Phosphorus pentoxide
Synonym(s):di-Phosphorus pentoxide;Phosphoric anhydride;Phosphorus pentoxide, 7.7 wt. % in methanesulfonic acid;Phosphorus(V) oxide;Sicapent
- CAS NO.:1314-56-3
- Empirical Formula: O5P2
- Molecular Weight: 141.94
- MDL number: MFCD00011440
- EINECS: 215-236-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:50:40
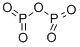
What is Phosphorus pentoxide?
Description
Phosphorus pentoxide (empirical formula P2O5) is known to many laboratory workers as a powerful desiccant. It is manufactured by burning elemental phosphorus in a current of dry air. P2O5?exists in several crystalline and amorphous forms, the most common of which is the crystalline P4O10?shown. In the fertilizer industry, phosphorus concentration is expressed as weight percent P2O5?equivalent.
Chemical properties
Phosphorus pentoxide is a white crystalline solid.
Physical properties
White, deliquescent, powdery solid; exhibits polymorphism; converts to several different crystalline forms on heating; the commercial material consists of hexagonal crystals; the hexagonal crystals on very rapid heating first melt at 420°C and then resolidify immediately to glassy orthorhombic crystals; slow heating of hexagonal crystals causes melting at 340°C which, on solidification, gives the same metastable orthorhombic form; the glassy material melts at about 580°C to a colorless and heavily viscous liquid; sublimes at 360°C; density of the commercial product 2.39g/cm3; reacts with water.
The Uses of Phosphorus pentoxide
Phosphorus(V) oxide is used as a drying and dehydrating agent, a condensation reagent in organic synthesis and a laboratory reagent. It is also used in sugar refining and in fire extinguishing. Phosphorus pentoxide in DMSO forms an Onodera reagent which oxidizes alcohols. It is capable of converting mineral acids to anhydrides.
The Uses of Phosphorus pentoxide
Drying and dehydrating agent. Condensing agent in organic synthesis.
The Uses of Phosphorus pentoxide
It is used as a dehydrating agent, in organic synthesis, and in hydrocarbon analysis.
What are the applications of Application
Phosphorus pentoxide is a dehydrating agent employed as a dessicant
Production Methods
Phosphorus pentoxide or phosphoric anhydride (P2O5) is formed by burning yellow phosphorus in dry air or oxygen.
Preparation
Phosphorus pentoxide is prepared by burning phosphorus in a plentiful supply of dry air or oxygen: P4 + 5O2 → P4O10 The crude product may contain a small amount of sesquioxide, P2O3, which may be removed by sublimation in ozonized oxygen.
Definition
ChEBI: Diphosphonate(2-) is a divalent inorganic anion obtained by removal of both protons from diphosphonic acid. It is a phosphorus oxoanion and a divalent inorganic anion. It is a conjugate base of a diphosphonate(1-).
General Description
A white amorphous powder. Corrosive to metals and tissue and moderately toxic.
Air & Water Reactions
Readily absorbs moisture from the air forming a syrup of meta-, pyro-, and orthophosphoric acids. Reacts violently with water releasing considerable heat [Oldbury Chemicals, p. 9].
Reactivity Profile
Phosphorus pentoxide reacts violently and exothermically with water. The heat can ignite surrounding or admixed combustible materials. Undergoes hazardous or violent reactions with metal hydroxides and oxides, formic acid, hydrogen fluoride and hydrofluoric acid, iodides, metals (in particular potassium and sodium), oxidizing agents (bromine pentafluoride, chlorine trifluoride, perchloric acid, oxygen difluoride, hydrogen peroxide), ammonia, and proparygl alcohol. [Bretherick, 5th ed., 1995, p. 1781; EPA, 1998]. A violent explosion occurs if a solution of perchloric acid in chloroform is poured over phosphorus pentaoxide [EPA, 1998].
Hazard
Phosphorus pentoxide is a strong irritant. It is corrosive to skin and contact with eyes can be injurious.
Health Hazard
Because of its dehydrating action, phosphorus pentoxide is a highly corrosive substance. It is an irritant to the eyes, skin, and mucous membranes.Inhalation of its vapors caused chronic pulmonary edema, injury to lungs, and hemorrhage in test animals. The LC50 values varied significantly with the species.
LC50 value, inhalation (rats): 127 mg/m3/h .
Fire Hazard
Reacts violently with water to evolve heat. Flammable poisonous gases may accumulate in tanks and hopper cars. Phosphorus pentoxide reacts violently with the following: ammonia, hydrofluoric acid, oxygen difluoride, potassium, sodium, propargyl alcohol, calcium oxide, sodium hydroxide and chlorine trifluoride. A violent explosion occurs if a solution of perchloric acid in chloroform is poured over phosphorus pentoxide. Avoid formic acid, hydrogen fluoride, inorganic bases, metals, oxidants, water. Readily absorbs moisture from air to form meta-, pryo-, or orthophosphoric acid.
Agricultural Uses
Phosphoric anhydride is another name for phosphorus pentoxide (P2O5). Anhydrides react with water to give acids. For example, sulphur trioxide reacts with water to give sulphuric acid, or acetic anhydride reacts with water to give acetic acid. Similarly, phosphorus pentoxide has great affinity for water and dissolves in it to give phosphoric acid, and therefore, is known as phosphoric anhydride.
Safety Profile
Poison by inhalation. A corrosive irritant to the eyes, shin, and mucous membranes. With the appropriate conditions it undergoes hazardous reactions with formic acid, hydrogen fluoride, inorganic bases, iodides, metals, methyl hydroperoxide, oxidants (e.g., bromine, pentafluoride, chlorine trifluoride, perchloric acid, oxygen Difluoride, hydrogen peroxide), 3-propynol, water. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of POx.
Potential Exposure
This material is used as an intermediate in organic synthesis, catalyst, condensing agent; dehydrating agent; in the preparation of acrylate esters, surfactants, sugar refining; medicine, fire extinguishing; and special glasses.
Purification Methods
It has been sublimed at 250o under vacuum into glass ampoules. It fumes in moist air and reacts violently with water. It is an excellent drying agent for use in desiccators. HARMFUL VAPOURS and attacks skin. [Manley J Chem Soc 121 331 1922, Klements in Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry (Ed. Brauer) Academic Press Vol I p 541 1963.]
Incompatibilities
Reacts violently and exothermically with water, forming ignition level heat and highly corrosive phosphoric acid. Keep away from the combination of moisture and combustible materials. Phosphorus pentoxide reacts violently with the following: perchloric acid; ammonia, hydrofluoric acid; oxidizers, hydrogen fluoride; formic acid, oxygen difluoride, potassium, sodium, propargyl alcohol; calcium oxide; inorganic bases; sodium hydroxide and chlorine trifluoride. Attacks many metals in presence of water. Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides, alcohols, ammonia. Undergoes hazardous or violent reactions with metal hydroxides and oxides, formic acid, hydrogen fluoride and hydrofluoric acid, iodides, metals (in particular potassium and sodium), ammonia, and proparygl alcohol.
Waste Disposal
Decompose with water, forming phosphoric and hydrochloric acids. The acids may then be neutralized and diluted slowly to solution of soda ash and slaked lime with stirring then flush to sewer with large volumes of water.
Properties of Phosphorus pentoxide
| Melting point: | 340 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 122 °C (1 mmHg) |
| Density | 2.3 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| vapor density | 4.9 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 1 mm Hg ( 384 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.433-1.436 |
| Flash point: | 340-360°C |
| storage temp. | no restrictions. |
| solubility | Soluble in sulfuric acid. Insoluble in acetone and ammonia. |
| appearance | White powder |
| form | Very Deliquescing Powder |
| color | White |
| Specific Gravity | 2.39 |
| PH Range | <2 |
| PH | 1 (5g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| Odor | Pungent odour |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in sulfuric acid. Insoluble in acetone and ammonia. Decomposes in water. |
| Sensitive | Moisture Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,7355 |
| Sublimation | 340-360 ºC |
| Stability: | Stability Stable, but reacts violently with water, alcohols, metals, sodium, potassium, ammonia, oxidizing agents, HF, peroxides, magnesium, strong bases. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 1314-56-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Diphosphorus pentoxide(1314-56-3) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Phosphorus pentoxide (1314-56-3) |
Safety information for Phosphorus pentoxide
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H314:Skin corrosion/irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P363:Wash contaminated clothing before reuse. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Phosphorus pentoxide
| InChIKey | YWEUIGNSBFLMFL-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Phosphorus pentoxide manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
Amar Enterprises
Triveni Interchem Private Limited (Group Of Triveni Chemicals)
ASM Organics
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 Phosphorous Pentoxide (P2O5) 99%View Details
Phosphorous Pentoxide (P2O5) 99%View Details -
 Phosphorus(V) oxide CAS 1314-56-3View Details
Phosphorus(V) oxide CAS 1314-56-3View Details
1314-56-3 -
 Phosphorus(V) oxide CAS 1314-56-3View Details
Phosphorus(V) oxide CAS 1314-56-3View Details
1314-56-3 -
 Phosphorus (V) pentoxide 98% CAS 1314-56-3View Details
Phosphorus (V) pentoxide 98% CAS 1314-56-3View Details
1314-56-3 -
 Powder Phosphorus Pentoxide CAS Reg. No. 1314-56-3, Grade Standard: Reagent GradeView Details
Powder Phosphorus Pentoxide CAS Reg. No. 1314-56-3, Grade Standard: Reagent GradeView Details
1314-56-3 -
 Phosphorus Pentoxide (1314-56-3), Grade Standard: Industrial Grade, Purity: 98%View Details
Phosphorus Pentoxide (1314-56-3), Grade Standard: Industrial Grade, Purity: 98%View Details
1314-56-3 -
 Phosphorus Pentoxide PowderView Details
Phosphorus Pentoxide PowderView Details
1314-56-3 -
 Phosphorus Pentoxide Powder, Purity: 99%, Grade Standard: Technical GradeView Details
Phosphorus Pentoxide Powder, Purity: 99%, Grade Standard: Technical GradeView Details
1314-56-3
