CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Solid |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 120-130 °C |
| Solubility | 8.50e-03 g/L |
| LogP | 0.86 |
| Dissociation Constants | 2.8 |
| Collision Cross Section | 204.4 Ų [M+H]+ [CCS Type: DT, Method: single field calibrated] |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 438.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| XLogP3 | 1.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 10 |
| Exact Mass | 438.21547206 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 438.21547206 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 95.9 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 32 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 648 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 3 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
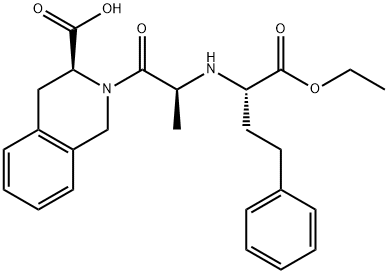
Quinapril is a member of the class of isoquinolines that is (3S)-2-L-alanyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid in which the alpha-amino group of the alanyl residue has been substituted by a 1-ethoxycarbonyl-4-phenylbutan-2-yl group (the all-S isomer). A prodrug for quinaprilat (by hydrolysis of the ethyl ester to the corresponding carboxylic acid), it is used as an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor (ACE inhibitor) used (generally as the hydrochloride salt) for the treatment of hypertension and congestive heart failure. It has a role as an EC 3.4.15.1 (peptidyl-dipeptidase A) inhibitor, a prodrug and an antihypertensive agent. It is a member of isoquinolines, a dicarboxylic acid monoester, an ethyl ester and a tertiary carboxamide.