Phenylhydrazine
Synonym(s):Hydrazinobenzene;Phenylhydrazine
- CAS NO.:100-63-0
- Empirical Formula: C6H8N2
- Molecular Weight: 108.14
- MDL number: MFCD00007573
- EINECS: 202-873-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-09-25 17:15:13
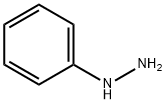
What is Phenylhydrazine?
Chemical properties
Phenylhydrazine is a colorless to pale yellow liquid or solid with a weak aromatic odor. It is soluble in water (values ranging from 145 to 837 g/litre at 24 °C have been reported) and is miscible with alcohol, ether, chloroform, benzene, and acetone. The conversion factor for phenylhydrazine is 1 ppm = 4.5 mg/m3 (at 20 °C, 101 kPa).
Physical properties
Yellow monoclinic crystals with a faint, aromatic odor. Turns red-brown on exposure to air.
The Uses of Phenylhydrazine
Phenylhydrazine is used in the manufactureof dyes and pharmaceuticals; as a stabilizerfor explosive; as a reagent for aldehydes,ketones, and sugars in chemical analysis; andin organic synthesis.
The Uses of Phenylhydrazine
Phenylhydrazine, as hydrochloride solution plus sodium acetate, reacts with polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones yielding osazones or diphenylhydrazones, yellow solids, of definite melting point and utilized in identification of sugars, e.g., phenyl-d-glucosazone, CH2OH (CHOH)3C: (NNHC6H5)CH:(NNHC6H5) plus aniline C6H5NH2 plus NH3.
Definition
ChEBI: A phenylhydrazine that is the monophenyl derivative of hydrazine.
Synthesis Reference(s)
Synthesis, p. 738, 1975 DOI: 10.1055/s-1975-23917
General Description
Pale yellow crystals. Melting point 66°F. Becomes an oily liquid. Toxic by ingestion, inhalation and skin absorption. Flash point 192°F. Autoignition temperature 345°F. Soluble in alcohol.
Air & Water Reactions
When exposed to air becomes red-brown. Slightly denser than water and slightly soluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Phenylhydrazine may ignite spontaneously when in contact with oxidants such as hydrogen peroxide or nitric acid, oxides of iron or copper, or manganese, lead, copper or their alloys. Will not polymerize [USCG, 1999].
Health Hazard
Phenylhydrazine is a moderate to highlytoxic compound and a carcinogen. Acutetoxic symptoms include hematuria, changesin liver and kidney, vomiting, convulsions,and respiratory arrest. Additional symptomsare lowering of body temperature and fallin blood pressure. Chronic exposure to thiscompound caused hemolytic anemia andsignificant body weight loss in rats. Anoral administration of 175 mg/kg was lethalto mice. An oral LD50 value in rat is188 mg/kg
Phenylhydrazine caused adverse repro ductive effect when dosed intraperitoneallyin pregnant mice. It caused jaundice, anemia,and behavioral deficit in offspring
Oral or subcutaneous administration ofphenylhydrazine or its hydrochloride produced lung and liver tumors in experimental animals. ACGIH lists this compoundas a suspected human carcinogen. The evidence of carcinogenicity of this compoundin human is inadequate.
Fire Hazard
Combustible liquid; flash point (closed cup) 89°C (192°F). It reacts with lead dioxide and strong oxidizing compounds vigorous to violently.
Safety Profile
Confirmed carcinogen with experimental carcinogenic data. Poison by ingestion, subcutaneous, and intravenous routes experimental reproductive effects Mutation data reported. Ingestion or subcutaneous injection can cause hemolysis of red blood cells. Other effects are damage to the spleen, liver, kidneys, and bone marrow. The most common effect of occupational exposure is the development of dermatitis, which, in sensitized persons, may be quite severe. Systemic effects include anemia and general weakness, gastrointestinal dsturbances, and injury to the kidneys. Flammable when exposed to heat, flame, or oxidizers. To fight fire, use alcohol foam. Violent reaction with 2phenylamino-3-phenyloxazirane. Reacts with perchloryl fluoride to form an explosive product. Vigorous reaction with lead(Ⅳ) oxide. Used as a chemical reagent, in organic synthesis, and in the manufacture of dyes and drugs. Dangerous; when heated to decomposition it emits highly toxic fumes of NOx; can react with oxidizing materials
Potential Exposure
Phenylhydrazine is a widely used reagent in conjunction with sugars, aldehydes, and ketones. In addition, to its use in the synthesis of dyes; pharmaceuticals, such as antipyrin; cryogenin, and pyramidone; and other organic chemicals. The hydrochloride salt is used in the treatment of polycythemia vera.
Carcinogenicity
Mice given 1mg phenylhydrazine orally each day, 7 days/week for 42 weeks had an increased incidence of total lung tumors. The incidence of malignant tumors also increased. In another study, mice administered 0.01% of the hydrochloride salt in drinking water (average of 0.63–0.81 mg/day) over their lifetimes had an increased incidence of blood vessel tumors. In contrast, mice given phenylhydrazine orally 5 days/week for 40 weeks at doses of 0.5 mg during the first 5 weeks and 0.25 mg thereafter failed to develop tumors.Higher doses could not be tested because of the marked anemia encountered. No leukemias occurred in mice treated with phenylhydrazine, and pulmonary tumors were infrequent . Oral administration or intraperitoneal injection (eight doses, each of 2.9 mg) of phenylhydrazine hydrochloride in mice failed to increase either pulmonary tumors or leukemia. The carcinogenic activity of hydrazine itself has been closely linked to its toxicity, that is, its irritant effect. The mechanism of action, it is postulated, is indirect alkylation of DNA, which is also closely connected to the toxic end point.
Shipping
UN2572 Phenylhydrazine, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials.
Purification Methods
Purify phenylhydrazine by chromatography, then crystallise it from pet ether (b 60-80o)/*benzene. Store it in the dark under N2 as it turns yellow, then red, on exposure to air. It is best stored as the hydrochloride salt; see below. [Coleman Org Synth Coll Vol I 442 1941, Shaw & Stratton J Chem Soc 5004 1962, Beilstein 15 IV 50.]
Incompatibilities
Phenylhydrazine is very reactive with carbonyl compounds, strong oxidizers; strong bases; alkali metals; ammonia, lead dioxide (violent). Attacks copper salts, nickel, and chromates.
Waste Disposal
Controlled incineration whereby oxides of nitrogen are removed from the effluent gas by scrubber, catalytic or thermal device.
Properties of Phenylhydrazine
| Melting point: | 18-21 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 238-241 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 1.098 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| vapor density | 4.3 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | <0.1 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 192 °F |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | Soluble in dilute acids. |
| form | Powder |
| pka | 8.79(at 15℃) |
| color | White to slightly blue or light beige |
| explosive limit | 1.1%(V) |
| Water Solubility | 145 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Sensitive | Air & Light Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,7293 |
| BRN | 606080 |
| Exposure limits | TLV-TWA skin 0.1 ppm (0.44 mg/m3)
(ACGIH), 5 ppm (22 mg/m3) (OSHA);
STEL 10 ppm (44 mg/m3) (OSHA); carcinogenicity: A2-Suspected Human Carcinogen
(ACGIH), Carcinogen (NIOSH).
. |
| Dielectric constant | 7.2(23℃) |
| Stability: | Stable, but may decompose in sunlight. May be air or light sensitive. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, metal oxides. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 100-63-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Hydrazine, phenyl-(100-63-0) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Phenylhydrazine (100-63-0) |
Safety information for Phenylhydrazine
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H317:Sensitisation, Skin H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H341:Germ cell mutagenicity H350:Carcinogenicity H372:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H400:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, acute hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Phenylhydrazine
Phenylhydrazine manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
Jayaveda Globaline LLP
Suvidhinath Laboratories
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Phenyl hydrazine 99%View Details
Phenyl hydrazine 99%View Details -
 Phenyl hydrazine CAS 100-63-0View Details
Phenyl hydrazine CAS 100-63-0View Details
100-63-0 -
 Phenylhydrazine pure CAS 100-63-0View Details
Phenylhydrazine pure CAS 100-63-0View Details
100-63-0 -
 Phenyl hydrazine, puriss CAS 100-63-0View Details
Phenyl hydrazine, puriss CAS 100-63-0View Details
100-63-0 -
 Phenyl hydrazine 98% (GC) CAS 100-63-0View Details
Phenyl hydrazine 98% (GC) CAS 100-63-0View Details
100-63-0 -
 Phenyl hydrazine, GR 99%+ CAS 100-63-0View Details
Phenyl hydrazine, GR 99%+ CAS 100-63-0View Details
100-63-0 -
 C6h8n2 Or C6h5nhnh2c13h11br Phenyl Hydrazine, Packaging Type: BagView Details
C6h8n2 Or C6h5nhnh2c13h11br Phenyl Hydrazine, Packaging Type: BagView Details
100-63-0 -
 Phenyl Hydrazine, For Laboratory, Packaging Size: 10-200kgView Details
Phenyl Hydrazine, For Laboratory, Packaging Size: 10-200kgView Details
100-63-0
