Phosphorus pentachloride
Synonym(s):Phosphorus pentachloride;Phosphorus(V) chloride;Phosphorus(V) chloride, polymer-bound
- CAS NO.:10026-13-8
- Empirical Formula: Cl5P
- Molecular Weight: 208.24
- MDL number: MFCD00011439
- EINECS: 233-060-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-09-25 17:15:13
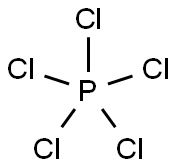
What is Phosphorus pentachloride?
Chemical properties
Phosphorus pentachloride is a pale yellow, fuming solid with an odor like hydrochloric acid.162℃ sublimation and partial decomposition. All decomposed into chlorine gas and phosphorus trichloride at 300℃. Soluble in carbon disulfide, carbon tetrachloride. Decomposed in water, hydrolyzed in moist air into phosphoric acid and hydrogen chloride, white smoke and special irritating odor occur, strongly irritate the eyes.
The Uses of Phosphorus pentachloride
Phosphorus pentachloride is used as a chlorinating agent to convert acids into acid chlorides, as a dehydrating agent, and as a catalyst.
The Uses of Phosphorus pentachloride
As catalyst in manufacture of acetylcellulose; for replacing hydroxyl groups by Cl, particularly for converting acids into acid chlorides.
Definition
ChEBI: Phosphorus pentachloride is a phosphorus halide.
General Description
Phosphorus pentachloride is a greenish-yellow crystalline solid with an irritating odor. Phosphorus pentachloride is decomposed by water to form hydrochloric and phosphoric acid and heat. This heat may be sufficient to ignite surrounding combustible material. Phosphorus pentachloride is corrosive to metals and tissue. Long term exposure to low concentrations or short term exposure to high concentrations can result in adverse health effects from inhalation.
Reactivity Profile
Phosphorus pentachloride is a lightly yellow, fuming crystalline material, highly caustic, corrosive and toxic. Flammable by chemical reaction. Violent exothermic reaction with water or steam. When heated to decomposition Phosphorus pentachloride emits highly toxic fumes of chlorides and oxides of phosphorus. Explosive reaction with alkaline metals (sodium, potassium), urea. Ignites on contact with fluorine. Violent reaction with aluminum, chlorine trioxide, hydroxylamine, magnesium oxide, nitrobenzene, phosphorus(III) oxide, potassium. Carbamates form explosive products [Bretherick, 5th ed., 1995, p. 1360]. Reaction with the mixture of chlorine and chlorine dioxide causes explosion [Mellor, 1941, vol. 2, p. 281; 1940, vol. 8, p. 1013].
Health Hazard
Phosphorus pentachloride vapors are a strong irritant to the eyes and mucous membranes. Contact with skin can cause acid burns, as it reacts readily with moisture to form hydrochloric and phosphoric acids:
PCl5+4H2O→ H3PO4+5HCl
Chronic exposure to this compound can result in bronchitis.
LC50 value, inhalation (rats): 205 mg (24 ppm)/m3 (NIOSH 1986).
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Safety Profile
Poison by inhalation. Moderately toxic by ingestion. A severe eye, skin, and mucous membrane irritant. Corrosive to body tissues. Flammable by chemical reaction. Explosive reaction with chlorine dioxide + chlorine, sodium, urea + heat. Reacts to form explosive products with carbamates, 3'-methy-2-nitrobenzanilide (product explodes on contact with air). Ignites on contact with fluorine. Reacts violently with moisture, ClO3, hydroxyl- amine, magnesium oxide, nitrobenzene, phosphorus(Ⅲ) oxide, K. To fight fire, use CO2, dry chemical. Incompatible with aluminum, chlorine dioxide, chlorine,diphosphorus trioxide, fluorine, hydroxylamine, magnesium oxide, 3'-methyl- 2-nitrobenzanilide, nitrobenzene, sodium, urea, water. Will react with water or steam to produce heat and toxic and corrosive fumes. Used as a catalyst, chlorinating and dehydrating agent. When heated to decomposition it emits highly toxic fumes of Cland POx.
Potential Exposure
Phosphorus pentachloride is used as a as a chlorinating and dehydrating agent and as a catalyst. It is used in the manufacture of agricultural chemicals;chlorinated compounds; gasoline additives, plasticizers and surfactants; and in pharmaceutical manufacture
Shipping
UN1806 Phosphorus pentachloride, Hazard class: 8; Labels: 8-Corrosive material.
Purification Methods
[All operations should be carried out in an efficient fume cupboard.] Sublime it at 160-170o in an atmosphere of chlorine. Excess chlorine is then displaced by dry N2 gas. All subsequent manipulations should be performed in a dry-box [Downs & Johnson J Am Chem Soc 77 2098 1955]. It fumes in moist air and attacks the eyes and the mucous membranes of the nose. It should not be breathed in and has very HARMFUL VAPOURS (wash burning eyes with aqueous NaHCO3).
Incompatibilities
Phosphorus pentachloride is a powerful oxidizer. Reacts with water (violent), magnesium oxide, chemically active metals, such as sodium and potassium, alkalis, amines, carbamates, aluminum powder, combustibles, fluorine, phosphorus pentoxide, phosphorus trioxide, and many other substances. Hydrolyzes in water (even in humid air) to form hydrochloric acid and phosphoric acid. Corrosive to many metals, forming flammable and explosive hydrogen gas. Attacks plastic and rubber.
Waste Disposal
Decompose with water, forming phosphoric and hydrochloric acids. Neutralize acids and dilute if necessary for discharge into the sewer system.
Properties of Phosphorus pentachloride
| Melting point: | 179-181°C (subl.) |
| Boiling point: | 160 °C |
| Density | 1.6 |
| vapor pressure | 0.016 hPa (20 °C) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Soluble in carbon disulfide and carbon tetrachloride. |
| form | macroporous |
| color | Yellow |
| Specific Gravity | 1.6 |
| Odor | Pungent odour |
| PH | 1 (5g/l, H2O)acidic |
| Water Solubility | decomposes |
| Sensitive | Moisture Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,7351 |
| Exposure limits | TLV-TWA 0.85 mg/m3 (0.1 ppm) (ACGIH), ~1 mg/m3 (0.1 ppm) (OSHA). . |
| Dielectric constant | 2.8(160℃) |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic, Moisture Sensitive |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 10026-13-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Phosphorus pentachloride(10026-13-8) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Phosphorus pentachloride (10026-13-8) |
Safety information for Phosphorus pentachloride
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H314:Skin corrosion/irritation H330:Acute toxicity,inhalation H373:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P314:Get medical advice/attention if you feel unwell. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Phosphorus pentachloride
| InChIKey | UHZYTMXLRWXGPK-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Phosphorus pentachloride manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
Abhishek Impex
ASM Organics
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Phosphorus pentachloride 98%View Details
Phosphorus pentachloride 98%View Details -
 10026-13-8 Phosphorus pentachloride 98%View Details
10026-13-8 Phosphorus pentachloride 98%View Details
10026-13-8 -
 Phosphorous pentachloride CAS 10026-13-8View Details
Phosphorous pentachloride CAS 10026-13-8View Details
10026-13-8 -
 PHOSPHOROUS PENTACHLORIDE For Synthesis CAS 10026-13-8View Details
PHOSPHOROUS PENTACHLORIDE For Synthesis CAS 10026-13-8View Details
10026-13-8 -
 Phosphorus pentachloride 97% CAS 10026-13-8View Details
Phosphorus pentachloride 97% CAS 10026-13-8View Details
10026-13-8 -
 Phosphorus pentachloride CAS 10026-13-8View Details
Phosphorus pentachloride CAS 10026-13-8View Details
10026-13-8 -
 Phosphorus pentachloride CAS 10026-13-8View Details
Phosphorus pentachloride CAS 10026-13-8View Details
10026-13-8 -
 25Kg Phosphorus Pentachloride, CrystalsView Details
25Kg Phosphorus Pentachloride, CrystalsView Details
10026-13-8
