Magnesium sulfate
Synonym(s):Magnesium sulfate anhydrous;Magnesium Sulfate, Anhydrous;Sulfuric Acid Magnesium Salt, Epsom salts
- CAS NO.:7487-88-9
- Empirical Formula: MgSO4
- Molecular Weight: 120.37
- MDL number: MFCD00011110
- EINECS: 231-298-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-29 14:06:09
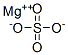
What is Magnesium sulfate?
Toxicity
LD50 = 1200 mg/kg (rat, subcutaneous). May be harmful if swallowed. May act as an irritant. Adverse reactions include hypotension, ECG changes, diarrhea, urinary retention, CNS depression and respiratory depression.
Description
Magnesium sulfate is strongly hygroscopic and often encountered as the heptahydrate sulfate mineral epsomite (MgSO4•7H2O), commonly called Epsom salt. And the monohydrate, MgSO4•H2O, is found as the mineral kieserite.
For medicine use, it is used in pregnant women to control seizures due to certain complications of pregnancy (eg, severe toxemia) and to control high blood pressure, severe brain function problems (encephalopathy), and seizures in children who have sudden, severe inflammation of the kidneys (acute nephritis). Besides, magnesium sulfate is also used as a laxative to relieve occasional constipation.
Chemical properties
Magnesium Sulfate is found widely in nature as either a double salt or as a hydrate, colorless crystals,very soluble in water, soluble in glycerol, sparingly soluble in alcohol.
Physical properties
In their hydrated form, these salts have a pH of 6.0 (5.5 to 6.5) in solution. These magnesium sulfates are white crystalline solids. Their densities are: 2.66 g/cm3 (anhydrous); 2.445 g/cm3 (monohydrate); 1.68 g/cm3 (heptahydrate). Solubilities in water are: anhydrous= 26.9 g/100 ml (0°C); monohydrate= 25.5 g/100 ml (20°C); heptahydrate=71 g/100 ml (20°C). Magnesium sulfate is found in nature in many salt deposits and mineral waters, occurring as hydrates or double salts. The heptahydrate or Epsom salt was discovered in 1695, found inthemineralwater at Epsom. Kieserite and epsomite are the two most important minerals. Other than these and the above hydrates, magnesium sulfate is also found in several other minerals, including langbeinite, leonite,vanthoffite,bloedite,kainite,polyhalite,
The Uses of Magnesium sulfate
In agriculture and gardening, magnesium sulfate is used to correct magnesium deficiency in soil, since magnesium is an essential element in the chlorophyll molecule.MgSO4 has been used in organic synthesis to remove water from nonaqueous solutions before the organic reaction is started. Since it is insoluble in most organic solvents, its addition forms hydrates that can be easily removed.
Epsom salt is also used to prepare footbaths, intended to soothe sore feet. The reason for the inclusion of the salt is partially cosmetic.
Background
A small colorless crystal used as an anticonvulsant, a cathartic, and an electrolyte replenisher in the treatment of pre-eclampsia and eclampsia. It causes direct inhibition of action potentials in myometrial muscle cells. Excitation and contraction are uncoupled, which decreases the frequency and force of contractions. (From AMA Drug Evaluations Annual, 1992, p1083)
Indications
Magnesium sulfate is used for immediate control of life-threatening convulsions in the treatment of severe toxemias (pre-eclampsia and eclampsia) of pregnancy and in the treatment of acute nephritis in children. Also indicated for replacement therapy in magnesium deficiency, especially in acute hypomagnesemia accompanied by signs of tetany similar to those of hypocalcemia. Also used in uterine tetany as a myometriat relaxant.
Definition
ChEBI: A magnesium salt having sulfate as the counterion.
Preparation
Hydrated magnesium sulfate occurs in nature as the minerals kieserite and epsomite. The salt is mined in large scale from these and other naturally occurring minerals. The salt also is prepared in the laboratory by the action of sulfuric acid on magnesium oxide, hydroxide, or carbonate followed by evaporation and crystallization:
MgO + H2SO4 → MgSO4 + H2O
Mg(OH)2 + H2SO4 → MgSO4 + 2H2O
MgCO3 + H2SO4 → MgSO4 + CO2 + H2O
Crystallization at temperatures between 1.8 and 48°C yields heptahydrate, MgSO4•7H2O. Below 1.8°C, a dodecahydrate , MgSO4•12H2O crystallizes out. Above 48°C crystals of lower hydrates form. The anhydrous salt is obtained by heating the heptahydrate at about 500°C in a rotary drum; or dehydrating above 150°C in the presence of sulfuric acid.
Production Methods
Magnesium sulfate is widely distributed in nature, e.g. in salt deposits as kieserite, as Epsom salt MgSO4 . 7H20, in the form of double salts such as kainite 4KCl . 4MgSO4 . 11H20 and langbeinite K2SO4 . 2MgSO4, and in brines. Large quantities of kieserite, Epsom salt and anhydrous magnesium sulfate are produced in the processing of potassium salts. Magnesium sulfate is also produced by reacting magnesium carbonate or seawatermagnesium hydroxide with sulfuric acid.
Indications
Magnesium sulfate prevents convulsions in preeclampsia and directly uncouples excitation–contraction in myometrial cells through inhibition of cellular action potentials. Furthermore, magnesium sulfate decreases calcium uptake by competing for its binding sites, activating adenylyl cyclase (thereby reducing intracellular calcium), and stimulating calcium-dependent adenosine triphosphatase (ATPase), which promotes calcium uptake by the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Magnesium is filtered by the glomerulus, so patients with low glomerular filtration will have low magnesium clearance. Although the compound does have some cardiac side effects, magnesium sulfate may be preferred over β- adrenergic agents in patients with heart disease, diabetes, hypertension, or hyperthyroidism.
Biological Functions
Magnesium sulfate may be effective in terminating refractory ventricular tachyarrhythmias, particularly polymorphic ventricular tachycardia. Digitalis-induced arrhythmias are more likely in the presence of magnesium deficiency. Magnesium sulfate can be administered orally, intramuscularly, or, preferably, intravenously,when a rapid response is intended.The loss of deep tendon reflexes is a sign of overdose.
Agricultural Uses
Magnesium sulphate is a white compound existing both in
anhydrous (rhombic) and hydrated crystalline forms. The
monohydrate MgSO4·H2O (monoclinic) occurs in nature
as kieserite. It is a greyish-white crystalline powder
which contains about 16 % magnesium and is used as a
fertilizer. It is regarded as a concentrated form of epsom
salt, having less water of crystallization. The commonest
hydrate is heptahydrate MgSO4·7H2O(also called
rhombic or epsom salt) which occurs naturally as the
mineral epsomite. It is a white powder with a bitter,
saline taste. The salt in the monocliic form loses its
structural water at 150°C, while the rhombic form loses
water at 200°C.
Magnesium sulphate is used in sizing and freproofng
cotton and silk, in tanning leather, in the manufacture of
fertilizers, in explosives and matches, in medicines as a
laxative, and as a veterinary medicine for the treatment of
inflammations and infected wounds.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Magnesium sulfate has anti-convulsant, anti-inflammatory and vasodilatory properties. Magnesium sulfate relaxes smooth muscles. In acute asthma patients, use both intravenous and nebulization of magnesium sulfate as additive treatment improves pulmonary function. Magnesium sulfate reduces preterm labor in high risk pregnant women.
Pharmacokinetics
Magnesium sulfate is a small colorless crystal used as an anticonvulsant, a cathartic, and an electrolyte replenisher in the treatment of pre-eclampsia and eclampsia. It causes direct inhibition of action potentials in myometrial muscle cells. Excitation and contraction are uncoupled, which decreases the frequency and force of contractions. Magnesium sulfate is gaining popularity as an initial treatment in the management of various dysrhythmias, particularly torsades de pointes, and dyrhythmias secondary to TCA overdose or digitalis toxicity.
Clinical Use
There is much debate as to the efficacy of magnesium sulfate. For effective inhibition of uterine activity, enough must be given to maintain a blood plasma level of at least 5.5 mEq/L. Even at this level, tocolysis may be hard to achieve.
Side Effects
The side effects of magnesium sulfate administration are dose dependent. As magnesium levels increase, skeletal muscle weakness increases and CNS depression and vascular dilation occur.
Cardiac muscle is not affected to a clinically evident degree when magnesium is administered at therapeutic levels, although magnesium can have profound myocardial effects during a gross overdose.
Other side effects of magnesium sulfate include the following: (1) Cutaneous vasodilation with flushing (2) Headache and dizziness (3) Nausea (4) Skeletal muscle weakness (5) Depression of deep tendon reflexes (6) Respiratory depression (7) ECG changes
Safety Profile
A poison by intravenous route. Moderately toxic by ingestion, intraperitoneal, and subcutaneous routes. Human systemic effects: heart changes, cyanosis, flaccid paralysis with appropriate anesthesia. An experimental teratogen. Mutation data reported. Potentially explosive reaction when heated with ethoxyethynyl alcohols (e.g., l-ethoxy 3-methyl-1-butyn-3-01). When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of SOx. See also SULFATES.
Magnesium sulfate Application
Magnesium sulfate is used widely in several industries including fertilizer, cement, textile, chemicals, and medicine. In the cement industry, it is used in manufacturing oxysulfate cement. In medicine, it is an analgesic and cathartic. An important application of anhydrous magnesium sulfate in the laboratory involves drying organic solvents required for syntheses and GC analysis. In the textile industry, magnesium sulfate is used in finishing composition for dressing cotton; for weighting and sizing silk; as a mordant for fixing basic dyestuffs on wool; and in fireproofing fabrics. It also is a component of certain types of electrolytic plating baths; of various photographic solutions; of cosmetic lotions. It is a catalyst carrier; a dietary supplement in cattle feed; a coagulant for rubber and plastic; and is used in making citric acid and several magnesium salts, such as magnesium stearate.
Metabolism
None
Purification Methods
Crystallise it from warm H2O (1g/mL) by cooling. Dry the heptahydrate (Epsom salt) at ~250o until it loses 25% of its weight. Its solubility in H2O is 36% at 20o, 55% at 60o and 74% at 100o; above 110o the solubility decreases with rise of temperature. Store it in a sealed container.
Precautions
Magnesium sulfate is not for use in patients with heart block or extensive myocardial damage. Use it with caution in patients with impaired renal function, in digitalized patients, and with concomitant use of other central nervous system depressants or neuromuscular blocking agents. Intravenous administration is contraindicated during the 2 hours preceding delivery. Oral administration is contraindicated in patients with abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, fecal impaction, or intestinal irritation, obstruction, or perforation.
References
1. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Magnesium_sulfate
2. https://www.drugs.com/cdi/magnesium-sulfate.html
3. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/magnesium_sulfate
4. http://www.emedicinehealth.com/drug-magnesium_sulfate/article_em.htm
Properties of Magnesium sulfate
| Melting point: | 1124 °C |
| Density | 1.07 g/mL at 20 °C |
| vapor density | <0.01 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | <0.1 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
| storage temp. | no restrictions. |
| solubility | H2O: 1 M at 20 °C, clear, colorless |
| form | powder (very fine) |
| color | slightly gray |
| Specific Gravity | 2.66 |
| Odor | at 100.00 %. odorless |
| PH | 7.9 (50g/l, H2O, 25℃) |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water. Slightly soluble in alcohol, glycerol. Insoluble in acetone. |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| λmax | λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.03 λ: 280 nm Amax: 0.02 |
| Merck | 14,5691 |
| Dielectric constant | 8.2(Ambient) |
| Stability: | Stable. Hygroscopic. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7487-88-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Magnesium sulfate(7487-88-9) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Magnesium sulfate (7487-88-9) |
Safety information for Magnesium sulfate
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H371:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P405:Store locked up. |
Computed Descriptors for Magnesium sulfate
Magnesium sulfate manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 MAGNESIUM SULPHATE 99%View Details
MAGNESIUM SULPHATE 99%View Details -
 Magnesium Sulphate 99%View Details
Magnesium Sulphate 99%View Details -
 MAGNESIUM SULPHATE 98%View Details
MAGNESIUM SULPHATE 98%View Details -
 Magnesium Sulphate 99%View Details
Magnesium Sulphate 99%View Details -
 Magnesium sulfate, anhydrous, anhydrous CAS 7487-88-9View Details
Magnesium sulfate, anhydrous, anhydrous CAS 7487-88-9View Details
7487-88-9 -
 Magnesium Sulfate CASView Details
Magnesium Sulfate CASView Details -
 Magnesium Sulfate CASView Details
Magnesium Sulfate CASView Details -
 95 % Powder Inflow Chemical Magnesium Sulphate, PP Sack bagView Details
95 % Powder Inflow Chemical Magnesium Sulphate, PP Sack bagView Details
139939-75-6
