Ammonium sulfate
Synonym(s):(NH₄)₂SO₄;Ammonium sulfate;Diammonium Sulfate, Sulfuric Acid Sodium Salt, Sulphuric Acid Sodium Salt;Mascagnite
- CAS NO.:7783-20-2
- Empirical Formula: H8N2O4S
- Molecular Weight: 132.14
- MDL number: MFCD00003391
- EINECS: 231-984-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:50:41
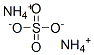
What is Ammonium sulfate?
Description
Ammonium sulfate was the first
nitrogenous fertilizer made by the Haber-Bosch process,
produced by the reaction of ammonia with sulfuric acid. In
contrast with the nitrate salt, it is chemically stable, not
highly hygroscopic. It also supplies supplemental sulfur to
soils that may be deficient in this element, but this is of
minor value when it is used on soils receiving applications
of ordinary superphosphate.
Physical properties
White crystalline solid; orthorhombic crystal; density 1.769 g/cm3 at 20°C; melts between 511 to 515°C (in a closed system): however, in an open system, it melts with decomposition at 280°C; readily dissolves in water (solubility, 70.6 g and 104 g per 100 g water at 0°C and 100°C, respectively); insoluble in acetone, alcohol and ether.
Occurrence
Ammonium sulfate occurs in trace concentrations in the upper atmosphere. It is widely used as a fertilizer for rice and other crops. It is a source of sulfur for the soil. It is also used as an additive to supply nutrient nitrogen in fermentation processes (e.g., yeast production from molasses). It also is used for fireproofing timber and plastics, and in treatment of hides, and leather production.
Ammonium sulfate application
Ammonium Sulfate is a reagent used in molecular biology and chromatography.
The Uses of Ammonium sulfate
Ammonium Sulfate is a dough conditioner, firming agent, and pro- cessing aid. May be used for the precipitation or fractionation of proteins or for purification of antibodies. Useful for crystallographic analysis of nucleic acids and proteins. manufacture of ammonia alum; in the manufacture of H2SO4 to free it from nitrogen oxides; analytical uses; freezing mixtures, flameproofing fabrics and paper; manufacture of viscose silk; tanning, galvanizing iron; in fractionation of proteins. The commercial grade is used as fertilizer.
Definition
ammonium sulphate: A whiterhombic solid, (NH4)2SO4; r.d. 1.77;decomposes at 235°C. It is very solublein water and insoluble in ethanol.It occurs naturally as the mineralmascagnite. Ammonium sulphatewas formerly manufactured from the‘ammoniacal liquors’ produced duringcoal-gas manufacture but is nowproduced by the direct reaction betweenammonia gas and sulphuricacid. It is decomposed by heating torelease ammonia (and ammoniumhydrogensulphate) and eventuallywater, sulphur dioxide, and ammonia.Vast quantities of ammoniumsulphate are used as fertilizers.
Production Methods
A significant commercial source of Ammonium sulfate is its creation as a byproduct in the manufacture of caprolactam, which yields several tons of the compound per ton of caprolactam made. Ammonium sulfate also is a byproduct of coke oven operations where the excess NH3 formed is neutralized with H2SO4 to form (NH4)2SO4. In the Meresburg reaction, natural or byproduct gypsum is reacted with ammonium carbonate: CaSO4·2H2O + (NH4)2CO3 CaCO3 + (NH4)2SO4 +2 H2O The product is stable, free-flowing crystals.
Reactions
Ammonium sulfate decomposes upon heating above 250 °C (482 °F), first forming ammonium bisulfate. Heating at higher temperatures results in decomposition into ammonia, nitrogen, sulfur dioxide, and water. It forms many double salts (ammonium metal sulfates) when its solution is mixed with equimolar solutions of metal sulfates and the solution is slowly evaporated.
Air & Water Reactions
Dissolves in water with evolution of some heat.
Reactivity Profile
Ammonium sulfate is acidic in aqueous solution. When a little Ammonium sulfate is added to fused potassium nitrite, a vigorous reaction occurs attended by flame [Mellor 2:702 1946-47].
Flammability and Explosibility
Not classified
Biochem/physiol Actions
Ammonium sulfate((NH4)2SO4) is mainly used as a soil fertilizer. It is also used as a wood preservative. This inorganic salt plays a role in flame retardant chemicals.
Safety Profile
Ammonium sulfate is moderately toxic by several routes. Human systemic effects by ingestion: hypermotility, diarrhea, nausea or vomiting. See also SULFATES. Incandescent reaction on heating with potassium chlorate. Reaction with sodmm hypochlorite gves the unstable explosive nitrogen trichloride. Incompatible with (K + NH4NO3), KNO2, (NaK + NH4NO3). When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of NOx, NH3, and SOx.
Purification Methods
Crystallise it twice from hot water containing 0.2% EDTA to remove metal ions, then finally from distilled water. Dry it in a desiccator for 2 weeks over Mg(ClO4)2. After 3 recrystallisations, ACS grade had Ti, K, Fe, Na at 11, 4.4, 4.4, 3.2 ppm respectively.
Properties of Ammonium sulfate
| Melting point: | >280 °C (dec.) (lit.) |
| Density | 1.77 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| vapor pressure | <1 Pa (25 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 26 °C |
| storage temp. | room temp |
| solubility | H2O: 1 M at 20 °C, clear, colorless |
| form | Solid |
| color | Yellow to orange |
| Specific Gravity | 1.769 |
| PH Range | 5 - 6 |
| PH | 5.0-6.0 (25℃, 1M in H2O) |
| Odor | Slight odor of ammonia |
| Water Solubility | 77 g/100 mL (25 ºC) |
| λmax | λ: 260 nm Amax: ≤0.037 λ: 280 nm Amax: ≤0.030 |
| Merck | 14,555 |
| Stability: | Stable. Contact with strong oxidizers may cause fire or explosion. Incompatible with strong bases. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7783-20-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Ammonium sulfate (7783-20-2) |
Safety information for Ammonium sulfate
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H303:Acute toxicity,oral H412:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P273:Avoid release to the environment. |
Computed Descriptors for Ammonium sulfate
| InChIKey | BFNBIHQBYMNNAN-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Ammonium sulfate manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
Cosmos Plastics & Chemicals
Dhairya International
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Ammonium Sulphate 98%View Details
Ammonium Sulphate 98%View Details -
 Ammonium Sulphate 99%View Details
Ammonium Sulphate 99%View Details -
 Ammonium sulphate 99%View Details
Ammonium sulphate 99%View Details -
 Ammonium sulfate 99%View Details
Ammonium sulfate 99%View Details -
 Ammonium sulfate 98%View Details
Ammonium sulfate 98%View Details -
 Ammonium sulfate 98%View Details
Ammonium sulfate 98%View Details -
 Ammonium sulfate, For analysis ACS CAS 7783-20-2View Details
Ammonium sulfate, For analysis ACS CAS 7783-20-2View Details
7783-20-2 -
 Ammonium Sulphate CASView Details
Ammonium Sulphate CASView Details
