Sitagliptin
- CAS NO.:486460-32-6
- Empirical Formula: C16H15F6N5O
- Molecular Weight: 407.31
- MDL number: MFCD09838015
- EINECS: 690-730-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-23 21:30:31
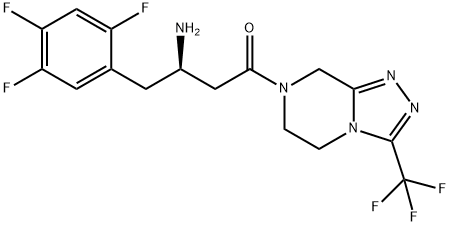
What is Sitagliptin?
Absorption
Sitagliptin is 87% orally bioavailable and taking it with or without food does not affect its pharmacokinetics. Sitagliptin reaches maximum plasma concentration in 2 hours.
Toxicity
Animal studies in pregnancy have shown no adverse effects on the mother or offspring at normal doses, however these results are not always applicable to humans. There is currently a voluntary registry of fetal exposure. Animal studies at 100 times the maximum recommended human dose resulted in an increase in rib malformations. Sitagliptin is excreted in the milk of rats but it is not known if it would also be expressed in human breast milk. Because many drugs are expressed in human breast milk, the risk and benefit of prescribing the medication must be considered. There is currently a lack of safety and effectiveness data in pediatric patients. No differences in safety and efficacy were observed in geriatric patients compared to younger patients, however caution should be used in this population as they are more likely to have reduced renal function. Sitagliptin has also been associated with a 34% relative risk increase for all cause infection. There was no significant difference in patient response across sex, age, race, ethnicity, and BMI.
Description
Sitagliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor, is a first-in-class oral drug launched for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. It acts by slowing the inactivation of incretins, which are endogenous peptides involved in the physiologic regulation of glucose homeostasis. Incretin hormones, including glucagonlike peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP), are released by the intestine throughout the day, and levels are increased in response to a meal. When blood glucose concentrations are normal or elevated,GLP-1 and GIP increase the synthesis and release of insulin from pancreatic b cells via intracellular signaling pathways involving cAMP. GLP-1 also lowers glucagon secretion from pancreatic αcells, which leads to reduced hepatic glucose production.
Originator
Merck (US)
The Uses of Sitagliptin
Labeled Sitagliptin , intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of Sitagliptin by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry.
The Uses of Sitagliptin
Sitagliptin is a useful pharmaceutical drug. Could be useful for treating intestinal inflammation, diabetes, pre-?diabetes, impaired glucose tolerance, hepatitis, and?/or inflammatory liver disease.
What are the applications of Application
Sitagliptin is a DPP-4 inhibitor
Background
Sitagliptin is an oral dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor used in conjunction with diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. The effect of this medication leads to glucose dependent increases in insulin and decreases in glucagon to improve control of blood sugar. Sitagliptin was granted FDA approval on October 16, 2006.
Indications
Sitagliptin is indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. It is not used to treat type 1 diabetes or patients with a history of pancreatitis.
It is also used in combination with metformin or ertugliflozin.
Definition
ChEBI: Sitagliptin is a triazolopyrazine that exhibits hypoglycemic activity. It has a role as a serine proteinase inhibitor, a hypoglycemic agent, an EC 3.4.14.5 (dipeptidyl-peptidase IV) inhibitor, an environmental contaminant and a xenobiotic. It is a triazolopyrazine and a trifluorobenzene.
brand name
Januvia
Mechanism of action
Sitagliptin's mechanism of action is through inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4), an enzyme that acts to degrade and inactivate glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1). The elevated GLP-1 level in response to sitagliptin results in increased insulin release after meals, and improved glucose tolerance.
brand name
Januvia
Pharmacokinetics
Sitagliptin inhibits DPP-4 which leads to increased levels of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide(GIP), decreased levels of glucagon, and a stronger insulin response to glucose.
Clinical Use
Treatment of type 2 diabetes in combination with metformin or a thiazolidinedione
Side Effects
A common side effect of Sitagliptin is headache. Low blood sugar may occur when it is taken with other diabetes medicines such as insulin or gliclazide.Sitagliptin may also have other side effects, including upper respiratory tract infections, stuffy or runny nose, sore throat stomach upset, diarrhoea, and swelling of the hands or legs. Severe can cause pancreatitis and liver problems. Serious allergic reactions are rare.
Metabolism
Sitagliptin is mostly not metabolised, with 79% of the dose excreted in the urine as the unchanged parent compound. Minor metabolic pathways are mediated mainly by cytochrome p450(CYP)3A4 and to a lesser extent by CYP2C8. After 18 hours, 81% of the dose has remained unchanged, while 2% has been N-sulfated to the M1 metabolite, 6% has been oxidatively desaturated and cyclized to the M2 metabolite, <1% glucuronidated at an unknown site to the M3 metabolite, <1% has been carbamoylated and glucuronidated to the M4 metabolite, 6% has been oxidatively saturated and cyclized to the M5 metabolite, and 2% has been hydroxylated at an unknown site to the M6 metabolite. The M2 metabolite is the cis isomer while the M5 metabolite is the trans isomer of the same metabolite.
Metabolism
Sitagliptin undergoes minimal metabolism, mainly by the
cytochrome P450 isoenzyme CYP3A4, and to a lesser
extent by CYP2C8.
Renal excretion of sitagliptin involves active tubular
secretion; it is a substrate for organic anion transporter-3
and P-glycoprotein.
Properties of Sitagliptin
| Melting point: | 114.1-115.7 °C |
| Boiling point: | 529.9±60.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.61±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Store at -20°C |
| solubility | DMSO : ≥ 50 mg/mL (122.76 mM) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 7.20±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | White to off-white |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C16H15F6N5O/c17-10-6-12(19)11(18)4-8(10)3-9(23)5-14(28)26-1-2-27-13(7-26)24-25-15(27)16(20,21)22/h4,6,9H,1-3,5,7,23H2/t9-/m1/s1 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 486460-32-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 1-Butanone, 3-amino-1-[5,6-dihydro-3-(trifluoromethyl)-1,2,4-triazolo[4,3-a]pyrazin-7(8H)-yl]-4-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)-, (3R)- (486460-32-6) |
Safety information for Sitagliptin
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Sitagliptin
| InChIKey | MFFMDFFZMYYVKS-SECBINFHSA-N |
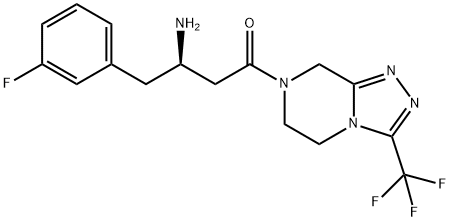
| SMILES | C(N1CCN2C(C(F)(F)F)=NN=C2C1)(=O)C[C@H](N)CC1=CC(F)=C(F)C=C1F |
Sitagliptin manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

![Benzenebutanoicacid,b-[[(1,1-diMethylethoxy)carbonyl]aMino]-2,4,5-trifluoro-,Methylester,(bR)-](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/20150408/GIF/881995-73-9.gif)
![2-CHLOROMETHYL-5-TRIFLUOROMETHYL-[1,3,4]OXADIAZOLE](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/723286-98-4.gif)
You may like
-
 Sitagliptin 98%View Details
Sitagliptin 98%View Details -
 Sitagliptin 99%View Details
Sitagliptin 99%View Details -
 Sitagliptin 98%View Details
Sitagliptin 98%View Details -
 Sitagliptin 98%View Details
Sitagliptin 98%View Details -
 Sitagliptin 486460-32-6 98%View Details
Sitagliptin 486460-32-6 98%View Details
486460-32-6 -
 Sitagliptin 99%View Details
Sitagliptin 99%View Details -
 Sitagliptin 98% CAS 486460-32-6View Details
Sitagliptin 98% CAS 486460-32-6View Details
486460-32-6 -
 Sitagliptin 98% (HPLC) CAS 486460-32-6View Details
Sitagliptin 98% (HPLC) CAS 486460-32-6View Details
486460-32-6
