Sodium tetraborate
Synonym(s):Borax;Borax, fused;di-Sodium tetraborate;Sodium tetraborate
- CAS NO.:1330-43-4
- Empirical Formula: B4Na2O7
- Molecular Weight: 201.22
- MDL number: MFCD00081185
- EINECS: 215-540-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:30
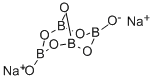
What is Sodium tetraborate?
Absorption
Boric acid is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, open wounds, and serous cavities but displays limited absorption in intact skin . Following intraperitoneal injection in mice, the peak concentration was reached in about 1.0-1.5 hr in the brain whereas the value was 0.5 hr in other tissues .
Toxicity
The acute oral LD50 in rats is 4500-5000 mg/kg and the intradermal LD50 in rabbits is 10,000 mg/kg. Individuals are likely to be exposed to boric acid from industrial manufacturing or processing. Local tissue injury from boric acid exposure is likely due to caustic effects. Systemic effects from boric acid poisoning usually occur from multiple exposures over a period of days and involve gastrointestinal, dermal, CNS, and renal manifestations. Gastrointestinal toxicity include persistent nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, epigastric pain, hematemesis, and blue-green discoloration of the feces and vomit . Following the onset of GI symptoms, a characteristic intense generalized erythroderma follows . Management of mild to moderate toxicity should be supportive. In case of severe toxicity, dialysis may be required in addition to supportive treatment.
Chemical properties
Sodium borate, Na2B407.10H20, also known as sodium tetraborate and sodium pyrobomte, is a white crystalline powder that melts at 120°C (248 °F). Sodium borate in its natural impure form is also known as borax, Borax is a noncombustible (an inherent fire retardant), bluish-gray or green, odorless crystalline powder or granules. Sodium borate is used in glass and ceramic enamel mixes,detergents, fertilizers, pharmaceuticals, and photograph.
The Uses of Sodium tetraborate
Sodium Tetraborate, is an important boron compound, which has a wide variety of applications. It is a component of many detergents, cosmetics, and enamel glazes. It is also used to make buffer solutions in biochemistry, as a fire retardant, as an anti-fungal compound for fiberglass, as a flux in metallurgy, neutron-capture shields for radioactive sources, a texturing agent in cooking, and as a precursor for other boron compounds.
The Uses of Sodium tetraborate
Refined borax (Na2B4O7) is an additive in laundry products such as soaps and water-softening compounds. Also used for cosmetics, body powders, and the manufacture of paper and leather. Borax is an environmentally safe natural herbicide and insecticide.
What are the applications of Application
Borax Anhydrous is a useful anhydrous borax for proteomics research
Indications
No FDA- or EMA-approved therapeutic indications on its own.
Production Methods
Anhydrous borax is produced from borax through high temperature fusion. On cooling, the clear, glass-like material is ground into fine white granules. Because of its higher bulk density, it is preferred where storage space is limited. It is used principally in the manufacture of glass, ceramics, and enamel.
General Description
Pale yellow solid or thick liquid with a faint odor of detergent. Mixes with water. Soap bubbles may be produced.
Air & Water Reactions
Water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
SODIUM PEROXOBORATE is incompatible with the following: Zirconium, strong acids, metallic salts . The true peroxoborate has been reported to detonate on light friction. The common "tetrahydrate" is not a peroxoborate, Sodium tetraborate is relatively stable under mild grinding with other substances.
Health Hazard
No adverse effects from inhaling borax have been reported. Ingestion may cause acute or chronic effects; initial symptoms are nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea; these may be followed by weakness, depression, headaches, skin rashes, drying skin, cracked lips, and loss of hair; shock may follow ingestion of large doses and may interfere with breathing. Eye contact with powder or solutions may cause irritation; no chronic effects have been recognized, but continued contact should be avoided. Local skin irritation may result from contact with powder or strong solutions; the latter may cause chronic dermatitis on prolonged contact, and if skin is broken, enough boron may be absorbed to cause boron poisoning (symptoms are similar to those for ingestion).
Agricultural Uses
Sodium tetraborate, also called borax, sodium borate, sodium pyroborate and sodium tetraborate decahydrate (Na2B4O7.10H2O) is a type of borate, and is used as a fertilizer to reduce boron deficiency. It is a white salt, finely ground for fertilizer application.
Sodium tetraborate(Na2B4O7) and sodium metaborate (Na2B2O4) are non-selective, taken up by roots, and have an unknown mechanism of action. Boron accumulates in reproductive structures after translocation from roots. Boron compounds are used for long-term, nonselective weed control in industrial and power line areas in combination with triazine and urea herbicides.
Pharmacokinetics
Boric acid exhibits minimal bacteriostatic and antifungal activities . Boric acid is likely to mediate antifungal actions at high concentrations over prolonged exposures .
Safety Profile
A nuisance dust. Experimental reproductive effects. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic vapors of B.
Potential Exposure
Borax is used as a soldering flux, preservative against wood fungus; and as an antiseptic. Used in ant poisons, for fly control around refuse and manure piles, as a larvicide. It is used in the manufacture of enamels and glazes, fiberglass insulation; sodium perborate bleach; in tanning, cleaning compounds; for fireproofing fabrics and wood; and in artificial aging of wood.
Metabolism
No metabolic pathways reported.
Purification Methods
Most of the water of hydration is removed from the decahydrate (see below) by evacuation at 25o for three days, followed by heating to 100o and evacuation with a high-speed diffusion pump. The dried sample is then heated gradually to fusion (above 966o), allowed to cool gradually to 200o, then tranferred to a desiccator containing P2O5 [Grenier & Westrum J Am Chem Soc 78 6226 1956]. [Becher in Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry (Ed. Brauer) Academic Press Vol I pp 794-795 1963.]
Incompatibilities
Dissolves in water forming a basic solution. Boron dust may form explosive mixture with air. Contact with strong oxidizers may be violent. Boron is incompatible with ammonia, bromine tetrafluoride, cesium carbide, chlorine, fluorine, interhalogens, iodic acid, lead dioxide, nitric acid, nitric oxide, nitrosyl fluoride, nitrous oxide, potassium nitrite, rubidium carbide, silver fluoride.
Waste Disposal
Borax, dehydrated: The material is diluted to the recommended provisional limit (0.10 mg/L) in water. The pH is adjusted to between 6.5 and 9.1 and then the material can be discharged into sewers or natural streams.
Properties of Sodium tetraborate
| Melting point: | 741 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 1575°C |
| Density | 2.367 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| vapor pressure | 7.3 hPa (1200 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.501 |
| Flash point: | 1575°C |
| storage temp. | Store at +5°C to +30°C. |
| solubility | H2O: 0.1 M at 20 °C, clear, colorless |
| form | Solid |
| color | White |
| Specific Gravity | 2.367 |
| PH | 9.0-10.5 (25℃, 0.1M in H2O) |
| Water Solubility | 26 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| λmax | λ: 260 nm Amax: ≤0.020 λ: 280 nm Amax: ≤0.015 |
| Merck | 14,8590 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 2 mg/m3; STEL 6 mg/m3 NIOSH: TWA 1 mg/m3 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with powdered metals. |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Sodium borate(1330-43-4) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Sodium tetraborate (1330-43-4) |
Safety information for Sodium tetraborate
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. P337+P313:IF eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Sodium tetraborate
| InChIKey | UQGFMSUEHSUPRD-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Sodium tetraborate manufacturer
Kronox Lab Sciences Pvt Ltd
katyayani organics
Polypharm Private Limited
Kezi Industries (Sam Industries)
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Sodium tetraborate 98%View Details
Sodium tetraborate 98%View Details -
 BUFFER SOLUTION pH 9.2View Details
BUFFER SOLUTION pH 9.2View Details -
 Sodium tetraborate, Anhydrous CAS 1330-43-4View Details
Sodium tetraborate, Anhydrous CAS 1330-43-4View Details
1330-43-4 -
 Sodium tetraborate, Anhydrous CAS 1330-43-4View Details
Sodium tetraborate, Anhydrous CAS 1330-43-4View Details
1330-43-4 -
 Sodium tetraborate, Anhydrous CAS 1330-43-4View Details
Sodium tetraborate, Anhydrous CAS 1330-43-4View Details
1330-43-4 -
 Sodium tetraborate, anhydrous CAS 1330-43-4View Details
Sodium tetraborate, anhydrous CAS 1330-43-4View Details
1330-43-4 -
 Buffer solution pH 9.2 CASView Details
Buffer solution pH 9.2 CASView Details -
 Buffer Solution pH 9.2 CASView Details
Buffer Solution pH 9.2 CASView Details