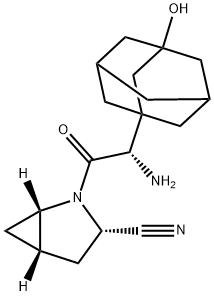
Vildagliptin
- CAS NO.:274901-16-5
- Empirical Formula: C17H25N3O2
- Molecular Weight: 303.4
- MDL number: MFCD08275142
- EINECS: 630-410-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-24 08:33:08

What is Vildagliptin?
Absorption
In a fasting state, vildagliptin is rapidly absorbed following oral administration. Peak plasma concentrations are observed at 1.7 hours following administration. Plasma concentrations of vildagliptin increase in an approximately dose-proportional manner.
Food delays Tmax to 2.5 hours and decreases Cmax by 19%, but has no effects on the overall exposure to the drug (AUC). Absolute bioavailability of vildagliptin is 85%.
Toxicity
The oral Lowest published toxic dose (TDLO) is 0.3 mg/kg in rats and 1 mg/kg in mice.
There is limited information regarding overdose with vildagliptin. In one study, patients experienced muscle pain, mild and transient paresthesia, fever, edema, and a transient increase in lipase levels at a dose of 400 mg. At 600 mg, one subject experienced edema of the feet and hands and increases in creatine phosphokinase (CPK), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), C-reactive protein (CRP) and myoglobin levels. Supportive management is recommended in case of an overdose. There is no known antidote, and vildagliptin and its major metabolite cannot be removed via hemodialysis.
Description
Vildagliptin, a DPP-4 inhibitor, was launched for the oral treatment of type 2 diabetes. Vildagliptin is the second DPP-4 inhibitor to reach the market behind sitagliptin, which was introduced in 2006. DPP-4 inhibitors act by slowing the inactivation of incretins, which are endogenous peptides involved in the physiologic regulation of glucose homeostasis. When blood glucose concentrations are normal or elevated, GLP-1 and GIP increase the synthesis and release of insulin from pancreatic βcells via intracellular signaling pathways involving cAMP. GLP-1 also lowers glucagon secretion from pancreatic α cells, which leads to reduced hepatic glucose production. However, although GLP-1 and GIP effectively lower blood glucose, they are short-lived as a result of rapid inactivation by the ubiquitous serine protease DPP-4. By inhibiting DPP-4, vildagliptin increases the concentration and duration of active incretin levels, which in turn results in increased insulin release and decreased glucagon levels in a glucose-dependent manner. Both vildagliptin and sitagliptin are potent, competitive, reversible inhibitors of DPP- 4 (IC50=3.5 and 18 nM, respectively), and they both show slow, tight-binding inhibition kinetics.
Chemical properties
White Solid
Originator
Novartis (US)
The Uses of Vildagliptin
Labelled Vildagliptin. It is a new oral anti-hyperglycemic agent of a new dipeptidyl peptidase-IV (DPP-IV) inhibitor class of drugs. Antidiabetic.
The Uses of Vildagliptin
A metabolite of Vildagliptin
The Uses of Vildagliptin
Vildagliptin (LAF-237) inhibits DPP?4 with IC50 of 2.3 nM
The Uses of Vildagliptin
The major metabolite of Vildagliptin
Background
Vildagliptin is an orally active antihyperglycemic agent that selectively inhibits dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4). It is used to treat type II diabetes in which GLP-1 secretion and insulinotropic effects are impaired. By inhibiting DPP-4, vildagliptin prevents the degradation of glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP), which are incretins that promote insulin secretion and regulate blood glucose levels. hormone. Elevated levels of GLP-1 and GIP improve glycemic control. In clinical trials, the risk of hypoglycemia with vildagliptin was relatively low.
What are the applications of Application
Vildagliptin is a CD26 inhibitor associated with immune response inhibition
Definition
ChEBI: Vildagliptin is an amino acid amide.
brand name
Galvus
Pharmacokinetics
Vildagliptin works to improve glycemic control in type II diabetes mellitus by enhancing the glucose sensitivity of beta-cells (β-cells) in pancreatic islets and promoting glucose-dependent insulin secretion. Increased GLP-1 levels leads to enhanced sensitivity of alpha cells to glucose, promoting glucagon secretion. Vildagliptin causes an increase in the insulin to glucagon ratio by increasing incretin hormone levels: this results in a decrease in fasting and postprandial hepatic glucose production. Vildagliptin does not affect gastric emptying. It also has no effects on insulin secretion or blood glucose levels in individuals with normal glycemic control.
In clinical trials, treatment with vildagliptin 50-100 mg daily in patients with type 2 diabetes significantly improved markers of beta-cells, proinsulin to insulin ratio, and measures of beta-cell responsiveness from the frequently-sampled meal tolerance test. Vildagliptin has improves glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) and fasting plasma glucose (FPG) levels.
Clinical Use
Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor:
Treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus in combination with other antidiabetic drugs
Side Effects
The most common adverse events reported in patients receiving vildagliptin included headache, nasopharyngitis, cough, constipation, dizziness, and increased sweating. Vildagliptin is not recommended for patients with liver impairment.
Synthesis
Vildagliptin is chemically derived in three steps starting from L-prolinamide via acylation with chloroacetyl chloride to produce 1-(chloroacetyl)-L-prolinamide, subsequent dehydration of the carboxamide group to the nitrile with trifluoroacetic anhydride, and condensation of the 1-(chloroacetyl)-L-prolinenitrile intermediate with 3-hydroxyadamantan-1-amine.
Precautions
Inform your healthcare professional if you:
Are allergic to this medication or any of the other ingredients of this medication
Are pregnant, planning to become pregnant or breastfeeding
Have pancreas problems such as pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas)
Have gallstones, drink alcohol very often or have very high levels of triglycerides (a type of cholesterol) in your blood. These medical conditions can increase your chances of getting pancreatitis.
Have kidney or liver problems
If you need to do fasting blood tests, do not take your medication until your blood has been taken and you have eaten.
Metabolism
About 69% of orally administered vildagpliptin is eliminated via metabolism not mediated by cytochrome P450 enzymes. Based on the findings of a rat study, DPP-4 contributes partially to the hydrolysis of vildagliptin. Vildagliptin is metabolized to pharmacologically inactive cyano (57%) and amide (4%) hydrolysis products in the kidney. LAY 151 (M20.7) is a major inactive metabolite and a carboxylic acid that is formed via hydrolysis of the cyano moiety: it accounts for 57% of the dose. Other circulating metabolites reported are an N-glucuronide (M20.2), an N-amide hydrolysis product (M15.3), two oxidation products, M21.6 and M20.9.
Metabolism
About 69
% of a dose of vildagliptin is metabolised,
mainly by hydrolysis in the kidney to inactive metabolites.
About 85
% of a dose is excreted in the urine (23
% as
unchanged drug), and 15
% in the faeces.
References
1) Balas?et al.?(2007),?The dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor vildagliptin suppresses endogenous glucose production and enhances islet function after single-dose administration in type 2 diabetic patients;? J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab.,?92?1249 2) Ahren?et al. (2004),?Inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 reduces glycemia, sustains insulin levels and reduces glucagon levels in type 2 diabetes;? J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab., 89?2078 3) Kosaraju?et al. (2013),?Vildagliptin: an anti-diabetes agent ameliorates cognitive deficits and pathology observed in streptozotocin-induced Alzheimer’s disease;? J. Pharm. Pharmacol.,?65?1773 4) Shimizu?et al. (2012),?DPP4 inhibitor vildagliptin preserves? β-cell mass through amelioration of endoplasmic reticulum stress in C/EBPB transgenic mice;? J. Mol. Endocrinol.,?49?125
Properties of Vildagliptin
| Melting point: | 153-155?C |
| Boiling point: | 531.3±50.0 °C(Predicted) |
| alpha | -78.3° (c = 9.73 in methanol) |
| Density | 1.27 |
| Flash point: | 275.1℃ |
| storage temp. | Keep in dark place,Inert atmosphere,Store in freezer, under -20°C |
| solubility | Soluble in DMSO (up to 45 mg/ml), in DMF (up to 20 mg/ml), or in Ethanol (up to 20 mg/ml). |
| form | solid |
| pka | 15.05±0.40(Predicted) |
| color | White |
| Stability: | Stable for 2 years from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions in DMSO, DMF, or ethanol may be stored at -20°C for up to 3 months |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C17H25N3O2/c18-9-14-2-1-3-20(14)15(21)10-19-16-5-12-4-13(6-16)8-17(22,7-12)11-16/h12-14,19,22H,1-8,10-11H2/t12?,13?,14-,16?,17?/m0/s1 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 274901-16-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Vildagliptin
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H332:Acute toxicity,inhalation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Vildagliptin
| InChIKey | SYOKIDBDQMKNDQ-XWTIBIIYSA-N |
| SMILES | N1(C(CNC23CC4CC(CC(O)(C4)C2)C3)=O)CCC[C@H]1C#N |
Vildagliptin manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
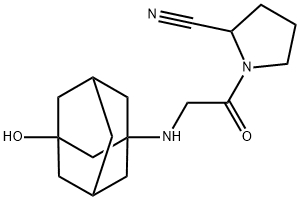
You may like
-
 Vildagliptin 99%View Details
Vildagliptin 99%View Details -
 ?274901-16-5 98%View Details
?274901-16-5 98%View Details
?274901-16-5 -
 Vildagliptin 99%View Details
Vildagliptin 99%View Details -
 Vildagliptin 99%View Details
Vildagliptin 99%View Details -
 VILDAGLIPTIN 98%View Details
VILDAGLIPTIN 98%View Details -
 Vildagliptin 98%View Details
Vildagliptin 98%View Details -
 VILDAGLIPTIN 99%View Details
VILDAGLIPTIN 99%View Details -
 Vildagliptin Api IntermediateView Details
Vildagliptin Api IntermediateView Details
274901-16-5
