Orthoboric acid
Synonym(s):Boric acid;TBE buffer
- CAS NO.:10043-35-3
- Empirical Formula: BH3O3
- Molecular Weight: 61.83
- MDL number: MFCD00236358
- EINECS: 233-139-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
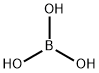
What is Orthoboric acid ?
Absorption
Boric acid is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, open wounds, and serous cavities but displays limited absorption in intact skin . Following intraperitoneal injection in mice, the peak concentration was reached in about 1.0-1.5 hr in the brain whereas the value was 0.5 hr in other tissues .
Toxicity
Acute oral LD50 is 2660 mg/kg in rat . Individuals are likely to be exposed to boric acid from industrial manufacturing or processing. Local tissue injury from boric acid exposure is likely due to caustic effects. Systemic effects from boric acid poisoning usually occur from multiple exposures over a period of days and involve gastrointestinal, dermal, CNS, and renal manifestations. Gastrointestinal toxicity include persistent nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, epigastric pain, hematemesis, and blue-green discoloration of the feces and vomit . Following the onset of GI symptoms, a characteristic intense generalized erythroderma follows . Management of mild to moderate toxicity should be supportive. In case of severe toxicity, dialysis may be required in addition to supportive treatment.
Description
Boric acid is a white, amorphous powder orcolorless, crystalline solid. Molecular weight=61.84;Boiling point=300℃ (decomposes: loses 1/2 its H2O);Freezing/Melting point=170.9℃ (decomposes above100℃). Saturated solutions: at 0℃, 2.6% acid; at 100℃,28% acid. Hazard Identification (based on NFPA-704 MRating System): Health 2, Flammability 0, Reactivity 1.Boric acid is soluble in water; solubility=4.7 g/100 mL at20℃.
Chemical properties
White powder or granules and odorless. It is incompatible with potassium, acetic anhydride, alkalis, carbonates, and hydroxides. Boric acid has uses in the production of textile fiberglass, flat panel displays, and eye drops. Boric acid is recognized for its application as a pH buffer and as a moderate antiseptic agent and emulsifier.
Chemical properties
Boric acid is a white, amorphous powder or colorless, crystalline solid.
Chemical properties
Boric acid occurs as a hygroscopic, white crystalline powder, colorless shiny plates, or white crystals.
Physical properties
Colorless, transparent triclinic crystal or white granule or powder; density 1.435 g/cm3; melts at 171°C under normal heating; however, slow heating causes loss of water; sparingly soluble in cold water (4.7% at 20°C); pH of 0.1M solution 5.1; readily dissolves in hot water (19.1% at 80°C and 27.5% at 100°C); also soluble in lower alcohols and moderately soluble in pyridine.
The Uses of Orthoboric acid
It is a precursor material for other boron compounds. A dilute water solution of boric acid is usually employed as a mild antiseptic and eyewash. Boric acid is too employed in leather manufacture, electroplating, and cosmetics.
The Uses of Orthoboric acid
Boric acid can be used to study molecular biology, DNA and RNA purification, biological buffers and molecular biology reagents. Boric acid has been used to test the toxic effects of boron on growth and antioxidant system parameters of maize (Zea mays L.) roots. Boric acid has also been used to study the effect of time period after boric acid injection on (10)B absorption in different regions of adult male rat′s brain.
The Uses of Orthoboric acid
For weatherproofing wood and fireproofing fabrics; as a preservative; manufacture of cements, crockery, porcelain, enamels, glass, borates, leather, carpets, hats, soaps, artificial gems; in nickeling baths; cosmetics; printing and dyeing, painting; photography; for impregnating wicks; electric condensers; hardening steel. Also used as insecticide for cockroaches and black carpet beetles.
Indications
No FDA- or EMA-approved therapeutic indications on its own.
Background
Boric acid, also known as hydrogen borate, is a weak monobasic Lewis acid of boron with the chemical formula H3BO3. Boric acid is typically utilized in industrial processing and manufacturing, but is also used as an additive in pharmaceutical products, cosmetics, lotions, soaps, mouthwash, toothpaste, astringents, and eyewashes . It is known to exhibit some antibacterial activity against infections such as bacterial vaginosis and candidiasis .
What are the applications of Application
Boric Acid is a commonly used molecular biology reagent that exhibits some antifungal activity
Definition
ChEBI: Boric acid is a member of boric acids. It has a role as an astringent. It is a conjugate acid of a dihydrogenborate.
Preparation
Boric acid is produced from borax, colemanite, or other inorganic borates by reaction with sulfuric acid or hydrochloric acid, and cooling the solution to proper temperature:
Na2B4O7 ? 10Η2Ο + H2SO4 → 4H3BO3 + Na2SO4 + 5H2O
It also may be prepared by extraction of weak borax brine with a kerosene solution of an aromatic diol, such as 2-ethyl-1,3-hexanediol or 3-chloro- 2-hydroxy-5-(1,1,3,3-tetramethylbutyl)benzyl alcohol. The diol-borate chelate formed separates into a kerosene phase. Treatment with sulfuric acid yields boric acid which partitions into aqueous phase and is purified by recrystallization.
Production Methods
Boric acid occurs naturally as the mineral sassolite. However, the majority of boric acid is produced by reacting inorganic borates with sulfuric acid in an aqueous medium. Sodium borate and partially refined calcium borate (colemanite) are the principal raw materials. When boric acid is made from colemanite, the fineground ore is vigorously stirred with mother liquor and sulfuric acid at about 908℃. The by-product calcium sulfate is removed by filtration, and the boric acid is crystallized by cooling the filtrate.
brand name
Alpagelle;Anojel;Anugard;Anojel;Anugard;Anusol hc;Anusol hc;Berlicetin;Betadrin;Berlicetin;Betadrin;Bluboro;Boroformal;Bluboro;Boroformal;Borogal;Borogal;Borsyre viskos;Cacimag;Borsyre viskos;Cacimag;Caclcifor;Caclcifor;Calcamyl-24;Calcibenzamin;Calcamyl-24;Calcibenzamin;Camilca;Camilca;Chibro;Coneolent;Chibro;Coneolent;Cutaden;Cutaden;Dissol;Ear-dry;Dissol;Ear-dry;Egosol-bs;Egosol-bs;Evercil;Fermakzem;Evercil;Fermakzem;Flex-care;Flex-care;Glaucadrine;Glucocalcium;Glaucadrine;Glucocalcium;Kalopsisi;Kerapos;Kalopsisi;Kerapos;Kodomo smarin;Kodomo smarin;Komex;Lindemil;Komex;Lindemil;Macaldex;Macaldex;Mentol sedans sulfamidad;Neo-smarin dia;Mentol sedans sulfamidad;Neo-smarin dia;Neo-vagipurin;Neo-vagipurin;Normol;O-biol;Normol;O-biol;Oestro-gynedron;Oestro-gynedron;Ophtalmin;Otocaina;Ophtalmin;Otocaina;Pedoz;Pedoz;Phoscanol;Phoscanol;Poly-gynedron;Preferal;Poly-gynedron;Preferal;Proculin;Proculin;Rhinophenazol;Saddle mate;Rhinophenazol;Saddle mate;Swim-ear;Swim-ear;Swim-eye;Swim-eye;Timazincum;Timazincum;Tipolin;Tricho-gynedron;Tipolin;Tricho-gynedron;Unisol;Unisol;Vetacalin-m;Alpagelle;Vetacalin-m.
World Health Organization (WHO)
Boric acid and some borates were formerly extensively used as disinfectants and antiinflammatory agents. By the late 1960s an association between the death of many infants and application of high concentrations of boric acid contained in topical preparations used in the treatment of napkin rash had been established. This led to the restriction of the use of boric acid in pharmaceutical preparations by many regulatory authorities. In some countries it is now permitted only as an ingredient in ophthalmological preparations.
General Description
Boric acid is a weak monobasic acid, it accepts OH- ions, hence is a Lewis acid. In boric acid, B is sp2 hybridized, forming a planar triangle structure. The principal oxide of boron, B2O3, is obtained as a vitreous solid by dehydration of boric acid at red heat.
Hazard
Toxic via ingestion. Use only weak solu- tions. Irritant to skin in dry form.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Pharmaceutical Applications
Boric acid is used as an antimicrobial preservative in eye drops,
cosmetic products, ointments, and topical creams. It is also used as
an antimicrobial preservative in foods.
Boric acid and borate have good buffering capacity and are used
to control pH; they have been used for this purpose in external
preparations such as eye drops.
Boric acid has also been used therapeutically in the form of
suppositories to treat yeast infections. In dilute concentrations it
is used as a mild antiseptic, with weak bacteriostatic and fungistatic
properties, although it has generally been superseded by more
effective and less toxic disinfectants.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Boric acid has antibacterial and fungicidal properties. It is used in the periodontal therapy as an irrigation solution as it elicits bactericidal effects in microbial biofilms in root canal. Boric acid may favor osteoblastic activity and inhibit bone loss. It inhibits Candida albicans fungal infection and has potential to treat vaginal infection.
Pharmacokinetics
Boric acid exhibits minimal bacteriostatic and antifungal activities . Boric acid is likely to mediate antifungal actions at high concentrations over prolonged exposures .
Safety
Boric acid is a weak bacteriostatic and antimicrobial agent, and has
been used in topical preparations such as eye lotions, mouthwashes
and gargles. It has also been used in US- and Japanese-approved
intravenous products. Solutions of boric acid were formerly used to
wash out body cavities, and as applications to wounds and ulcers,
although the use of boric acid for these purposes is now regarded as
inadvisable owing to the possibility of absorption. Boric acid is
not used internally owing to its toxicity. It is poisonous by ingestion
and moderately toxic by skin contact. Experimentally it has proved
to be toxic by inhalation and subcutaneous routes, and moderately
toxic by intraperitoneal and intravenous routes.
Boric acid is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and from
damaged skin, wounds, and mucous membranes, although it does
not readily permeate intact skin. The main symptoms of boric acid
poisoning are abdominal pain, diarrhea, erythematous rash
involving both skin and mucous membrane, and vomiting. These
symptoms may be followed by desquamation, and stimulation or
depression of the central nervous system. Convulsions, hyperpyrexia,
and renal tubular damage have been known to occur.
Death has occurred from ingestion of less than 5 g in young
children, and of 5–20 g in adults. Fatalities have occurred most
frequently in young children after the accidental ingestion of
solutions of boric acid, or after the application of boric acid powder
to abraded skin.
The permissible exposure limit (PEL) of boric acid is 15 mg/m3
total dust, and 5 mg/m3 respirable fraction for nuisance dusts.
LdLo (man, oral): 429 mg/kg
LdLo (woman, oral): 200 mg/kg
LdLo (infant, oral): 934 mg/kg
LdLo (man, skin): 2.43 g/kg
LdLo (infant, skin): 1.20 g/kg
LD50 (mouse, oral): 3.45 g/kg
LD50 (mouse, IV): 1.24 g/kg
LD50 (mouse, SC): 1.74 g/kg
LD50 (rat, oral): 2.660 g/kg
LD50 (rat, IV): 1.33 g/kg
LD50 (rat, SC): 1.4 g/kg
Potential Exposure
Boric acid is a fireproofing agent for wood; a preservative, and an antiseptic. It is used in the manufacture of glass, pottery, enamels, glazes, cosmetics, cements, porcelain, borates, leather, carpets, hats, soaps; artificial gems; in tanning leather; printing, dyeing, painting, and photography.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seekmedical attention immediately. If this chemical contactsthe skin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediately with soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical has been inhaled, remove fromexposure, begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing hasstopped and CPR if heart action has stopped. Transferpromptly to a medical facility. When this chemical hasbeen swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and induce vomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.
Metabolism
No metabolic pathways reported.
storage
Boric acid is hygroscopic and should therefore be stored in an airtight, sealed container. The container must be labeled ‘Not for Internal Use’.
Shipping
UN 3077 Environmentally hazardous substances, solid, n.o.s., Hazard class: 9; Labels: 9—Miscellaneous hazardous material, Technical Name Required.
Purification Methods
Crystallise the acid three times from H2O (3mL/g) between 100o and 0o, after filtering through sintered glass.Dry it to constant weight over metaboric acid in a desiccator. It is steam volatile. After two recrystallisations of ACS grade. it had Ag at 0.2 ppm. Its solubility (%) in H2O is 2.66 at 0o, 4.0 at 12o and 24 at 80o. At 100o it loses H2O to form metaboric acid (HBO2). When it is heated to redness or slowly to 200o, or over P2O5 in vacuo, it dehydrates to boric anhydride (B2O3) [1303-82-6] to give a white hard glass or crystals with m ~294o.The glass softens on heating and liquefies at red heat. It is an astringent, a fungicide and an antibacterial. [McCulloch J Am Chem Soc 59 2650 1937, Kelly J Am Chem Soc 63 1137 1941, Taylor & Cole J Chem Soc 70 1926, Conti J Soc Chem Ind 44 343T 1925.]
Incompatibilities
Boric acid decomposes in heat above 100 C, forming boric anhydride and water. Boric acid is hygroscopic; it will absorb moisture from the air. Boric acid aqueous solution is a weak acid; incompatible with strong reducing agents including alkali metals and metal hydrides (may generate explosive hydrogen gas); acetic anhydride, alkali carbonates, and hydroxides. Violent reaction with powdered potassium metal, especially if impacted. Attacks iron in the presence of moisture.
Incompatibilities
Boric acid is incompatible with water, strong bases and alkali metals. It reacts violently with potassium and acid anhydrides. It also forms a complex with glycerin, which is a stronger acid than boric acid.
Waste Disposal
Boric acids may be recovered from organic process wastes as an alternative to disposal.
Regulatory Status
Accepted for use as a food additive in Europe. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (IV injections; ophthalmic preparations; (auricular) otic solutions; topical preparations). Reported in the EPA TSCA Inventory. In the UK, the use of boric acid in cosmetics and toiletries is restricted. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients.
Properties of Orthoboric acid
| Melting point: | 160 °C (dec.) (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 219-220 °C (9.7513 mmHg) |
| Density | 1.440 g/cm3 |
| vapor pressure | 2.6 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
| storage temp. | Store at +5°C to +30°C. |
| solubility | H2O: soluble |
| form | working solution |
| pka | 8.91±0.43(Predicted) |
| Specific Gravity | 1.435 |
| color | ≤10(APHA) |
| Odor | Odorless |
| PH | 3.6-4.4 (25℃, saturated solution in H2O) |
| PH Range | 3.8 - 4.8 |
| Water Solubility | 49.5 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| λmax | λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.05 λ: 280 nm Amax: 0.05 |
| Merck | 14,1336 |
| BRN | 1697939 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 2 mg/m3; STEL 6 mg/m3 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 10043-35-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | B(OH)3(10043-35-3) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Orthoboric acid (10043-35-3) |
Safety information for Orthoboric acid
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Health Hazard GHS08 |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. P405:Store locked up. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Orthoboric acid
| InChIKey | KGBXLFKZBHKPEV-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Orthoboric acid manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
New Products
3-Iodophenylacetic acid 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 3-(hexyloxy)-4-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,2,5-thiadiazole 2-Hexyn-1-ol Dibenzo-18-crown-6 Nickel(II) perchlorate hexahydrate, 98% 4-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 95% 3-Bromo-4-fluoroaniline, 97% Sodium tetraborate decahydrate, 98% Palladium(II) acetate, trimer, Pd 99% 4-Bromo-2-chlorotoluene, 97% N N Dimethylformamide Dimethyl Acetal (Dmf Dma) 2,3-Dichloro Benzoyl Cyanide [Side Chain] Bis(2-Chloroethyl) Amine Hydrochloride L-Glutamic Acid Diethyl Ester Hydrochloride 5-(Difluoromethoxy)-2-Mercaptobenzimidazole 1-Ethyl-3-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-Carbodiimide Hydrochloride [EDC Hcl] 1,4-Napthoquinone Bromoiodomethane Sodium Bicarbonate Methylene Dichloride (MDC) Ethyl Acetate Indole-3-Carbinol (I3C)Related products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Boric Acid 10043-35-3 disinfectants APIView Details
Boric Acid 10043-35-3 disinfectants APIView Details
10043-35-3 -
 Boric Acid CAS 10043-35-3View Details
Boric Acid CAS 10043-35-3View Details
10043-35-3 -
 Boric Acid (ER) CAS 10043-35-3View Details
Boric Acid (ER) CAS 10043-35-3View Details
10043-35-3 -
 Boric Acid ACS CAS 10043-35-3View Details
Boric Acid ACS CAS 10043-35-3View Details
10043-35-3 -
 Boric Acid for molecular biology CAS 10043-35-3View Details
Boric Acid for molecular biology CAS 10043-35-3View Details
10043-35-3 -
 Boric acid CAS 10043-35-3View Details
Boric acid CAS 10043-35-3View Details
10043-35-3 -
 Boric acid AR 99.5% CAS 10043-35-3View Details
Boric acid AR 99.5% CAS 10043-35-3View Details
10043-35-3 -
 Boric acid (powder) 99.5% CAS 10043-35-3View Details
Boric acid (powder) 99.5% CAS 10043-35-3View Details
10043-35-3
