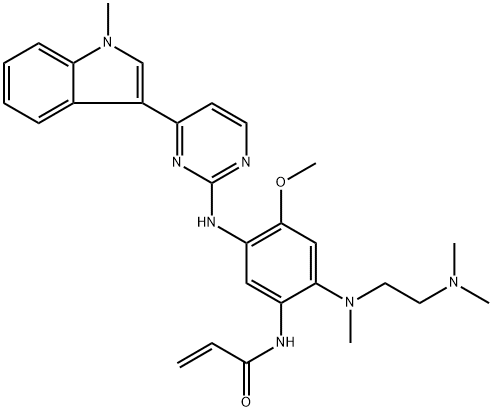
Dapagliflozin
- CAS NO.:461432-26-8
- Empirical Formula: C21H25ClO6
- Molecular Weight: 408.88
- MDL number: MFCD13182359
- EINECS: 639-683-0
- Update Date: 2025-12-26 18:10:20
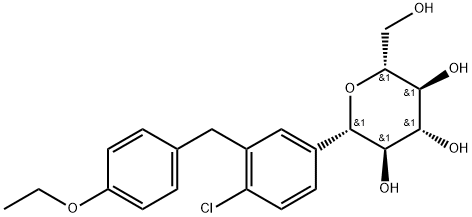
What is Dapagliflozin?
Absorption
Oral dapagliflozin reaches a maximum concentration within 1 hour of administration when patients have been fasting. Following oral administration of dapagliflozin, the maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) is usually attained within 2 hours under fasting state. The Cmax and AUC values increase dose proportionally with an increase in dapagliflozin dose in the therapeutic dose range. The absolute oral bioavailability of dapagliflozin following the administration of a 10 mg dose is 78%. Administration of dapagliflozin with a high-fat meal decreases its Cmax by up to 50% and prolongs Tmax by approximately 1 hour but does not alter AUC as compared with the fasted state. These changes are not considered to be clinically meaningful and dapagliflozin can be administered with or without food.
Toxicity
Age, gender, race, and body weight do not affect dapagliflozin dosing requirements. Although age does not affect dosing requirements, safety has not been established in pediatric populations and patients at an especially advanced age may be more susceptible to adverse effects.
Animal studies in pregnancy showed no fetal toxicity in the first trimester but exposure later in pregnancy was associated with renal pelvic dilatation and maternal toxicity at much higher doses than the maximum recommended human dose. Due to this data, dapagliflozin is not recommended in the second and third trimester of pregnancy. Dapagliflozin is excreted in milk from rats, though this may not necessarily be the case in humans.
Children under 2 years old who are exposed to dapagliflozin may be at risk of improper kidney development.
Dapagliflozin is not recommended in patients with a creatinine clearance below 45mL/min and is contraindicated in patients with creatinine clearance below 30mL/min. Dose adjustments are not necessary in patients with hepatic impairment at any stage, although the risk and benefit to the patient must be assessed as there is limited data on dapagliflozin use in this population.
Description
The Australian Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) and the European Commission approved dapagliflozin in October and November 2012, respectively, as an adjunct to diet and exercise for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Dapagliflozin is a potentially attractive therapy due to its glucosesensitive and insulin-independent mechanism of action. It is a first-in-class selective SGLT2 inhibitor (IC50=1.1 nM; selectivity vs. SGLT1 >1000) that lowers the renal threshold for reabsorption of glucose, allowing excess glucose to be eliminated via the kidneys. In normal rats, administration of dapagliflozin promotes dose-dependent excretion of up to 1900 mg of glucose over a 24 h period, with amaximal effect at 3 mg/kg. In a ratmodel of diabetes, pretreatment with the pancreatic toxin streptozotocin results in hyperglycemia that is reduced 55% by administration of a single 0.1 mg/kg dose of dapagliflozin compared with vehicle. Aryl O-glucoside SGLT2 inhibitors were early entrants into the clinic, but the aryl C-glucoside linkage found in dapagliflozin confers resistance to glucosidase-mediated metabolism leading to improved clinical utility relative to aryl O-glucosides. The modified carbohydrate–aglycone linkage required concomitant adjustment from an ortho- to a meta-substituted arylglucoside to achieve potent SGLT2 inhibition. Dapagliflozin was synthesized in several steps via reaction of an aryllithium with per-silylated gluconolactone to form the key C-glucoside linkage. An alpha-selective reduction of the resultant anomeric glycoside gave the desired beta-Carylglucoside. The main circulating (inactive) metabolite is the result of 3-O-glucuronidation of the glucosylmoiety. Of the minority metabolites, the main oxidative species result from O-dealkylation of the ethoxy-group and hydroxylation of the biarylmethane moiety.
Description
Inhibiting renal glucose reabsorbtion through the sodium-
Chemical properties
White Solid
Originator
Bristol-Myers Squibb (United States)
The Uses of Dapagliflozin
A sodium-glucose transporter 2 inhibitor.
The Uses of Dapagliflozin
therapeutic for diabetes I or II, and hyperglycemia
Indications
Dapagliflozin is indicated as an adjunct treatment to improve glycemic control in adult patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus along with diet and exercise.For patients with chronic kidney disease at risk of progression, dapagliflozin in used to reduce the risk of sustained eGFR decline, end-stage kidney disease, cardiovascular death, and
hospitalization for heart failure.
Dapagliflozin is also indicated to either reduce the risk of cardiovascular death, hospitalization for heart failure, and urgent heart failure visit in adults with heart failure or reduce the risk of hospitalization for heart failure in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus and either established cardiovascular disease or multiple cardiovascular risk factors.
Background
Dapagliflozin is a sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor, and it was the first SLGT2 inhibitor to be approved. indicated for managing diabetes mellitus type 2. Dapagliflozin has been investigated either as monotherapy or as an adjunct treatment with insulin or other oral hypoglycemic agents.
Dapagliflozin was originally approved by the FDA on Jan 08, 2014, to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes in conjunction with diet and exercise. It was later approved to reduce the risk of kidney function decline, kidney failure, cardiovascular death, and hospitalization for heart failure in adults with chronic kidney disease in April 2021.
What are the applications of Application
Dapagliflozin is a SGLT-2 inhibitor
Definition
ChEBI: A C-glycosyl comprising beta-D-glucose in which the anomeric hydroxy group is replaced by a 4-chloro-3-(4-ethoxybenzyl)phenyl group. Used (in the formo f its propanediol monohydrate) to improve glycemic ontrol, along with diet and exercise, in adults with type 2 diabetes.
brand name
Forxiga
Pharmacokinetics
Dapagliflozin also reduces sodium reabsorption and increases the delivery of sodium to the distal tubule. This may influence several physiological functions including, but not restricted to, lowering both pre- and afterload of the heart and downregulation of sympathetic activity, and decreased intraglomerular pressure which is believed to be mediated by increased tubuloglomerular feedback.
Clinical Use
Selective and reversible inhibitor of sodium-glucose
co-transporter 2:
Treatment of type 2 diabetes
in vitro
ec50 values of 1.1 nm for hsglt2 and 1.4 μm for hsglt1 determined for dapagliflozin corresponded to 1200-fold selectivity for sglt2 as compared with phlorizin’s 10-fold selectivity. dapagliflozin inhibitory potencies against rat sglt (rsglt)2 and hsglt2 were comparable, but the selectivity of dapagliflozin for rsglt2 versus rsglt1 decreased to 200-fold [1].
in vivo
in vivo, dapagliflozin acutely induced renal glucose excretion in diabetic and normal rats, improved glucose tolerance in normal rats, as well as reduced hyperglycemia in zucker diabetic fatty rats after single oral doses ranging between 0.1 and 1.0 mg/kg [2].
Metabolism
Dapagliflozin is primarily glucuronidated to become the inactive 3-O-glucuronide metabolite(60.7%). Dapagliflozin also produces another minor glucuronidated metabolite(5.4%), a de-ethylated metabolite(<5%), and a hydroxylated metabolite(<5%). Metabolism of dapagliflozin is mediated by cytochrome p-450(CYP)1A1, CYP1A2, CYP2A6, CYP2C9, CYP2D6, CYP3A4, uridine diphosphate glucuronyltransferase(UGT)1A9, UGT2B4, and UGT2B7. Glucuronidation to the major metabolite is mediated by UGT1A9.
Metabolism
Dapagliflozin is extensively metabolised, primarily to dapagliflozin 3-O-glucuronide, which is an inactive metabolite. The formation of dapagliflozin 3-O-glucuronide is mediated by UGT1A9, an enzyme present in the liver and kidney, and CYP-mediated metabolism was a minor clearance pathway in humans. About 75% of the dose is excreted in the urine and 21% in the faeces.
References
[1] meng w, ellsworth ba, nirschl aa, mccann pj, patel m, girotra rn, wu g, sher pm, morrison ep, biller sa, zahler r, deshpande pp, pullockaran a, hagan dl, morgan n, taylor jr, obermeier mt, humphreys wg, khanna a, discenza l, robertson jg, wang a, han s, wetterau jr, janovitz eb, flint op, whaley jm, washburn wn. discovery of dapagliflozin: a potent, selective renal sodium-dependent glucose cotransporter 2 (sglt2) inhibitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. j med chem. 2008 mar 13;51(5):1145-9.
[2] han s, hagan dl, taylor jr, xin l, meng w, biller sa, wetterau jr, washburn wn, whaley jm. dapagliflozin, a selective sglt2 inhibitor, improves glucose homeostasis in normal and diabetic rats. diabetes. 2008 jun;57(6):1723-9.
[3] bailey cj, iqbal n, t'joen c, list jf. dapagliflozin monotherapy in drug-naïve patients with diabetes: a randomized-controlled trial of low-dose range. diabetes obes metab. 2012 oct;14(10):951-9.
Properties of Dapagliflozin
| Melting point: | 55-58°C |
| Boiling point: | 609.0±55.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.349 |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 13.23±0.70(Predicted) |
| color | White to Pale Yellow |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
Safety information for Dapagliflozin
Computed Descriptors for Dapagliflozin
Dapagliflozin manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Dapagliflozin 99%View Details
Dapagliflozin 99%View Details -
 DAPAGLIFLOZIN 98%View Details
DAPAGLIFLOZIN 98%View Details
34546-2354-435 -
 Dapagliflozin propanediol 99%View Details
Dapagliflozin propanediol 99%View Details -
 Dapagliflozin 98%View Details
Dapagliflozin 98%View Details -
 Dapagliflozin propanediol monohydrate 98%View Details
Dapagliflozin propanediol monohydrate 98%View Details -
 Dapagliflozin 461432-26-8 98%View Details
Dapagliflozin 461432-26-8 98%View Details
461432-26-8 -
 Dapagliflozin 99%View Details
Dapagliflozin 99%View Details -
 Dapagliflozin 98% CAS 461432-26-8View Details
Dapagliflozin 98% CAS 461432-26-8View Details
461432-26-8
