Triclocarban
Synonym(s):1-(4-Chlorophenyl)-3-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)urea;3,4,4′-Trichlorocarbanilide;TCC;Triclocarban
- CAS NO.:101-20-2
- Empirical Formula: C13H9Cl3N2O
- Molecular Weight: 315.58
- MDL number: MFCD00013254
- EINECS: 202-924-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-23 21:30:31
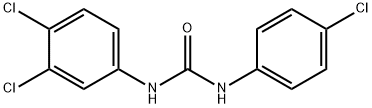
What is Triclocarban?
Absorption
A human exposure study in a small group of subjects demonstrated that a portion of the TCC present in bar soaps is absorbed through the skin and is excreted in urine as N-glucuronides .
Because they are produced and used in large quantities in various products, they are absorbed into the human body of the general population .
The absorption of triclocarban during a human pharmacokinetic study was estimated at 0.6% of the 70 + or - 15 mg of triclocarban in the soap used. The triclocarban-N-glucuronide urine concentration varied considerably among the study subjects, and continuous daily use of the soap led to steady-state levels of excretion .
Toxicity
Ld50 of 2100 mg/kg in mice .
There has been concern voiced over the endocrine effect of triclocarban ande, in particular, on estrogen , ,,.
One study determined that triclocarban by itself stimulates AroB (brain aromatase) gene expression only slightly, but TCC strongly enhances the overexpression of AroB that is induced by exogenous estrogen. TCC has the potential to elevate levels of aromatase enzymes and, thereby, levels of endogenous estrogens in the developing brain . The effects of triclocarban on the endocrine system are presently not fully elucidated.
Description
Triclocarban, along with its cousin triclosan, is an antibacterial and antifungal component of personal care products such as soaps, toothpaste, and deodorants. It has been in use since the 1960s, but it has recently come under fire from the US Food and Drug Administration.
A rule proposed by the FDA in December 2013 would require manufacturers of antibacterial soaps and body washes to demonstrate that their products are safe for everyday use and are more effective than products without antibacterials. Proponents of the rule argue that users'' risk of bacterial infection is low; and therefore, the antibacterial additives are not needed. Producers rebut this argument by citing dozens of studies that show that antibacterial soaps significantly reduce bacteria levels on skin compared with ordinary soaps.
More recently, a bill in the New York State assembly would, if passed, ban the sale of antibacterial personal care products in that state.
Chemical properties
white crystals or powder
Originator
Cutisan,Innothera,France,1960
The Uses of Triclocarban
Labelled Triclocarban
The Uses of Triclocarban
Used as bacteriostat and antiseptic in soaps and other cleansing compositions. Antiseptic, disinfectant.
Indications
Triclocarban (TCC), or 3,4,4'-trichlorocarbanilide, is an antibacterial agent used in bar and liquid soaps and body washes .
Background
Triclocarban, with the chemical formula C13H9Cl3N2O is an antibacterial agent that is particularly effective against Gram-positive bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus. It is a bacteriostatic compound that has been found in antibacterial soaps and other personal care products. In 2017, the US FDA prohibited the marketing of over-the-counter (OTC) consumer antiseptic wash products containing triclocarban due to negative health effects such as bacterial resistance or hormonal effects , .
What are the applications of Application
Triclocarban is an antiseptic and bacteriostat
Definition
ChEBI: A member of the class of ureas that is urea substituted by a 4-chlorophenyl and a 3,4-dichlorophenyl group at positions 1 and 3 respectively.
Manufacturing Process
To a suitable reaction vessel equipped with a thermometer, agitator and reflux condenser and containing 8.1 parts by weight (substantially 0.05 mol) of 3,4-dichloroaniline in approximately 57 parts by weight of diethyl ether is added dropwise a solution of 7.7 parts by weight (substantially 0.05 mol) of 4- chlorophenyl isocyanate in approximately 15 parts by weight of diethyl ether at such a rate so as to maintain gentle reflux. Upon completion of the isocyanate addition the reaction mass is agitated for about one hour. The mass is filtered and the residue washed with diethyl ether. The dried product is a white fluffy solid which on recrystallization from ethanol gives fine white plates of 4,3',4'-trichlorocarbanilide, melting point 255.2°C to 256.0°C (88.0% yield)
Therapeutic Function
Disinfectant
General Description
Fine white plates or white powder.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
A halogenated amide. Organic amides/imides react with azo and diazo compounds to generate toxic gases. Flammable gases are formed by the reaction of organic amides/imides with strong reducing agents. Amides are very weak bases (weaker than water). Imides are less basic yet and in fact react with strong bases to form salts. That is, they can react as acids. Mixing amides with dehydrating agents such as P2O5 or SOCl2 generates the corresponding nitrile. The combustion of these compounds generates mixed oxides of nitrogen (NOx).
Fire Hazard
The flash point of Triclocarban has not been determined. Triclocarban is, however, probably combustible.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Biochem/physiol Actions
3,4,4′-Trichlorocarbanilide interferes with mammalian reproduction and can cause methemoglobinemia in humans.
Pharmacokinetics
The antimicrobial mechanism underlying the bacteriostatic and bactericidal effects of triclocarban is believed to be an unspecific adsorption to cell membranes and interruption of their function. As a result, the growth of gram-positive as well as gram-negative bacteria is inhibited .
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic byintraperitoneal route. When heated to decomposition itemits very toxic fumes of Clí and NOx.
Metabolism
Blood levels after parenteral injection are low and comparison of the radioactivity and chemical determinations suggest rapid metabolism of the Triclocarban .
Human metabolism of TCC involves direct glucuronidation to form N- and N'- glucuronides as well as ring hydroxylation to 2'-hydroxy-TCC and 6-hydroxy-TCC, which are further metabolized to sulfate and glucuronide conjugates. In human subjects given a single oral dose of TCC, 27% of the dose was excreted in the urine within 80 hours. About 70% of the administered dose was excreted in the feces within 5 days .
The major urinary metabolites were N-glucuronides (average levels, 30 ng/mL) and a major plasma metabolite was the sulfate conjugate of 2'-OH-TCC (levels ranged from 0-20 ng/mL .
The maximum plasma level occurred 2.8 hr after dosing and was 3.7 nmol-equivalents of TCC per g of plasma (approximately 1.2 ppm). Biotransformation of TCC was rapid but did not appear to involve splitting of the basic TCC structure. The major plasma metabolites were N- and N'-glucuronides of TCC which were eliminated with half-life approximately 2 hr to the urine and 2'-hydroxy-TCC sulfate and 6-hydroxy-TCC sulfate (the o-hydroxy-TCC sulfates) which were removed with half life approximately 20 hr (presumably into the bile) .
Properties of Triclocarban
| Melting point: | 254-256 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 344.2±42.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.5732 (rough estimate) |
| vapor pressure | <0.1 mm Hg ( 25 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.6300 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 150 °C |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Room Temperature |
| solubility | methanol: soluble |
| form | neat |
| pka | 12.77±0.70(Predicted) |
| form | Solid |
| color | Fine plates |
| Water Solubility | <0.1 g/100 mL at 26 ºC |
| Merck | 14,9654 |
| Stability: | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents strong bases. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 101-20-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | 3,4,4'-Trichloro carbanilide(101-20-2) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Triclocarban (101-20-2) |
Safety information for Triclocarban
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P273:Avoid release to the environment. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Triclocarban
| InChIKey | ICUTUKXCWQYESQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 101-20-2 98%View Details
101-20-2 98%View Details
101-20-2 -
 Triclocarban 98%View Details
Triclocarban 98%View Details
101-20-2 -
 3,4,4'-Trichlorocarbanilide CAS 101-20-2View Details
3,4,4'-Trichlorocarbanilide CAS 101-20-2View Details
101-20-2 -
 Triclocarban 98% CAS 101-20-2View Details
Triclocarban 98% CAS 101-20-2View Details
101-20-2 -
 3,4,4′-Trichlorocarbanilide, 99% CAS 101-20-2View Details
3,4,4′-Trichlorocarbanilide, 99% CAS 101-20-2View Details
101-20-2 -
 3,4,4′-Trichlorocarbanilide CAS 101-20-2View Details
3,4,4′-Trichlorocarbanilide CAS 101-20-2View Details
101-20-2 -
 Triclocarban CAS 101-20-2View Details
Triclocarban CAS 101-20-2View Details
101-20-2 -
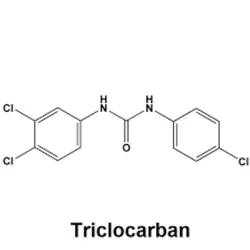 Triclocarban (TCC)View Details
Triclocarban (TCC)View Details
101-20-2
