Potassium bromide
Synonym(s):Hydrobromic Acid Potassium Salt;Potassium bromide;Potassium bromide solution
- CAS NO.:7758-02-3
- Empirical Formula: BrK
- Molecular Weight: 119
- MDL number: MFCD00011358
- EINECS: 231-830-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:34

What is Potassium bromide?
Chemical properties
Potassium bromide is a white or colourless crystalline solid with an irritating strong bitter and salty taste.KBr is hygroscopic, deliquescent, very soluble in water, soluble in some polar organic solvents such as glycerol, ethylene glycol, liquid ammonia and hot ethanol, but insoluble in acetone. The aqueous solution is neutral (pH about 7). It crystallises in the same cubic rock salt structure as sodium chloride. When dissolved, KBr dissociates completely into its ions, making it a useful source of bromide ions for double replacement or salt metabolism reactions. This is used in the production of silver bromide photographic film. KBr is also used as a sedative in the treatment of convulsions. Because of its range of transparency to infrared radiation, KBr is used both as a matrix for solid samples and as a prism material in infrared spectroscopy.
The Uses of Potassium bromide
Potassium bromide was used as a secondary halide in combination with an iodide in the paper negative processes, the albumen on glass process, and the wet collodion processes. When silver bromide gelatin emulsion was invented, potassium bromide was the primary halide. It was also used in combination with either bichloride of mercury, copper sulfate, or potassium ferricyanide in photographic bleaches and as a restrainer in alkaline developers used for gelatin plates and developing-out papers.
What are the applications of Application
Potassium bromide is used to remove peripheral membrane proteins and as a source of bromine
Definition
ChEBI: Potassium bromide is a metal bromide salt with a K(+) counterion. It is used in the manufacture of photographic film, developer, film thickener, toner and color photo bleach.
What are the applications of Application
Potassium bromide is widely used in optics because KBr has a low refractive index and a wide spectral range into the infrared with nearly no absorption. As a result, KBr is widely used as infrared optical windows, as infrared beamsplitters, and as substrates for interferometers. Commonly KBr is used in transmission infrared spectroscopy as a media for powder samples. The KBr and powder are ground together and pressed, using a die, into a thin disc under vacuum. The disc suspends the sample without contributing to the transmitted signal. Potassium bromide has also been used in synthesis, commonly as a source of bromide ions. For example, double displacement of KBr and bismuth nitrate yielded nanosheets of bismuth oxybromide. Solutions of KBr have also been found to be useful shape-control agents or crystal-habit modifiers in formation of metal nanocrystals, including palladium nanorods and bimetallic platinum-paladium nanocrystals. KBr is a common source of bromide ions used as nucleophiles in organic chemistry.
Preparation
Potassium bromide was produced by the action of bromine on hot potassium hydroxide solution or Reacting elemental bromine with potassium hydroxide or potassium iodide will produce the potassium bromide salt:
KOH + Br2 → KBr + HOBr
KI + Br2 → KBr + I2
The reaction of bromine with potassium carbonate and urea is the basis of the process. The first step of the process involves the addition of K2SO4 to the potassium carbonate solution, followed by heating to 80 °C. After the lead-containing precipitate is removed by filtration, the bromine and urea are added, and the temperature and pH are adjusted to 30 °C and 6.0-6.5, respectively. Potassium bromide is recovered by recrystallization after reduction of volume of the reacting solution by evaporation. The sulfate can be removed from the solution by addition of BaBr2.
Air & Water Reactions
Water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
Potassium bromide is not in generally strongly reactive. A weak reducing agent, incompatible with oxidizing agents. Also incompatible with salts of mercury and silver. Violent reactions occur with bromine trifluoride. May react with nitrous ether spirit, many alkaloidal salts and starch. May also react with acids . Reacts with concentrated sulfuric acid to generate fumes of hydrogen bromide.
Hazard
Toxic by ingestion and inhalation
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for Potassium bromide are not available; however, Potassium bromide is probably nonflammable.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Biochem/physiol Actions
Potassium bromide (KBr) is used as an anticonvulsant and sedative. KBr is used for optical windows and prisms. KBr is transparent in the wide wavelength range from near ultraviolet to long wave infrared. It is employed in the sample preparation for infrared transmission spectra.
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by ingestion and intraperitoneal routes. Large doses can cause central nervous system depression. Prolonged inhalation may cause skin eruptions. Mutation data reported. Violent reaction with BrF3. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of K2O and Br-. See also BROMIDES.
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
Bromides are used both as primary therapy and as adjunctive therapy
to control seizures in dogs that are not adequately controlled by
phenobarbital (or primidone) alone (when steady state trough phenobarbital
levels are >30 mcg/mL for at least one month). While
historically bromides were only recommended for use alone in patients
suffering from phenobarbital (or primidone) hepatotoxicity,
they are more frequently used as a drug of first choice.
Although not frequently used, bromides are also considered
suitable by some for use in cats with chronic seizure disorders, but
cats may be more susceptible to the drug’s adverse effects.
Side Effects
Common side effects of Potassium bromide include: nausea, thirst and excessive urination, drowsiness or lethargy, and cough. Prolonged or excessive use may lead to high levels of bromide in the body's blood, producing the toxic syndrome of "bromotoxicosis". The presenting symptoms include drowsiness, weakness, muscle tremors and aches, loss of appetite, constipation, and skin rashes. Therefore, bromide levels should be monitored regularly.
Purification Methods
Crystallise the bromide from distilled water (1mL/g) between 100o and 0o. Wash it with 95% EtOH, followed by Et2O. Dry it in air, then heat it at 115o for 1hour, pulverize it, then heat it in a vacuum oven at 130o for 4hours. It has also been crystallised from aqueous30% EtOH, or EtOH, and dried over P2O5 under vacuum before heating in an oven.
Properties of Potassium bromide
| Melting point: | 734 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 1435 °C/1 atm (lit.) |
| Density | 3.119 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor density | 7.14 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 175 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.559 |
| Flash point: | 1435°C |
| storage temp. | Store at +5°C to +30°C. |
| solubility | H2O: 1 M at 20 °C, clear, colorless |
| form | random crystals |
| color | White |
| Specific Gravity | 2.75 |
| PH | 5.0-8.8 (25℃, 50mg/mL in H2O) |
| Water Solubility | 650 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| λmax | λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.01 λ: 280 nm Amax: 0.01 |
| Merck | 14,7618 |
| Dielectric constant | 4.8700000000000001 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong acids, bromine trifluoride and bromine trichloride. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7758-02-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Potassium bromide(7758-02-3) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Potassium bromide (7758-02-3) |
Safety information for Potassium bromide
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P337+P313:IF eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Potassium bromide
| InChIKey | IOLCXVTUBQKXJR-UHFFFAOYSA-M |
Potassium bromide manufacturer
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
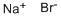

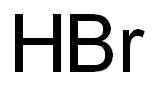
You may like
-
 Potassium bromide 99%View Details
Potassium bromide 99%View Details -
 Potassium bromide crystal optic disc, 13mm x 2mm, Polished both sides CASView Details
Potassium bromide crystal optic disc, 13mm x 2mm, Polished both sides CASView Details -
 Potassium bromide crystal optic disc, 22mm x 4mm, Polished both sides CASView Details
Potassium bromide crystal optic disc, 22mm x 4mm, Polished both sides CASView Details -
 Potassium bromide crystal optic disc, Polished on both sides CASView Details
Potassium bromide crystal optic disc, Polished on both sides CASView Details -
 POTASSIUM BROMIDE 0.5M (0.5N) STANDARDIZED SOLUTION traceable to NIST CASView Details
POTASSIUM BROMIDE 0.5M (0.5N) STANDARDIZED SOLUTION traceable to NIST CASView Details -
 POTASSIUM BROMIDE For IR Spectroscopy CASView Details
POTASSIUM BROMIDE For IR Spectroscopy CASView Details -
 POTASSIUM BROMIDE 1M (1N) STANDARDIZED SOLUTION traceable to NIST CASView Details
POTASSIUM BROMIDE 1M (1N) STANDARDIZED SOLUTION traceable to NIST CASView Details -
 POTASSIUM BROMIDE Extra Pure CASView Details
POTASSIUM BROMIDE Extra Pure CASView Details
