followed by acylation and baseinduced
elimination of the resulting aminal and careful hydrolysis gave rise to dihydropyrrole 111 with full retention of stereochemical
configuration in 95% yield. Amidation followed by Simmons¨C
Smith cyclopropanation employing methylene iodide converted
111 to the cyclopropanated product 112, which was then converted
to the key coupling partner 113.
The core of saxagliptin was formed by the amide coupling of
amino acid 109 and methanoprolinamide 113 to give amide 114
in 95% yield (Scheme c). Subsequent dehydration of the primary
amide 114 using trifluoroacetic acid anhydride and ethyl nicotinate
gave nitrile 115 in 98% yield. Removal of both the alcohol
and amine protecting groups with HCl afforded saxagliptin (XVIII)
in 88% yield.

Metabolism
The metabolism of saxagliptin is primarily mediated by cytochrome P450 3A4/5 (CYP3A4/5). 50% of the absorbed dose will undergo hepatic metabolism. The major metabolite of saxagliptin, 5-hydroxy saxagliptin, is also a DPP4 inhibitor, which is one-half as potent as saxagliptin.
Metabolism
Metabolism is mainly by cytochrome P450 3A4/5.
The major metabolite of saxagliptin is also a selective,
reversible, competitive DPP 4 inhibitor, half as potent as
saxagliptin.
Saxagliptin and 5-hydroxy saxagliptin are excreted in
the urine; there may be some active renal excretion of
unchanged saxagliptin. There is also some elimination via
the faeces.
Properties of Saxagliptin
| Melting point: | 103 - 107°C |
| Boiling point: | 548.7±35.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.35 |
| Flash point: | 548.7℃ |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Sparingly) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 15.12±0.40(Predicted) |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Stability: | Temperature Sensitive |
Safety information for Saxagliptin
Computed Descriptors for Saxagliptin
Saxagliptin manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 361442-04-8 Saxagliptin 98%View Details
361442-04-8 Saxagliptin 98%View Details
361442-04-8 -
 361442-04-8 98%View Details
361442-04-8 98%View Details
361442-04-8 -
 Saxagliptin 98%View Details
Saxagliptin 98%View Details
361442-04-8 -
 Saxagliptin 361442-04-8 98%View Details
Saxagliptin 361442-04-8 98%View Details
361442-04-8 -
 Saxagliptin 95% CAS 361442-04-8View Details
Saxagliptin 95% CAS 361442-04-8View Details
361442-04-8 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4