Quinapril
- CAS NO.:85441-61-8
- Empirical Formula: C25H30N2O5
- Molecular Weight: 438.52
- MDL number: MFCD00865783
- EINECS: 1312995-182-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2023-05-04 17:34:43
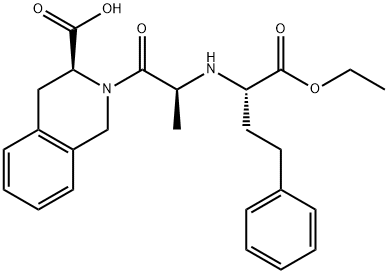
What is Quinapril?
Absorption
Quinapril if 50-80% bioavailable. Quinapril has a Tmax of <1 hour, while quinaprilat has a Tmax of 2.5h. The Cmax of quinaprilat is highly variable but reaches 1526ng/mL with an AUC of 2443ng*h/mL in healthy males given a 10mg dose. A high fat meal reduces the absorption of quinapril by 25-30%.
Toxicity
The oral LD50 in rats is 3541mg/kg and in mice is 1739mg/kg.
Patients experiencing an overdose may present with symptoms of severe hypotension. Due to the extensive protein binding of quinapril and the active metabolite quinaprilat, hemodialysis is not expected to remove the drug from circulation. Treat patients with symptomatic and supportive measures, including normal saline infusions to restore normal blood pressure.
Description
Quinapril is an orally active, non-sulfhydryl ACE inhibitor reportedly useful in the treatment of essential hypertension. The main claimed advantage of quinapril compared with other available ACE inhibitors is its side-effect profile. It is also effective in the management of congestive heart failure.
Originator
Warner-Lambert (USA)
The Uses of Quinapril
Antihypertensive; enzyme inhibitor (angiotensin-converting).
Indications
Quinapril is indicated for the treatment of hypertension and as an adjunct therapy in the treatment of heart failure. Quinapril in combination with hydrochlorothiazide is indicated for the treatment of hypertension.
Background
Quinapril is the ethyl ester prodrug of the non-sulfhydryl angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor quinaprilat. It is used to treat hypertension and heart failure. ACE inhibitors are commonly used as a first line therapy in the treatment of hypertension, along with thiazide diuretics or beta blockers.
Quinapril was granted FDA approval on 19 November 1991. A combination tablet with hydrochlorothiazide was also approved on 28 December 1999.
Definition
ChEBI: Quinapril is a member of the class of isoquinolines that is (3S)-2-L-alanyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid in which the alpha-amino group of the alanyl residue has been substituted by a 1-ethoxycarbonyl-4-phenylbutan-2-yl group (the all-S isomer). A prodrug for quinaprilat (by hydrolysis of the ethyl ester to the corresponding carboxylic acid), it is used as an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor (ACE inhibitor) used (generally as the hydrochloride salt) for the treatment of hypertension and congestive heart failure. It has a role as an EC 3.4.15.1 (peptidyl-dipeptidase A) inhibitor, a prodrug and an antihypertensive agent. It is a member of isoquinolines, a dicarboxylic acid monoester, an ethyl ester and a tertiary carboxamide.
brand name
Accupril (Pfizer); Quinapril (Lupin); Quinapril (Ranbaxy) ;Accupro.
Pharmacokinetics
Quinapril is a prodrug of an angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor used in the treatment of hypertension or adjunct in the treatment of heart failure. Quinapril has a wide therapeutic window and a long duration of action as it is given in doses of 10-80mg once daily.
Clinical Use
Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor:
Hypertension
Congestive heart failure
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Anaesthetics: enhanced hypotensive effect.
Analgesics: antagonism of hypotensive effect and
increased risk of renal impairment with NSAIDs;
hyperkalaemia with ketorolac and other NSAIDs.
Antihypertensives: increased risk of hyperkalaemia,
hypotension and renal failure with ARBs and
aliskiren.
Bee venom extract: possible severe anaphylactoid
reactions when used together.
Ciclosporin: increased risk of hyperkalaemia and
nephrotoxicity.
Cytotoxics: increased risk of angioedema with
everolimus.
Diuretics: enhanced hypotensive effect;
hyperkalaemia with potassium-sparing diuretics.
ESAs: increased risk of hyperkalaemia; antagonism
of hypotensive effect.
Gold: flushing and hypotension with sodium
aurothiomalate.
Lithium: reduced excretion (possibility of enhanced
lithium toxicity).
Potassium salts: increased risk of hyperkalaemia.
Tacrolimus: increased risk of hyperkalaemia and
nephrotoxicity.
Metabolism
Quinapril is de-esterified to the active quinaprilat or dehydrated to form the inactive PD109488. PD109488 can undergo O-deethylation to form another inactive metabolite, PD113413.
Metabolism
Quniapril is a prodrug which is metabolised in the liver
to its active form, quinaprilat, and to minor inactive
metabolites.
Quinaprilat is eliminated primarily by renal excretion.
Properties of Quinapril
| Melting point: | 120-130°C |
| Boiling point: | 662.0±55.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.217±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| pka | 3.39±0.20(Predicted) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 85441-61-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Quinapril
Computed Descriptors for Quinapril
Quinapril manufacturer
Ralington Pharma
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 85441-61-8 Quinapril 98%View Details
85441-61-8 Quinapril 98%View Details
85441-61-8 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8