L-Proline
Synonym(s):(S)-Pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid;(S)-(-)-Proline;L -Proline;L-Proline;Pro
- CAS NO.:147-85-3
- Empirical Formula: C5H9NO2
- Molecular Weight: 115.13
- MDL number: MFCD00064318
- EINECS: 205-702-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-26 18:10:20
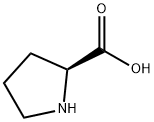
What is L-Proline?
Description
The synthesis of L-proline predates its isolation from natural sources. In 1900, Richard M. Willst?tter, a German chemist and Nobel laureate, prepared the D,L-racemate from N-methylproline.
In 1901, Emil Fischer, another German Nobel laureate, isolated the L-form of proline from egg albumen and hydrolyzed casein.
Chemical properties
L-Proline, an amino acid, is colorless to white crystal or crystalline powder that has a slight, characteristic odor with a slightly sweet taste. It is soluble in water, insoluble in ethanol, diethyl ether and n-butanol, yellow in case of hydrated ninhydrin test solution, glacial acetic acid Red after acidification; pH=6.3, decomposition point is 220-222°C; specific optical rotation [α]20D-85° (0.5-2.0mg/ml, H2O), [α]20D-60.4° (0.5-2.0mg /ml, 5mol/LHCl). It is synthesized from L-glutamine and L-glutamate via L-ornithine in intestine, and from L-ornithine in liver. It is widely used as an ingredient in infusion and infant formula.
Occurrence
Reported found as a component in many proteins; also widely occurring as the free acid in natural products. A major constituent of collagen, the main fibrous protein found in bone, cartilage and other connective tissue.
The Uses of L-Proline
L-Proline is an amino acid and precursor (with vitamin C) for collagen, the building block of the structure of tendons, ligaments, arteries, veins and muscles. It is important in wound healing.
The Uses of L-Proline
L-Proline is used as asymmetric catalysts in organic synthesis and asymmetric aldol cyclization. It is involved in the Michael addition of dimethyl malonate to alfa-beta-unsaturated aldehydes. It is a precursor of hydroxyproline in collagen. It is an active component of collagen and involved in the proper functioning of joints and tendons. It finds uses in pharmaceutical, biotechnological applications due to its osmoprotectant property. Further, it is used with ninhydrin in the chromatography.
What are the applications of Application
L-Proline is a catalyst used in a Michael addition of dimethyl malonate to αβ-unsaturated aldehydes.
Preparation
Synthesis of L-proline: Using glutamic acid as a raw material, it is esterified with absolute ethanol under the catalysis of sulfuric acid, and triethanolamine is added to free the aminosulfate to obtain glutamic acid-δ-ethyl ester. The glutamic acid-δ-ethyl ester is then reduced with a metal reducing agent potassium borohydride to obtain crude proline, which is finally separated and purified to obtain crude L-proline.
Definition
ChEBI: L-proline is pyrrolidine in which the pro-S hydrogen at position 2 is substituted by a carboxylic acid group. L-Proline is the only one of the twenty DNA-encoded amino acids which has a secondary amino group alpha to the carboxyl group. It is an essential component of collagen and is important for proper functioning of joints and tendons. It also helps maintain and strengthen heart muscles. It has a role as a micronutrient, a nutraceutical, an algal metabolite, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae metabolite, an Escherichia coli metabolite, a mouse metabolite and a member of compatible osmolytes. It is a glutamine family amino acid, a proteinogenic amino acid, a proline and a L-alpha-amino acid. It is a conjugate base of a L-prolinium. It is a conjugate acid of a L-prolinate. It is an enantiomer of a D-proline. It is a tautomer of a L-proline zwitterion.
Biotechnological Production
Direct fermentation using analogue-resistant mutants of coryneform bacteria or Serratia marcescens is an economic production method. An isoleucine auxotrophic mutant of Brevibacterium flavum having resistance to sulfaguanidine and D,L-3,4-dehydroproline (DP) is able to accumulate 40 g/L L-proline. Brevibacterium flavum AP113 is claimed to produce 97.5 g/L L-proline; this mutant is characterized by isoleucine auxotrophy, resistance to DP, and osmotic pressure and incapable to degrade Lproline. A proline oxidase-less strain of Serratia marcescens, having resistance to DP, thiazoline-4-carboxylate and azetidine-2-carboxylate, overproduces 58.5 g/L L-proline into the culture medium. By amplification of the genes proA and proB in this type of regulatory mutant, a construct was obtained which yields 75 g/L L-proline.
Benefits
L-proline is considered a non-essential amino acid as it can be synthesised from arginine via the urea cycle in liver, and from glutamine/glutamic acid in the intestinal epithelium. It has a number of beneficial properties including connective tissue strengthening, Stronger Connective Tissue, Decreased Risk Of Heart Disease, Maintenance Of Muscle Tissueand skin health.
General Description
L-Proline is a non-essential amino acid that serves as a building block for proteins. It is particularly useful in the formation of peptides, which are crucial for the structure and function of various proteins. This amino acid is significant in the commercial production of therapeutic recombinant proteins and monoclonal antibodies, where it is often included as a component of cell culture media.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Proline is a cyclic, non-essential, hydrophobic amino acid. It is a proteinogenic amino acid which is crucial for primary metabolism. In peptide chains, proline residues confer structural constraints and enhance the susceptibility of proximal peptide bonds to protease activity.
Purification Methods
A likely impurity is hydroxyproline. Purify L-proline via its picrate which is crystallised twice from water, then decomposed with 40% H2SO4. The picric acid is extracted with diethyl ether, the H2SO4 in solution is precipitated with Ba(OH)2, and the filtrate is evaporated. The residue is crystallised from hot absolute EtOH [Mellan & Hoover J Am Chem Soc 73 3879 1951] or EtOH/Et2O. Its solubility in H2O is >100%. It sublimes at 182-187o/0.3mm with 99.4% recovery and unracemised [Gross & Gradsky J Am Chem Soc 77 1678 1955]. It is hygroscopic and is stored in a desiccator. [Greenstein & Winitz The Chemistry of the Amino Acids J. Wiley, Vol 3 pp 2178-2199 1961, Beilstein 22 III/IV 8, 22/1 V 31.]
Structure and conformation
L-proline, also known as L-pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid, is a neutral amino acid. Although proline is classified as an amino acid, it is strictly speaking an imino acid, since it contains an imino group (carbon-nitrogen double bond). Due to its cyclic pyrrolidine side chain it is classified as a nonpolar aliphatic amino acid.
Properties of L-Proline
| Melting point: | 228 °C (dec.) (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 215.41°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | -85.5 º (c=4, H2O) |
| Density | 1.35 |
| vapor pressure | 0Pa at 25℃ |
| FEMA | 3319 | L-PROLINE |
| refractive index | -85 ° (C=4, H2O) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | H2O: 50 mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| appearance | white crystals |
| pka | 1.95, 10.64(at 25℃) |
| color | White |
| Odor | at 100.00 %. odorless |
| PH | 6.0-7.0 (25℃, 1M in H2O) |
| optical activity | [α]20/D 85.0±1.0°, c = 5% in H2O |
| Water Solubility | soluble |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| λmax | λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.05 λ: 280 nm Amax: 0.05 |
| JECFA Number | 1425 |
| Merck | 14,7780 |
| BRN | 80810 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 147-85-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Proline(147-85-3) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | L-Proline (147-85-3) |
Safety information for L-Proline
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for L-Proline
| InChIKey | ONIBWKKTOPOVIA-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
L-Proline manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![(αS)-Cyclohexanebutanoic Acid α-[[(1S)-1-Carboxyethyl]aMino]
cyclohexanebutanoic Acid α-Ethyl Ester](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/460720-14-3.gif)
You may like
-
 L-Proline 99% SUPPLIERView Details
L-Proline 99% SUPPLIERView Details
147-85-3 -
 L-Proline 99%View Details
L-Proline 99%View Details -
 L-Proline ExiPlus CAS 147-85-3View Details
L-Proline ExiPlus CAS 147-85-3View Details
147-85-3 -
 Proline BP CAS 147-85-3View Details
Proline BP CAS 147-85-3View Details
147-85-3 -
 L-Proline for cell culture CAS 147-85-3View Details
L-Proline for cell culture CAS 147-85-3View Details
147-85-3 -
 L-Proline USP CAS 147-85-3View Details
L-Proline USP CAS 147-85-3View Details
147-85-3 -
 L-Proline CASView Details
L-Proline CASView Details -
 L Proline Cas No 147 85 3, For Food Industry, Purity: 99View Details
L Proline Cas No 147 85 3, For Food Industry, Purity: 99View Details
147-85-3
