L-Glutamine
Synonym(s):(S)-2,5-Diamino-5-oxopentanoic acid;L -Glutamic acid 5-amide;L -Glutamine;Glavamin;Levoglutamide
- CAS NO.:56-85-9
- Empirical Formula: C5H10N2O3
- Molecular Weight: 146.14
- MDL number: MFCD00008044
- EINECS: 200-292-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-25 11:31:46
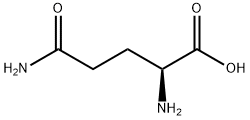
What is L-Glutamine?
Absorption
Absorption is efficient and occurs by an active transport mechanism. Tmax is 30 minutes after a single dose . Absorption kinetics following multiple doses has not yet been determined.
Toxicity
Doses of L-glutamine up to 21 grams daily appear to be well tolerated. Reported adverse reactions are mainly gastrointestinal and not common. They include constipation and bloating. There is one older report of two hypomanic patients whose manic symptoms were exacerbated following the use of 2 to 4 grams daily of L-glutamine. The symptoms resolved when the L-glutamine was stopped. These patients were not rechallenged, nor are there any other reports of this nature.
The most common adverse effects observed in clinical trials of Endari were constipation (21%), nausea (19%), headache (18%), abdominal pain (17%), cough (16%), extremity pain (13%), back pain (12%), and chest pain (12%) .
Description
Glutamine (abbreviated as Gln or Q) is one of the 20 amino acids encoded by the standard genetic code. It is not recognized as an essential amino acid, but may become conditionally essential in certain situations, including intensive athletic training or certain gastrointestinal disorders.Its side-chain is an amide formed by replacing the side-chain hydroxyl of glutamic acid with an amine functional group, making it the amide of glutamic acid. Its codons are CAA and CAG. In human blood, glutamine is the most abundant free amino acid, with a concentration of about 500–900 μmol / l .
Chemical properties
White crystalline powder
Chemical properties
White, odorless crystals or crystalline powder having a slightly sweet taste. It is soluble in water and practically insoluble in alcohol and in ether. Its solutions are acid to litmus. It melts with decomposition at about 185°C.
Chemical properties
L-glutamine is odorless, but has a slightly sweet taste L-glutamine performs a major role in DNA synthesis and sup- ports the immune system by means of glutathione synthesis.
Occurrence
Occurrences in nature
Glutamine is the most abundant naturally occurring, nonessential amino acid in the human body, and one of the few amino acids that can directly cross the blood-brain barrier.In the body, it is found circulating in the blood, as well as stored in the skeletal muscles. It becomes conditionally essential (requiring intake from food or supplements) in states of illness or injury.Dietary sources
Dietary sources of L-glutamine include beef, chicken, fish, eggs, milk, dairy products, wheat, cabbage, beets, beans, spinach, and parsley. Small amounts of free L-glutamine are also found in vegetable juices.
Aiding gastrointestinal functionGlutamine-enriched diets have been linked with maintenance of gut barrier function and cell differentiation, suggesting glutamine may help to protect the lining of the gastrointestinal tract or mucosa. People who have inflammatory bowel disease (ulcerative colitis and Crohn' s disease) may not have enough glutamine, but two clinical trials found taking glutamine supplements did not improve symptoms of Crohn' s disease.
The Uses of L-Glutamine
L-Glutamine is an essential amino acid that is a crucial component of culture media that serves as a major energy source for cells in culture. L-Glutamine is very stable as a dry powder and as a frozen solution. In liquid media or stock solutions, however, L-glutamine degrades relatively rapidly. Optimal cell performance usually requires supplementation of the media with L-glutamine prior to use.
The Uses of L-Glutamine
L-Glutamine is one of the 20 amino acids encoded by the standard genetic code. Its codons are CAA and CAG. Glutamine is a substance naturally produced in the body to help regulate cell growth and function. There may also be man-made versions of these subs
The Uses of L-Glutamine
amine protecting agent
Indications
Used for nutritional supplementation, also for treating dietary shortage or imbalance.
Used to reduce the acute complications of sickle cell disease in adult and pediatric patients 5 years of age and older .
Background
A non-essential amino acid present abundantly throughout the body and is involved in many metabolic processes. It is synthesized from glutamic acid and ammonia. It is the principal carrier of nitrogen in the body and is an important energy source for many cells. An oral formulation of L-glutamine was approved by the FDA in July 2017 for use in sickle cell disease . This oral formulation is marketed under the tradename Endari by Emmaus Medical.
What are the applications of Application
L-Glutamine is a non-essential amino acid
Definition
ChEBI: An optically active form of glutamine having L-configuration.
Preparation
By isolation from sugar beet juice.
brand name
Nutrestore (Nutritional Restart).
Biological Functions
Glutamine plays a role in a variety of biochemical functions, including :
Protein synthesis, as any other of the 20 proteinogenic amino acids
Regulation of acid-base balance in the kidney by producing ammonium
Cellular energy, as a source, next to glucose
Nitrogen donation for many anabolic processes, including the synthesis of purines
Carbon donation , as a source , refilling the citric acid cycle
Nontoxic transporter of ammonia in the blood circulation.
Synthesis Reference(s)
Tetrahedron: Asymmetry, 17, p. 245, 2006 DOI: 10.1016/j.tetasy.2005.12.023
Journal of the Chemical Society, p. 3315, 1949 DOI: 10.1039/JR9490003315
General Description
Pharmaceutical secondary standards for application in quality control, provide pharma laboratories and manufacturers with a convenient and cost-effective alternative to the preparation of in-house working standards. L-glutamine is the most abundant amino acid in the body. It is essential for the synthesis of L-asparagine. It also helps in muscle growth through protein synthesis and increased growth hormone levels.
Biochem/physiol Actions
L-Glutamine is an essential amino acid that is a crucial component of culture media that serves as a major energy source for cells in culture. L-Glutamine is very stable as a dry powder and as a frozen solution. In liquid media or stock solutions, however, L-glutamine degrades relatively rapidly. Optimal cell performance usually requires supplementation of the media with L-glutamine prior to use.
Pharmacokinetics
Like other amino acids, glutamine is biochemically important as a constituent of proteins. Glutamine is also crucial in nitrogen metabolism. Ammonia (formed by nitrogen fixation) is assimilated into organic compounds by converting glutamic acid to glutamine. The enzyme which accomplishes this is called glutamine synthetase. Glutamine can then be used as a nitrogen donor in the biosynthesis of many compounds, including other amino acids, purines, and pyrimidines.
L-glutamine improves nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) redox potential .
Safety Profile
Mddly toxic by ingestion. Human systemic effects: euphoria. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx.
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
Glutamine has been used as a GI protectant and in an attempt to
enhance GI healing in conditions where GI epithelium is damaged
(Parvo enteritis, chemotherapy, etc.).
A study that evaluated the efficacy of glutamine supplementation
in cats with methotrexate-induced enteritis found no difference
between cats supplemented with glutamine and those that
were not. (Marks, Cook et al. 1999)
Metabolism
Exogenous L-glutamine likely follows the same metabolic pathways as endogenous L-glutamine which is involved in the formation of glutamate, proteins, nucleotides, and amino acid sugars .
Purification Methods
Likely impurities are glutamic acid, ammonium pyroglutamate, tyrosine, asparagine, isoglutamine, arginine. Crystallise it from water or aqueous EtOH. [Greenstein & Winitz The Chemistry of the Amino Acids J. Wiley, Vol 3 pp 1929-1925 1961, Beilstein 4 IV 3038.]
Producing and consuming organs
Producers
Glutamine is synthesized by the enzyme glutamine synthetase from glutamate and ammonia. The most relevant glutamine-producing tissue is the muscle mass, accounting for about 90% of all glutamine synthesized. Glutamine is also released, in small amounts, by the lung and the brain. Although the liver is capable of relevant glutamine synthesis, its role in glutamine metabolism is more regulatory than producing, since the liver takes up large amounts of glutamine derived from the gut.
Consumers
The most eager consumers of glutamine are the cells of intestines, the kidney cells for the acid - base balance, activated immune cells, and many cancer cells. In respect to the last point mentioned, different glutamine analogues, such as DON, Azaserine or Acivicin, are tested as anticancer drugs.
Examples for the usage of glutamine
In catabolic states of injury and illness, glutamine becomes conditionally essential (requiring intake from food or supplements). Glutamine has been studied extensively over the past 10–15 years, and has been shown to be useful in treatment of injuries, trauma, burns, and treatment - related side effects of cancer, as well as in wound healing for postoperative patients. Glutamine is also marketed as a supplement used for muscle growth in weight lifting , body building, endurance, and other sports. Evidence indicates glutamine, when orally loaded, may increase plasma HGH levels by stimulating the anterior pituitary gland. In biological research, L-glutamine is commonly added to the media in cell culture. However, the high level of glutamine in the culture media may inhibit other amino acid transport activities.
Properties of L-Glutamine
| Melting point: | 185 °C (dec.) (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 265.74°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | 32.25 º (c=10, 2 N HCl) |
| Density | 1.47 g/cm3 (20℃) |
| refractive index | 6.8 ° (C=4, H2O) |
| FEMA | 3684 | L-GLUTAMINE |
| Flash point: | 185°C |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | H2O: 25 mg/mL |
| form | solution |
| pka | 2.17(at 25℃) |
| color | White |
| PH | 5.0-6.0 (25℃, 0.1M in H2O) |
| Odor | at 100.00 %. very mild milky custard cocoa oily |
| optical activity | [α]20/D +33.0±1°, c = 5% in 5 M HCl |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water, dimethyl sulfoxide and ethanol. Insoluble in methanol, ether, benzene, acetone, ethyl acetate and chloroform. |
| Decomposition | 185 ºC |
| λmax | λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.01 λ: 280 nm Amax: 0.01 |
| JECFA Number | 1430 |
| Merck | 14,4471 |
| BRN | 1723797 |
| Stability: | Moisture and light sensitive. Incompatible with moisture, strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 56-85-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | L-Glutamine(56-85-9) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | L-Glutamine (56-85-9) |
Safety information for L-Glutamine
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for L-Glutamine
| InChIKey | ZDXPYRJPNDTMRX-VKHMYHEASA-N |
L-Glutamine manufacturer
Aditya Molecules
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 L-Glutamine 98%View Details
L-Glutamine 98%View Details -
 L-Glutamine for cell culture CAS 56-85-9View Details
L-Glutamine for cell culture CAS 56-85-9View Details
56-85-9 -
 imported Powder L-Glutamine (Cas No.56-85-9), Purity: Min 99%, Packaging Size: 25kgView Details
imported Powder L-Glutamine (Cas No.56-85-9), Purity: Min 99%, Packaging Size: 25kgView Details
56-85-9 -
 Glutam 15 gm (L-Glutamine Sachets), Getwell, Packaging Type: PouchesView Details
Glutam 15 gm (L-Glutamine Sachets), Getwell, Packaging Type: PouchesView Details
56-85-9 -
 L-GlutamineView Details
L-GlutamineView Details
56-85-9 -
 L-GlutamineView Details
L-GlutamineView Details
56-85-9 -
 L - Glutamine, BoxView Details
L - Glutamine, BoxView Details
56-85-9 -
 L-GlutamineView Details
L-GlutamineView Details
56-85-9