Copper(II) chloride
- CAS NO.:7447-39-4
- Empirical Formula: Cl2Cu
- Molecular Weight: 134.45
- MDL number: MFCD00010972
- EINECS: 231-210-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
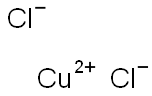
What is Copper(II) chloride?
Absorption
Mean copper absorption of 57 percent (range 40 to 70 per cent) following oral administration of 0.4 - 4.5 mg copper (as copper acetate) to four volunteers. An early human study suggested a maximum blood copper concentration was reached some two hours after oral copper chloride administration (1.5 - 12 mg copper)
Toxicity
LD50 not available Copper toxicity can produce prostration, behavior change, diarrhea, progressive marasmus, hypotonia, photophobia and peripheral edema. Such symptoms have been reported with a serum copper level of 286 mcg/dl. Copper toxicity can also result in hemolysis and liver toxicity, including hepatic necrosis which may be fatal. D-penicillamine has been reported effective as an antidote.
Description
Copper chloride is a brownish-yellow powder.Molecular weight =134.44. Boiling point =993℃ (decomposes below this point); Freezing/Melting point =498℃.Hazard Identification (based on NFPA-704 M RatingSystem): Health 2, Flammability 0, Reactivity 0. Soluble inwater.
Chemical properties
Cupric chloride, CuCI2, also known as copper chloride, is a yellowish- brown solid that is soluble in water and alcohol. The dihydrate of cupric chloride, CUCI2·H20, is a green crystalline solid that is soluble in water. Cupric chloride is used in the textile industry as a mordant in the dyeing and printing of fabrics. Itis also used in refining gold,silver,and copper.
Chemical properties
Cupric Chloride, brown-yellow powder, quite soluble in cold H2O or alcohol, very soluble in hot H2O. Catalyst for several organic syntheses, including production of vinyl chloride monomer.
The Uses of Copper(II) chloride
Isomerization and cracking catalyst, mordant in dyeing and printing fabrics, in electroplating baths for plating Cu on Al, in photography as a fixer, as a pigment for glass and ceramic.Copper(II) chloride is used as a co-catalyst with palladium(II) chloride used in the Wacker process to prepare ethanol from ethane. It acts as an effective catalyst for the tetrahydropyranylation of alcohols. It is involved in the production of vinyl chloride and dichloroethane as well as in the chlorination of aromatic hydrocarbons. It acts as deodorizing and desulfurizing agent in the petroleum industry, a mordant in textiles industry and in electrotyping baths for plating copper.
The Uses of Copper(II) chloride
Supplement (trace mineral).
The Uses of Copper(II) chloride
Noble-Metal Nanostructures with Controlled Morphologies
Indications
For use as a supplement to intravenous solutions given for total parenteral nutrition (TPN).
Background
Cupric chloride, for injection, is a sterile, nonpyrogenic solution intended for use as an additive to solutions for Total Parenteral Nutrition (TPN).
What are the applications of Application
Copper(II) chloride is a compound used with palladium in catalytic synthesis of 3-haloindoles
Definition
ChEBI: An inorganic chloride of copper in which the metal is in the +2 oxidation state.
General Description
Cupric chloride and ammonia contains various concentrations of cupric chloride in ammonium hydroxide. This forms a copper ammonia complex. Cupric chloride is corrosive to skin, eyes, mucous membranes and metal. Cupric chloride is used to etch copper from printed circuit boards.
Reactivity Profile
CUPRIC CHLORIDE has weak oxidizing or reducing powers. Redox reactions can however still occur. The majority of compounds in this class are slightly soluble or insoluble in water. If soluble in water, then the solutions are usually neither strongly acidic nor strongly basic. These compounds are not water-reactive.
Health Hazard
TOXIC; inhalation, ingestion or skin contact with material may cause severe injury or death. Contact with molten substance may cause severe burns to skin and eyes. Avoid any skin contact. Effects of contact or inhalation may be delayed. Fire may produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may be corrosive and/or toxic and cause pollution.
Fire Hazard
Non-combustible, substance itself does not burn but may decompose upon heating to produce corrosive and/or toxic fumes. Some are oxidizers and may ignite combustibles (wood, paper, oil, clothing, etc.). Contact with metals may evolve flammable hydrogen gas. Containers may explode when heated.
Pharmacokinetics
Copper is an essential nutrient which serves as a co factor for serum ceruloplasmin, an oxidase necessary for proper formation of the iron carrier protein, transferrin. Copper also helps maintain normal rates of red and white blood cell formation. Providing copper during Total Parenteral Nutrition helps prevent development of the following deficiency symptoms: Leukopenia, neutropenia, anemia, depressed ceruloplasmin levels, impaired transferrin formation, secondary iron deficiency and osteoporosis.
Safety Profile
Poison by intravenous and intraperitoneal routes. Experimental reproductive effects. Mutation data reported. See also COPPER COMPOUNDS and CHLORIDES. Can react violently with K and Na. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of Cl-.
Potential Exposure
Copper chloride is used in petroleum,textiles, metallurgy, photography, agricultural products,feed additives, and wood preservation. It is also used inlight-sensitive paper manufacturing, glass pigments, ceramics, and in making cyclonitrile.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seekmedical attention immediately. If this chemical contactsthe skin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediately with soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical has been inhaled, remove fromexposure, begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing hasstopped and CPR if heart action has stopped. Transferpromptly to a medical facility. When this chemicalhas been swallowed, get medical attention. If victim isconscious, administer water or milk. Do not inducevomiting.
Metabolism
Not Available
storage
Color Code—White: Corrosive or Contact Hazard;Store separately in a corrosion-resistant location. Prior toworking with this chemical you should be trained on itsproper handling and storage. Store in tightly closed containers in a cool, well-ventilated area away from incompatiblematerials listed above, moisture, and heat.
Shipping
UN2802 Copper chloride, Hazard class: 8; Labels: 8-Corrosive material.
Purification Methods
Crystallise the chloride from hot dilute aqueous HCl (0.6mL/g) by cooling in a CaCl2-ice bath. It is dehydrated by heating on a steambath under vacuum. It is deliquescent in moist air but efflorescent in dry air. The dihydrate is emerald green but blue when free from solvent. Concentrated solutions are yellow-green in colour but are blue when free from solvent. Concentrated solutions are yellow-green and become yellow on adding conc HCl. A very dilute solution is pure blue due to Cu(H2O)42+ [Donan & Bassett J Chem Soc 81 939 1902.]. CuCl2 is very deliquescent and is soluble in MeOH or EtOH to give green crystals of Cu(ROH)2Cl2. [Glemser & Sauer in Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry (Ed. Brauer) Academic Press Vol II p 1008 1965.]
Incompatibilities
Contact with strong acids forms monovalent copper salts and toxic hydrogen chloride gas. Forms shock-sensitive and explosive compounds with potassium, sodium, sodium hypobromite, nitromethane, acetylene. Keep away from moisture and alkali metals. Attacks metals in the presence of moisture. Reacts with moist air to form cupric chloride dihydrate. May attack some metals, paints, and coatings. May be able to ignite combustible materials.
Properties of Copper(II) chloride
| Melting point: | 620 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 993°C/760mmHg |
| Density | 3.386 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor pressure | 0Pa at 25℃ |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | H2O: soluble |
| form | powder |
| color | Yellow-brown |
| Specific Gravity | 3.386 |
| PH | 3.5 (50g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| Water Solubility | 620 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Sensitive | Air Sensitive & Hygroscopic |
| Merck | 14,2633 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 1 mg/m3 NIOSH: IDLH 100 mg/m3; TWA 1 mg/m3 |
| Stability: | Stable. Reacts violently with potassium and sodium. Contact with acetylene may form explosive acetylides. Hygroscopic. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7447-39-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Copper chloride(7447-39-4) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Cupric chloride (7447-39-4) |
Safety information for Copper(II) chloride
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Copper(II) chloride
Copper(II) chloride manufacturer
New Products
3-Iodophenylacetic acid 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 3-(hexyloxy)-4-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,2,5-thiadiazole 2-Hexyn-1-ol Dibenzo-18-crown-6 Nickel(II) perchlorate hexahydrate, 98% 4-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 95% 3-Bromo-4-fluoroaniline, 97% Sodium tetraborate decahydrate, 98% Palladium(II) acetate, trimer, Pd 99% 4-Bromo-2-chlorotoluene, 97% N N Dimethylformamide Dimethyl Acetal (Dmf Dma) 2,3-Dichloro Benzoyl Cyanide [Side Chain] Bis(2-Chloroethyl) Amine Hydrochloride L-Glutamic Acid Diethyl Ester Hydrochloride 5-(Difluoromethoxy)-2-Mercaptobenzimidazole 1-Ethyl-3-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-Carbodiimide Hydrochloride [EDC Hcl] 1,4-Napthoquinone Bromoiodomethane Sodium Bicarbonate Methylene Dichloride (MDC) Ethyl Acetate Indole-3-Carbinol (I3C)Related products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Copper(II) chloride CAS 7447-39-4View Details
Copper(II) chloride CAS 7447-39-4View Details
7447-39-4 -
 Copper(II) chloride CAS 7447-39-4View Details
Copper(II) chloride CAS 7447-39-4View Details
7447-39-4 -
 Copper(II) chloride CAS 7447-39-4View Details
Copper(II) chloride CAS 7447-39-4View Details
7447-39-4 -
 Copper(II) chloride, Anhydrous CAS 7447-39-4View Details
Copper(II) chloride, Anhydrous CAS 7447-39-4View Details
7447-39-4 -
 Copper(II) chloride, Anhydrous CAS 7447-39-4View Details
Copper(II) chloride, Anhydrous CAS 7447-39-4View Details
7447-39-4 -
 Copper(II) chloride, Anhydrous CAS 7447-39-4View Details
Copper(II) chloride, Anhydrous CAS 7447-39-4View Details
7447-39-4 -
 Cupric Chloride pure CAS 7447-39-4View Details
Cupric Chloride pure CAS 7447-39-4View Details
7447-39-4 -
 Copper(ii) chloride 97% CAS 7447-39-4View Details
Copper(ii) chloride 97% CAS 7447-39-4View Details
7447-39-4
