Hyaluronic acid
- CAS NO.:9004-61-9
- Empirical Formula: C14H22NNaO11
- Molecular Weight: 403.31
- MDL number: MFCD00131348
- EINECS: 232-678-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-02-28 12:01:23
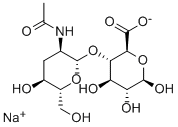
What is Hyaluronic acid?
Absorption
There is limited information in the literature regarding the human absorption and pharmacokinetics of hyaluronic acid. When administered to rats in the oral form, hyaluronic acid is broken down to oligosaccharides by intestinal bacteria and absorbed in the colon. In pharmacokinetic studies of beagle dogs, HA was readily absorbed and rapidly excreted. When applied topically, HA with low molecular weight ranging from 20-300 kDa is absorbed through the stratum corneum, and HA with high molecular weight (1000-1400 kDa) does not penetrate the stratum corneum. The bioavailability of hyaluronic acid depends on its molecular weight.
Toxicity
The oral LD50 of the sodium salt of hyaluronic acid is >800 mg/kg in the rat. Overdose information is not readily available in the literature. The safety profile for hyaluronic acid favourable, however, single case reports of death following vaginal injection of hyaluronic acid are published; the deaths likely occurred due to poor procedure regulation.
Description
According to the Merck Index, hyaluronic acid (HA; sometimes called hyaluronan) is “a natural high-viscosity mucopolysaccharide”. As shown in the images, it consists of repeating two-glucoside units. The molar mass of the natural material is between 106 and 107 g/cm3.
In the human body, highly viscous HA and its sodium salt are a major constituent of synovial fluid; they are also found in the vitreous humor and the umbilical cord. Its name is derived from hyalos, the Greek word for vitreous.
In 1934, Karl Meyer and John W. Palmer at Columbia University (New York) isolated HA from the vitreous humor of cattle eyes and measured many of its properties. Twenty years later, Meyer and Bernard Weissman described the structure of HA taken from umbilical cords.
HA-containing synovial fluid is a natural lubricant for the soft tissues that support natural or artificial joints such as hips and knees, helping them to function smoothly. HA scavenges radicals generated by inflammation. It is sometimes injected into arthritic joints to ease pain and assist movement.
HA is approved for use in some eye surgeries, but there is no evidence of its effectiveness in cosmetic anti-aging products. It can be used, however, as a dermal filler in the face to reduce wrinkles and provide fullness.
The Uses of Hyaluronic acid
hyaluronic acid is a glycosaminoglycan component. Hyaluronic acid occurs naturally in the dermis. It is thought to play a critical role in healthy skin by controlling the physical and biochemical characteristics of epidermal cells. It also regulates general skin activity, such as water content, elasticity, and the distribution of nutrients. Its water-absorption abilities and large molecular structure allow the epidermis to achieve greater suppleness, proper plasticity, and turgor. Hyaluronic acid is a natural moisturizer with excellent water-binding capabilities. In a solution of 2 percent hyaluronic acid and 98 percent water, the hyaluronic acid holds the water so tightly that it appears to create a gel. However, it is a true liquid in that it can be diluted and will exhibit a liquid’s normal viscous flow properties. When applied to the skin, hyaluronic acid forms a viscoelastic film in a manner similar to the way it holds water in the intercellular matrix of dermal connective tissues. This performance and behavior suggests that hyaluronic acid makes an ideal moisturizer base, allowing for the delivery of other agents to the skin. Manufacturers claim that the use of hyaluronic acid in cosmetics results in the need for much lower levels of lubricants and emollients in a formulation, thereby providing an essentially greaseless product. Furthermore, its ability to retain water gives immediate smoothness to rough skin surfaces and significantly improves skin appearance. For the benefits of hyaluronic acid to be realized in a cosmetic, the product needs to be applied on a regular basis as it is broken down in skin within 24 to 48 hours of application. note, this is not the case with hyaluronic acid injections as the technology used is different.
The Uses of Hyaluronic acid
Synovitis agent (veterinary).
The Uses of Hyaluronic acid
Hyaluronic acid is a naturally derived, non - immunogenic, non - adhesive glycosaminoglycan that plays a prominent role in various wound - healing processes, as it as it is naturally angiogenic when degraded to small fragments. Hyaluronic acid promotes early inflammation which is critical for initiating wound healing, but then moderates later stages of the process, allowing matrix stabilization and reduction of long term inflammation. Hyaluronic acid is a main source for pharmaceutical, medical and cosmetic application.
Indications
The intra-articular preparations of hyaluronic acid are indicated for knee pain associated with osteoarthritis. Hyaluronic acid is used in cosmetic applications to prevent and reduce the appearance of wrinkles on the face, and as a dermal filler to correct facial imperfections or other imperfections on other parts of the body. It is frequently an ingredient in topical applications for wound healing and symptomatic treatment of skin irritation from various causes. Hyaluronic acid may also be indicated in ophthalmological preparations or oral capsules to treat discomfort caused by dry eyes or conjunctivitis and for its protective qualities during and before eye surgery. Finally, hyaluronic acid can be used off-label to coat the bladder for relief of interstitial cystitis symptoms.
Background
Hyaluronic acid (HA) is an anionic, nonsulfated glycosaminoglycan found in connective, epithelial, and neural tissues; it was first isolated in 1934. Karl Meyer and John Palmer obtained glycosaminoglycan (GAG) from the bovine eye, giving it the name “hyaluronic acid”. HA is involved in many important physiological processes, including but not limited to wound healing, tissue regeneration, and joint lubrication. It demonstrates unique viscoelasticity, moisturizing, anti-inflammatory qualities, and other important properties that prove beneficial in various clinical applications.
HA is used in drug delivery systems for the treatment of cancer, ophthalmological conditions, joint conditions, and aesthetic imperfections. Several preparations of hyaluronic acid have been approved by the FDA and are available in oral, topical, and injectable forms. A popular use of hyaluronic acid in recent years is cosmetic injection due to its ability to minimize the appearance of wrinkles and aging-related skin imperfections.
Definition
ChEBI: A mucopolysaccharide composed of N-acetylglucosamine and glucuronic acid subunits. It is found in the connective tissues of vertebrates.
Definition
hyaluronic acid: A glycosaminoglycan(mucopolysaccharide) that ispart of the matrix of connective tissue.Hyaluronic acid binds cells togetherand helps to lubricate joints.It may play a role in the migration ofcells at wounds; this activity ceaseswhen hyaluronidase breaks downhyaluronic acid.
brand name
Equron [Veterinary] (Fort Dodge Animal Health); Legend (Bayer Animal Health); Synacid [Veterinary] (Schering-Plough Animal Health).
Pharmacokinetics
HA has long-acting lubricant, shock absorbing, joint stabilizing, and water balancing properties. It is similar to the naturally occurring glycosaminoglycan (GAG) in joints. Hyaluronic acid works by acting as a lubricant and shock absorber, facilitating joint mobility and thereby reducing osteoarthritic pain. Hyaluronic acid has antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, and analgesic effects. The water-balancing properties and viscoelasticity of hyaluronic acid are beneficial in cosmetic injections, imparting volume and reducing the appearance of imperfections and wrinkles. Due to the abovementioned properties, HA has a protective effect on the eyes and cornea.
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
Hyaluronic acid is a natural complex sugar of the glycosaminoglycan family and is a long-chain polymer containing repeating disaccharide units of Na-glucuronate-N-acetylglucosamine. Hyaluronic acid is indicated for use as a surgical aid in cataract extraction (intra-and extracapsular), IOL implantation, corneal transplant, glaucoma filtration and retinal attachment surgery. In surgical procedures in the anterior segment of the eye, instillation of hyaluronic acid serves to maintain a deep anterior chamber within corneal endothelium and other surrounding tissues. Furthermore, its viscoelasticity helps to push back the vitreous face and prevent formation of a postoperative flat chamber. In posterior segment surgery hyaluronic acid serves as a surgical aid to gently separate, maneuver and hold tissues. Hyaluronic acid creates a clear field of vision thereby facilitating intra- and post-operative inspection of the retina and photocoagulation.
Metabolism
Hyaluronic acid is degraded by a family of enzymes called hyaluronidases. In animals, it is metabolized into oligosaccharides by intestinal bacteria and subsequently reabsorbed in the large intestine.
Properties of Hyaluronic acid
| Melting point: | n/a |
| storage temp. | −20°C |
| solubility | H2O: 5 mg/mL, clear, colorless |
| appearance | transparent, viscous fluid or white powder |
| form | Lyophilized Powder |
| color | White |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 9004-61-9 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Hyaluronic acid (9004-61-9) |
Safety information for Hyaluronic acid
Computed Descriptors for Hyaluronic acid
| InChIKey | MAKUBRYLFHZREJ-IUPJJCKZNA-M |
| SMILES | [C@@H]1(O[C@H]2[C@H](O)[C@H]([C@H](O)O[C@@H]2C(=O)[O-])O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1NC(=O)C.[Na+] |&1:0,2,3,5,6,9,15,18,21,r| |
Hyaluronic acid manufacturer
Jaffs Dyechem Private Limited
Related products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 9004-61-9 Hyaluronic acid 99%View Details
9004-61-9 Hyaluronic acid 99%View Details
9004-61-9 -
 Hyaluronic acid 98%View Details
Hyaluronic acid 98%View Details
9004-61-9 -
 Hyaluronic Acid from Cockscomb CAS 9004-61-9View Details
Hyaluronic Acid from Cockscomb CAS 9004-61-9View Details
9004-61-9 -
 9004-61-9 Hyaluronic acid 98%View Details
9004-61-9 Hyaluronic acid 98%View Details
9004-61-9 -
 Hyaluronic acid 9004-61-9 98%View Details
Hyaluronic acid 9004-61-9 98%View Details
9004-61-9 -
 9004-61-9 99%View Details
9004-61-9 99%View Details
9004-61-9 -
 Hyaluronic Acid 97% CAS 9004-61-9View Details
Hyaluronic Acid 97% CAS 9004-61-9View Details
9004-61-9 -
 Hyaluronic Acid CASView Details
Hyaluronic Acid CASView Details