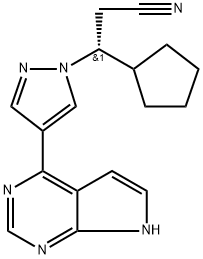
Ruxolitinib
- CAS NO.:941678-49-5
- Empirical Formula: C17H18N6
- Molecular Weight: 306.37
- MDL number: MFCD12031592
- EINECS: 1312995-182-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-26 18:10:20
What is Ruxolitinib?
Absorption
Following oral administration, ruxolitinib undergoes rapid absorption and the peak concentrations are reached within one hour after administration. Over a single-dose range of 5 mg to 200 mg, the mean maximal plasma concentration (Cmax) increases proportionally. Cmax ranged from 205 nM to 7100 nM and AUC ranged from 862 nM x hr to 30700 nM x hr. Tmax ranges from one to two hours following oral administration. Oral bioavailability is at least 95%.
Toxicity
The oral LD50 was 250 mg/kg.
Single doses of ruxolitinib up to 200 mg were tolerated well. Higher doses than recommended repeat doses are associated with myelosuppression, including leukopenia, anemia, and thrombocytopenia. There is no known antidote for overdoses with ruxolitinib: it is recommended that patients are given appropriate supportive treatment. Hemodialysis is not expected to enhance the elimination of ruxolitinib.
Description
Tofacitinib (trade names Xeljanz and Jakvinus; Pfizer) and ruxolitinib (Jakafi and Jakavi; Incyte Pharmaceuticals and Novartis) are Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors that are used to treat rheumatoid arthritis and myelofibrosis, respectively. Tofacitinib (structure 1) was the first to be developed; it was the outgrowth of research performed at the National Institutes of Health by John O''Shea and co-workers.
Ruxolitinib (structure 2) did not come along until about 5 years ago. It may also be useful for treating other disease such as lymphoma, pancreatic cancer, and polycythemia vera.
Both drugs are now being looked at to treat a very widespread but much less serious condition: hair loss. A Columbia University team led by Angela M. Christiano observed that administering the drugs orally to mice promoted hair growth. The downside was that the animals'' immune systems were compromised, so the researchers applied the drugs topically and obtained similar hair growth results.
It turns out that JAK inhibition is the key to this effect as it is for disease treatment. The drugs inhibit a kinase pathway in dormant hair follicle cells that causes the cells to transcribe DNA. Inhibiting the pathway "wakes up" the cells, and hair growth ensues.
Description
In November 2011, the U.S. FDA approved ruxolitinib (INCB018424) for the treatment of patients with intermediate or high-risk myelofibrosis. Ruxolitinib is an ATP-competitive inhibitor of JAK1 and JAK2 (IC50's of 3.3±1.2 nM and 2.8±1.2 nM, respectively) and inhibition occurs regardless of the JAK2V617F mutational status. Ruxolitinib is a moderately potent inhibitor of the related JAK, TYK2 (IC50=19±3.2 nM) but is selective versus JAK3 (IC50=428±243 nM). It was also selective versus a panel of 26 other kinases at concentrations approximately 100-fold the IC50 of JAK1 and JAK2. Inhibition of JAK1 and JAK2 downregulates the JAK-signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) pathway, inhibiting myeloproliferation, inducing apoptosis, and reducing numerous cytokine plasma levels.
Originator
Incyte Corporation (United States)
Characteristics
Class: non-receptor tyrosine kinase
Treatment: MF, PV, cGVHD
Oral bioavailability >95%
Elimination half-life = 3 h
Protein binding = 97%
The Uses of Ruxolitinib
Ruxolitinib is a selective Janus tyrosine kinase (JAK1 and JAK2) inhibitor used in the treatment of myeloproliferative neoplasms and psoriasis.
The Uses of Ruxolitinib
A JAK family kinase inhibitor of JAK1, JAK2 and JAK3 with IC50s of 2.7 nM, 4.5 nM and 322 nM, respectively
The Uses of Ruxolitinib
INCB018424 is the first potent, selective, JAK1/2 inhibitor to enter the clinic with IC50 of 3.3 nM/2.8 nM, >130-fold selectivity for JAK1/2 versus JAK3. Phase 3
The Uses of Ruxolitinib
Janus-associated kinases (JAKs) are cytoplasmic tyrosine kinases that are required for activating the signaling of certain cytokines and growth factor receptors. A JAK2 gene fusion mutation, JAK2V617F, that causes unchecked activation of various growth factors and cytokines, has been linked to myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs), including polycythemia vera, essential thrombocythemia, and primary myelofibrosis. Ruxolitinib is a potent ATP mimetic that inhibits both JAK1 and JAK2 with IC50 values of 2.7 and 4.5 nM, respectively and is relatively less selective for JAK3 (IC50 = 322 nM). It can block interleukin-6 (IL-6) signaling (IC50 = 281 nM) and proliferation of JAK2V617F+ Ba/F3 cells (IC50 = 127 nM). In primary cultures, ruxolitinib preferentially suppresses erythroid progenitor colony formation from JAK2V617F+ polycythemia vera patients (IC50 = 67 nM) versus healthy donors (IC50 > 400 nM). In a mouse model of JAK2V617F+ MPN, 90 mg/kg ruxolitinib reduced splenomegaly, decreased circulating levels of IL-6 and TNF-α, eliminated neoplastic cells, and prolonged survival of the treated animals.[Cayman Chemical]
Indications
Ruxolitinib is indicated for the treatment of the following conditions:
Topical ruxolitinib is indicated for:
Background
Ruxolitinib, formerly known as INCB018424 or INC424, is an anticancer drug and a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor. It is a potent and selective inhibitor of JAK1 and JAK2, which are tyrosine kinases involved in cytokine signalling and hematopoiesis. Myeloproliferative neoplasms, such as myelofibrosis and polycythemia vera, are often characterized by aberrant activation of the JAK-STAT pathway, leading to abnormal blood cell counts and thrombotic complications. By inhibiting JAK1 and JAK2, ruxolitinib works to block the dysregulated cell signalling pathways and prevents abnormal blood cell proliferation. Due to a large number of patients with myeloproliferative neoplasms who have JAK2 mutations, ruxolitinib was the first ATP-competitive inhibitor of JAK1 and JAK2 ever developed.
Ruxolitinib was first approved for the treatment of adult patients with myelofibrosis by the FDA in 2011, followed by EMA's approval in 2012. In 2014, it was approved for the treatment of polycythemia vera in adults who have an inadequate response to or are intolerant of hydroxyurea and in 2019, ruxolitinib was approved for use in steroid-refractory acute graft-versus-host disease in adults and children. The topical formulation of ruxolitinib is used to treat atopic dermatitis and vitiligo. It is being investigated for other inflammatory skin conditions.
Ruxolitinib has been investigated to treat patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) accompanied by severe systemic hyperinflammation. In phase II clinical trials, ruxolitinib improved chest computed tomography and improved recovery in patients with lymphopenia. However, phase III clinical trials later determined that ruxolitinib was inadequate in meeting its primary endpoint of reducing the number of hospitalized COVID-19 patients who experienced severe complications thus the drug was not approved as a treatment for COVID-19.
What are the applications of Application
Ruxolitinib is a potent Janus-associated kinase (JAK) inhibitor, selective to JAK1, JAK2, and JAK3.
Definition
ChEBI: A pyrazole substituted at position 1 by a 2-cyano-1-cyclopentylethyl group and at position 3 by a pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl group. Used as the phosphate salt for the treatment of patients with intermediate or high-risk myelofibrosis, includ ng primary myelofibrosis, post-polycythemia vera myelofibrosis and post-essential thrombocythemia myelofibrosis.
Indications
The JAK family includes four isoforms, JAK1, JAK2, JAK3, and tyrosine kinase (TYK2). Ruxolitinib (Jakafi(R), Incyte Corp.) was the first approved JAK inhibitor, which inhibits both JAK1 and JAK2, used for the treatment of different types of myelofibrosis. Tofacitinib (Xeljanz(R), Pfizer) was approved by FDA as a JAK3-selective inhibitor for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and is one of the only two FDA-approved kinase inhibitors for non-oncological indications.
brand name
Jakafi
Pharmacokinetics
Ruxolitinib is an antineoplastic agent that inhibits cell proliferation, induces apoptosis of malignant cells, and reduces pro-inflammatory cytokine plasma levels by inhibiting JAK-induced phosphorylation of signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT). Inhibition of STAT3 phosphorylation, which is used as a marker of JAK activity, by ruxolitinib is achieved at two hours after dosing which returned to near baseline by 10 hours in patients with myelofibrosis and polycythemia vera. In clinical trials, ruxolitinib reduced splenomegaly and improved symptoms of myelofibrosis. In a mouse model of myeloproliferative neoplasms, administration of ruxolitinib was associated with prolonged survival. Ruxolitinib inhibits both mutant and wild-type JAK2 ; however, JAK2V617F mutation, which is often seen in approximately 50% of patients with myelofibrosis, was shown to reduce ruxolitinib sensitivity, which may also be associated with possible resistance to JAK inhibitor treatment.
Clinical Use
Tyrosine kinase inhibitor:
Treatment of disease related splenomegaly or
symptoms in patients with primary myelofibrosis
(MF), post polycythaemia vera (PV) myelofibrosis
or post-essential thrombocythemia myelofibrosis
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Antibacterials: concentration increased by
clarithromycin and telithromycin, reduced dose of
ruxolitinib; concentration reduced by rifampicin.
Antifungals: reduce dose of ruxolitinib with
fluconazole, itraconazole, ketoconazole, posaconazole
and voriconazole.
Antipsychotics: avoid with clozapine, risk of
agranulocytosis.
Antivirals: reduce dose of ruxolitinib with
boceprevir, indinavir, lopinavir, ritonavir, saquinavir
and telaprevir.
Metabolism
More than 99% of orally-administered ruxolitinib undergoes metabolism mediated by CYP3A4 and, to a lesser extent, CYP2C9. The major circulating metabolites in human plasma were M18 formed by 2-hydroxylation, and M16 and M27 (stereoisomers) formed by 3-hydroxylation. Other identified metabolites include M9 and M49, which are formed by hydroxylation and ketone formation. Not all metabolite structures are fully characterized and it is speculated that many metabolites exist in stereoisomers. Metabolites of ruxolitinib retain inhibitory activity against JAK1 and JAk2 to a lesser degree than the parent drug.
Metabolism
Ruxolitinib is mainly metabolised by CYP3A4 (>50%), with additional contribution from CYP2C9 to produce 2 major and active metabolites. About 74% of a dose is excreted in the urine and about 22% via the faeces.
Storage
Store at -20°C
References
1) Verstovsek?et al. (2009),?Therapeutic potential of JAK2 inhibitors; Hematology Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program,?2009(1)?636 2) Quintas-Cardama?et al. (2010),?Preclinical characterization of the selective JAK1/2 inhibitor INCB01824: Therapeutic implications for the treatment of myeloproliferative neoplasms; Blood,?115?3109 3) Farr et al. (2017) Targeting cellular senescence prevents age-related bone loss in mice; Nat. Med. 23 1072 4) Li?et al.?(2017)?Identification of a novel functional JAK1 S646P mutation in acute lymphoblastic leukemia; Oncotarget?8?34687
Properties of Ruxolitinib
| Melting point: | 84-89°C |
| Density | 1.40 |
| storage temp. | -20° |
| solubility | Soluble in DMSO (up to 28 mg/ml) or in Ethanol (up to 15 mg/ml with warming). |
| pka | 11.63±0.50(Predicted) |
| form | White powder. |
| color | White |
| Stability: | Stable for 1 year from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions in DMSO or ethanol may be stored at -20° for up to 3 months. |
| InChI | InChI=1/C17H18N6/c18-7-5-15(12-3-1-2-4-12)23-10-13(9-22-23)16-14-6-8-19-17(14)21-11-20-16/h6,8-12,15H,1-5H2,(H,19,20,21)/t15-/s3 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 941678-49-5 |
Safety information for Ruxolitinib
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for Ruxolitinib
| InChIKey | HFNKQEVNSGCOJV-UJHUVDBMNA-N |
| SMILES | [C@@H](C1CCCC1)(N1N=CC(C2N=CN=C3NC=CC=23)=C1)CC#N |&1:0,r| |
Ruxolitinib manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Ruxolitinib 98% (HPLC) CAS 941678-49-5View Details
Ruxolitinib 98% (HPLC) CAS 941678-49-5View Details
941678-49-5 -
 Ruxolitinib (5Mg) Novartis Jakavi 5 Mg, 4x14View Details
Ruxolitinib (5Mg) Novartis Jakavi 5 Mg, 4x14View Details
941678-49-5 -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8