Phosphorus oxitrichloride
Synonym(s):Phosphorus(V) oxide chloride;Phosphoryl chloride
- CAS NO.:10025-87-3
- Empirical Formula: Cl3OP
- Molecular Weight: 153.33
- MDL number: MFCD00011443
- EINECS: 233-046-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02

What is Phosphorus oxitrichloride?
Description
Phosphorus oxychloride is a colourless liquid with a strong, very characteristic odour. Hydrolysis very easily occurs, which is accompanied by the release of fumes, and its products are phosphoric acid and hydrogen chloride. The reaction of phosphorus oxychloride with water is very rapid. Due to the high exothermicity of the process and the release of high amounts of suffocating hydrogen chloride, transport and storage should be carried out in tightly closed containers protected against moisture or water ingress.
Chemical properties
Phosphorus oxychloride is a clear, colorless to yellow, fuming, oily liquid with a pungent and musty odor. density 1.645 g/mL; freezes at 1°C; boils at 105.5°C; reacts with water and ethanol.
The Uses of Phosphorus oxitrichloride
Phosphorus oxychloride is an important intermediate in the production of triarylphosphate esters (e.g., triphenyl phosphate and tricresyl phosphate), which have been used as flame retardants and plasticizers for PVC. It is acutely toxic to the eyes, throat, and respiratory tract. Phosphorus oxychloride is also used in nuclear reprocessing, as chlorinating agent, especially to replace oxygen in organic compounds, as solvent in cryoscopy and the semiconductor industry.
The Uses of Phosphorus oxitrichloride

A solution of the SM (6.5 g, 18.3 mmol) in POCl3 (21 mL) was heated to reflux for 2 h, after which time it was cooled to RT and poured carefully into a stirring mixture of ice (200 mL) and saturated aq NaHCO3 (20 mL). The resulting mixture was extracted with EtOAc (2 x 250 mL). The combined org layers were washed with H2O, brine, dried (Na2SO4), and concentrated in vacuo. The residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (3% EtOAc/hexane) to provide the product. [5.1 g, 15 mmol]
Preparation
Phosphorus oxychloride can be prepared from phosphorus trichloride or phosphorus pentachloride. It can be obtained from phosphorus trichloride by cautious addition of potassium chlorate:3PCl3 + KClO3 → 3POCl3 + KCl The oxychloride also is obtained by the action of boric acid or oxalic acid with phosphorus pentachloride: 3PCl5 + 2B(OH)3 → 3POCl3 + B2O3 + 6HCl PCl5 + (COOH)2 → POCl3 + CO + CO2 + 2HCl Phosphorus oxychloride also is made by heating calcium phosphate in a current of chlorine and carbon monoxide at 350°C: 2Ca3(PO4)2 + 9Cl2 + 6CO → 4POCl3 + 6CaCO3 Alternatively, heating a mixture of calcium phosphate and carbon in a current of chlorine at 750°C yields the oxychloride.
Definition
A white crystalline solid. It is a monobasic acid forming the anion H2PO2 – in water. The sodium salt, and hence the acid, can be prepared by heating yellow phosphorus with sodium hydroxide solution. The free acid and its salts are powerful reducing agents.
Reactivity Profile
Phosphorus oxychloride is water reactive. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, alcohols, bases (including amines). May react vigorously or explosively if mixed with diisopropyl ether or other ethers in the presence of trace amounts of metal salts [J. Haz. Mat., 1981, 4, 291]. Combining the chloride with zinc dust caused immediate ignition, due to the formation of phosphine gas which ignites, [Mellor, 1940, Vol. 8, 1025]. An exotherm starting with the mixing of Phosphorus oxychloride with acetone (a ketone) lead to an explosion, may behave similarly with other ketones, [Organic Process Research and Development, Vol.4, No. 6,200, "Phosphorus oxychloride and Acetone: An Incompatibility Investigation Using ARC."]
Hazard
The compound is highly irritating to skin, eyes and mucous membranes. Inhaling its vapors can cause pulmonary edema.
Health Hazard
Inhalation of vapors of phosphorus oxychloride produced acute and chronic toxicity in test subjects. In humans, exposure to its vapors may cause headache, dizziness, weakness, nausea, vomiting, coughing, chest pain, bronchitis, and pulmonary edema. Most of these symptoms are manifested from chronic exposure to its vapors.
LC50 value, inhalation (rats): 48 ppm (301 mg/m3)/4 h
Vapors of this compound are an irritant to the eyes and mucous membranes. The liquidis corrosive and can cause skin burns. An oral LD50 value for rats is documented to be 380 mg/kg (NIOSH 1986)..
Fire Hazard
Poisonous, corrosive, and irritating gases are generated when Phosphorus oxychloride is heated or is in contact with water. Phosphorus oxychloride may ignite other combustible materials (wood, paper, oil, etc.). Phosphorus oxychloride reacts violently with water. When heated to decomposition, Phosphorus oxychloride emits toxic fumes of chlorides and oxides of phosphorus; Phosphorus oxychloride will react with water or steam to produce heat and toxic and corrosive fumes. Incompatible with carbon disulfide; N,N-dimethylformamide; 2,5-dimethylpyrrole; 2,6-dimethyl- pyridine N-oxide; dimethylsulfoxide; Ferrocene-1,1-dicarboxylic acid; water; and zinc. Do not store with combustible materials, particularly fibrous organic materials, or with electrical or other equipment that can be corroded. Reacts violently with moisture.
Safety Profile
Poison by inhalation and ingestion. A corrosive eye, skin, and mucous membrane irritant. Potentially explosive reaction with water evolves hydrogen chloride and phosphine, which then ignites. Explosive reaction with 2,6dimethylpyridine N-oxide, dimethyl sulfoxide, ferrocene1 ,l'-dicarboxylic acid, pyridne N-oxide (above bO'C), sodmm + heat. Violent reaction or ignition with BI3, carbon disulfide, 2,5-dimethyl pyrrole + dimethyl formamide, organic matter, zinc powder. Reacts with water or steam to produce heat and toxic and corrosive fumes. Incompatible with carbon disulfide, N,Ndimethyl-formamide, 2,5-dunethylpyrrole, 2,6-dimethylpyridine N-oxide, dimethylsulfoxide, ferrocene1 ,I-dicarboxylic acid, water, zinc. When heated to decomposition it emits highly toxic fumes of Cland POx
Potential Exposure
Phosphorus oxychloride is used in the manufacture of pesticides, pharmaceuticals, plasticizers, gasoline additives; and hydraulic fluids.
Shipping
UN1810 Phosphorus oxychloride, Hazard class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, 8-Corrosive material, Hazard Zone B.
Purification Methods
Distil the liquid under reduced pressure to separate it from the bulk of the HCl and the phosphoric acid (from hydrolysis); the middle fraction is re-distilled into ampoules containing a little purified mercury. These ampoules are sealed and stored in the dark for 4-6weeks with occasional shaking to facilitate reaction of any free chloride with the mercury. The POCl3 is then again fractionally distilled and stored in sealed ampoules in the dark until required [Herber J Am Chem Soc 82 792 1960]. Lewis and Sowerby [J Chem Soc 336 1957] refluxed their distilled POCl3 with Na wire for 4hours, then removed the Na and again distilled. Use Na only with almost pure POCl3 to avoid explosions. HARMFUL VAPOURS; work in an efficient fume cupboard.
Incompatibilities
A powerful oxidizer. Violently decomposes in water, forming heat and hydrochloric and phosphoric acids. Violent reaction with alcohols, phenols, amines, reducing agents; combustible materials; carbon disulfide; dimethylformamide, and many other many materials. Rapid corrosion of metals, except nickel and lead.
Waste Disposal
Pour onto sodium bicarbonate. Spray with aqueous ammonia and add crushed ice. Neutralize and pour into drain with running water. In accordance with 40CFR165, follow recommendations for the disposal of pesticides and pesticide containers. Must be disposed properly by following package label directions or by contacting your local or federal environmental control agency, or by contacting your regional EPA office.
Properties of Phosphorus oxitrichloride
| Melting point: | 1.25 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 107 °C |
| Density | 1.645 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor density | 5.3 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 104 mm Hg ( 50 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 105.8°C |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | Phosphorus(V) oxychloride is soluble in many organic solvents. |
| form | Liquid |
| appearance | Colorless liquid |
| color | Colorless |
| Specific Gravity | 1.692 (15/15℃) |
| PH | 1.0 (5g/l, H2O, 25℃) |
| Odor | Pungent odour |
| Water Solubility | reacts exothermically |
| Sensitive | Moisture Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,7349 |
| Dielectric constant | 14.0(22℃) |
| Exposure limits | TLV-TWA0.628 mg/m3 (0.1 ppm)(ACGIH). |
| Stability: | Stable. Reacts violently with water. Incompatible with many metals, alcohols, amines, phenol, DMSO, strong bases. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 10025-87-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Phosphoryl chloride(10025-87-3) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Phosphorus oxychloride (10025-87-3) |
Safety information for Phosphorus oxitrichloride
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H314:Skin corrosion/irritation H330:Acute toxicity,inhalation H372:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P314:Get medical advice/attention if you feel unwell. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Phosphorus oxitrichloride
| InChIKey | XHXFXVLFKHQFAL-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Phosphorus oxitrichloride manufacturer
ASM Organics
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

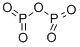
You may like
-
 Phosphorus (V) oxychloride supplierView Details
Phosphorus (V) oxychloride supplierView Details
10025-87-3 -
 Phosphorous oxychloride CAS 10025-87-3View Details
Phosphorous oxychloride CAS 10025-87-3View Details
10025-87-3 -
 Phosphorus (V) oxychloride 98% CAS 10025-87-3View Details
Phosphorus (V) oxychloride 98% CAS 10025-87-3View Details
10025-87-3 -
 PHOSPHORUS OXYCHLORIDE Extra Pure CAS 10025-87-3View Details
PHOSPHORUS OXYCHLORIDE Extra Pure CAS 10025-87-3View Details
10025-87-3 -
 Phosphorus Oxychloride Pocl 3 CASView Details
Phosphorus Oxychloride Pocl 3 CASView Details -
 Phosphorous Oxychloride (10025-87-3), 99%, 50Kg DrumView Details
Phosphorous Oxychloride (10025-87-3), 99%, 50Kg DrumView Details
10025-87-3 -
 Phosphorus Oxychloride Pocl 3, 97%, 50 Litre BarrelView Details
Phosphorus Oxychloride Pocl 3, 97%, 50 Litre BarrelView Details
10025-87-3 -
 Phosphorous Oxychloride, 98%, 25Kg DrumView Details
Phosphorous Oxychloride, 98%, 25Kg DrumView Details
10025-87-3
