L-Carnosine
Synonym(s):β-Alanyl-L -histidine
- CAS NO.:305-84-0
- Empirical Formula: C9H14N4O3
- Molecular Weight: 226.23
- MDL number: MFCD00005207
- EINECS: 206-169-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-26 12:07:08
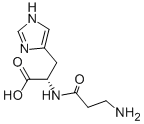
What is L-Carnosine?
Description
L-Carnosine is a dipeptide composed of β-alanine and L-histidine, distributed in various tissues including the olfactory bulb, skeletal muscle, brain, kidney, spleen, and human skeletal muscle, and possesses multiple functions. It can chelate with metals such as copper, cobalt, nickel, cadmium, and zinc to form complexes. Daily gavage administration of 60 mg/kg L-carnosine significantly reduced the levels of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) in the plasma of diabetic rats. In a cerebral hemorrhage model, administration of 1000 mg/kg L-carnosine alleviated cerebral edema, blood-brain barrier disruption, microglial activation, and neuronal apoptosis. In a rat model of bile duct ligation-induced cirrhosis, intraperitoneal injection of 250, 500, or 1000 mg/kg L-carnosine reduced hepatic protein carbonylation and necrosis. In a mouse model of LPS-induced acute lung injury, the peptide also reduced myeloperoxidase activity, reactive oxygen species production, TNF-α and IL-6 levels in lung tissue, and improved alveolar hemorrhage, interstitial edema and leukocyte infiltration.
Chemical properties
white to off-white crystalline.
History
Carnosine, a dipeptide composed of beta-alanine and L-histidine, was first identified in beef extracts by Russian chemists Gulewitch and Amiradzibi in 1900.
The Uses of L-Carnosine
L-Carnosine is a naturally occurring histidine-containing compound whose primary biological function is as a cytoplasmic buffer. In addition, it is believed to act as a neurotransmitter, regulate enzyme activity, and chelate heavy metals; simultaneously, carnosine is also an antioxidant that inhibits soluble guanylate cyclase.
Definition
ChEBI: Carnosine is a dipeptide that is the N-(beta-alanyl) derivative of L-histidine. It has a role as an anticonvulsant, an antioxidant, an antineoplastic agent, a human metabolite, a Daphnia magna metabolite, a mouse metabolite, a neuroprotective agent and a geroprotector. It is a conjugate acid of a carnosinate. It is a tautomer of a carnosine zwitterion.
Benefits
L-Carnosine is a strong anti-glycosylation, free radical scavenging,anti-oxidant,anti-aging, anti-pollution.Brightenand repairthe skin. white powder.Its recommended dosage is 0.05~2%.
Synthesis Reference(s)
The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 48, p. 392, 1983 DOI: 10.1021/jo00151a026
General Description
Carnosine is a dipeptide comprising beta-alanine and histidine. It is found in muscular and other tissues. It has strong oxidant property as it can scavenge both reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS). Carnosine acts as a cytosolic buffering agent and as a regulator of macrophage function.1 Attributing to its ability to form complexes with transition metals, it is used to regulate the content of transition metal ions in biological fluids and tissues.
Carnosine can prevent aging and can be used to prevent or treat complications of diabetes such as nerve damage, eye disorders (cataracts), and kidney problems.2 Potential therapeutic actions of carnosine include antihypertensive effects, immunomodulation, would healing, and antitumor/chemopreventive effects. The chelate compound of zinc ion and carnosine has been used in Japan for gastritis, gastric ulcers, and dyspepsia symptoms.3
Biochem/physiol Actions
L-Carnosine is a dipeptide present at millimolar concentrations in the brain, muscle, and eye lens. In experimental models, it functions as a potent antioxidant, scavenging oxygen free radicals and chelating transition metal ions. It inhibits protein-protein and protein-DNA cross-linking induced by hypochlorite anions and toxic aldehydes, specifically acetaldehyde, formaldehyde, and malondialdehyde, the latter being a primary product of lipid peroxidation. Furthermore, L-Carnosine blocks nonenzymatic protein glycation by aldose and ketose reducing sugars, thereby preventing the formation of toxic advanced glycation end products (AGEs). These properties establish its relevance in the study of aging, atherosclerosis, Alzheimer's disease, and diabetic complications.
Side Effects
L-Carnosine is generally regarded as safe for short-term oral administration and topical use in adults. Infrequent adverse effects may include rash, pruritus, xerostomia, altered appetite, fatigue, or vivid dreams. Severe, though rare, adverse reactions associated with zinc carnosine may involve leukopenia, gastrointestinal dysfunction, and sideroblastic anemia. Milder side effects reported include abdominal cramps, dyspepsia, and nausea.
Safety Profile
Mildly toxic by intraperitoneal route. An experimental teratogen. Other experimental reproductive effects. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx.
Side Effects
Stomach upset
Headache
Nausea
Vomiting
Purification Methods
Likely impurities are histidine and β-alanine. Crystallise L-carnosine from water by adding EtOH in excess. Recrystallise it from aqueous EtOH by slow addition of EtOH to a strong aqueous solution of the dipeptide. Its solubility in H2O is 33.3% at 25o. [Vinick & Jung J Org Chem 48 392 1983, Turner J Am Chem Soc 75 2388 1953, Sifford & du Vigneaud J Biol Chem 108 753 1935, Beilstein 25 H 516, 25 I 717, 25 II 408.]
References
1. P. J. Quinn, A. A. Boldyrev, V. E. Formazuyk, Carnosine: Its properties, functions and potential therapeutic applications, Molecular Aspects of Medicine, 1992, vol. 13, pp. 379-444 DOI:10.1016/0098-2997(92)90006-L
2. https://www.webmd.com/vitamins/ai/ingredientmono-1038/carnosine
3. G. M. Halpern, Zinc-Carnosine: Nature’s Safe and Effective Remedy for Ulcers, 2005, ISBN-10 0757002749
4. l-Carnosine, a Substrate of Carnosinase-1, Influences Glucose Metabolism DOI:10.2337/db07-0177
5. L-carnosine (beta-alanyl-L-histidine) and carcinine (beta-alanylhistamine) act as natural antioxidants with hydroxyl-radical-scavenging and lipid-peroxidase activities. DOI:10.1042/BJ3040509
6. Boldyrev, A.A., Aldini, G., and Derave, W. Physiology and pathophysiology of carnosine. Physiol. Rev. 93(4), 1803-1845 (2013). DOI:10.1152/physrev.00039.2012
7.
Ghodsi, R., and Kheirouri, S. Carnosine and advanced glycation end products: A systematic review. Amino Acids 50(9), 1177-1186 (2018). DOI:10.1007/s00726-018-2592-9
8. Tanaka, K.I., Sugizaki, T., Kanada, Y., et al. Preventive effects of carnosine on lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury. Sci. Rep. 7:42813, (2017). DOI:10.1038/srep42813
Properties of L-Carnosine
| Melting point: | 253 °C (dec.) (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 367.84°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | 20.9 º (c=1.5, H2O) |
| Density | 1.2673 (rough estimate) |
| vapor pressure | 0Pa at 25℃ |
| refractive index | 21 ° (C=2, H2O) |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | DMSO (Very Slightly), Water (Slightly) |
| form | crystalline |
| pka | 2.62(at 25℃) |
| color | White |
| Odor | at 100.00?%. odorless |
| Water Solubility | almost transparency |
| Merck | 14,1850 |
| BRN | 87671 |
| Stability: | Stable, but may be heat sensitive - store cold. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 305-84-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | L-Histidine, .beta.-alanyl- (305-84-0) |
Safety information for L-Carnosine
Computed Descriptors for L-Carnosine
| InChIKey | CQOVPNPJLQNMDC-ZETCQYMHSA-N |
L-Carnosine manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Carnosine 99%View Details
Carnosine 99%View Details
305-84-0 -
 L-Carnosine 98% CAS 305-84-0View Details
L-Carnosine 98% CAS 305-84-0View Details
305-84-0 -
 L Carnosine Powder, 25 KgView Details
L Carnosine Powder, 25 KgView Details
305-84-0 -
 L Carnosine PowderView Details
L Carnosine PowderView Details
305-84-0 -
 L - CarnosineView Details
L - CarnosineView Details
305-84-0 -
 L Carnosine Powder, 25 KgView Details
L Carnosine Powder, 25 KgView Details
305-84-0 -
 L- CarnosineView Details
L- CarnosineView Details
305-84-0 -
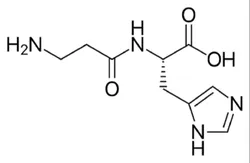 L-CarnosineView Details
L-CarnosineView Details
305-84-0
