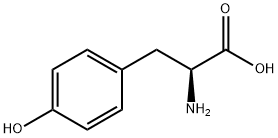
L(+)-Arginine
Synonym(s):L-Arginine;ARG;(S)-2-Amino-5-guanidinopentanoic acid;Abelson murine leukemia viral oncogene homolog 2;Abelson tyrosine-protein kinase 2
- CAS NO.:74-79-3
- Empirical Formula: C6H14N4O2
- Molecular Weight: 174.2
- MDL number: MFCD00002635
- EINECS: 200-811-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-26 16:58:18
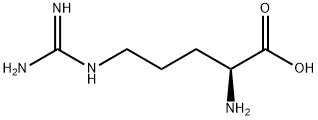
What is L(+)-Arginine?
Description
L-Glutamine and?L-arginine are classified as semi-essential or conditionally essential amino acids, which means that the human body can synthesize them under some health conditions but not others. Both are abundant in many foods.
Neither?D-glutamine nor?D-arginine is common in nature, so the?L-amino acids are usually referred to without prefixes. In 1883, German chemists Ernst. Schulze and E. Bosshard isolated?L-glutamine from the juice of sugarbeets. It is the most common amino acid in human blood and a key component of proteins.
In 1886, Schulze was also the first to isolate?L-arginine, in this case from lupin seedlings. It is also an important amino acid in protein biosynthesis.
It turns out that a difference in occurrence between these two amino acids makes a huge difference in huge animals. This year, while examining the melanocortin system* of cetaceans, Roger D. Cone at the University of Michigan (Ann Arbor) and colleagues discovered that the?two suborders of the sea mammals have different components at position 156 in the melanocortin-4 receptor. Glutamine is at this position in baleen whales, whereas toothed whales and dolphins contain arginine instead.
Cone’s group found that arginine in the receptor suppresses the beasts’ appetites relative to the glutamine-containing receptor. They believe that this difference contributes to the much larger sizes of baleen whales.
*The melanocortin system is an important regulator of metabolism, food intake, and fat storage.
Chemical properties
White crystalline powder
Chemical properties
Arginine is a diaminomonocarboxylic acid. The nonessential amino acid, arginine, is a urea cycle amino acid and a precursor for the neurotransmitter nitric oxide, which plays a role in the regulation of the brain’s system of dilation and constriction of small blood vessels. It is strongly alkaline and its water solutions absorb carbon dioxide from the air (FCC, 1996). Functionality in foods includes, but is not limited to, nutrient and dietary supplement
Physical properties
Solubility 14.87 (20 ℃) g/100 g H2O, pI 10.76, dissociation constants: pK1 2.01, pK2 9.04 (a-NH2), pK3 12.48 (guanidyl).
Occurrence
Reported present in cheese, chocolate, eggs, meat, nuts and other products.
The Uses of L(+)-Arginine
Amino acid; nutrient.
The Uses of L(+)-Arginine
L-Arginine is used for heart and blood vessel conditions which includes congestive heart failure (CHF), chest pain, high blood pressure and coronary artery disease. It plays a vital role in the treatment of cardiovascular disease due to it being antiatherogenic, anti-ischemic, antiplatelet and antithrombotic. It acts as a growth stimulant and is involved in the treatment of erectile dysfunction in men. It is an important ingredient of tooth paste which provides effective relief for sensitive teeth.
The Uses of L(+)-Arginine
L-Arginine has been used:
- as a Roswell park memorial institute medium (RPMI) media component in the isolation and culture of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs)
- as a RPMI media component for tissue culture
- in DMEM medium for the identification and quantification of phosphorylation sites by stable isotope labeling by amino acids in cell culture (SILAC) and LCMS/MS
What are the applications of Application
L-Arginine is a precursor of nitric oxide synthesis that induces vasodilation
Definition
ChEBI: An L-alpha-amino acid that is the L-isomer of arginine.
Aroma threshold values
Detection at 100%, faint.
Taste threshold values
Taste characteristics at 1000 ppm: hint of sourness.
General Description
L-Arginine is an amino acid that plays a key role in many physiological processes such as tissue repair and reproduction. It is a key precursor for synthesizing nitric oxide in mammals. Due to these factors, the dietary supplementation with L-arginine may show a range of health benefits.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Substrate of nitric oxide synthase, which is converted to citrulline and nitric oxide (NO). Induces insulin release by a nitric oxide-dependent mechanism.
Side Effects
Nausea, abdominal pain and diarrhea
Bloating
Gout
Headache
Allergic response
Airway inflammation or worsening of asthma symptoms
Safety Profile
Mutation data reported. Whenheated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx.
Synthesis
Enzymatically, arginine is formed in two reactions from citrulline. The first reaction (citrulline + succinate) is catalyzed by the enzyme arginosuccinate synthetase. It is ATP dependent and with the formation of a new C–N bond in the gaunidino group of arginosuccinate, water is removed and ATP is hydrolyzed. The second reaction is catalyzed by arginine synthetase and involves the scission of arginosuccinate with the formation of arginine and fumaric acid.
Drug interactions
L-arginine may interact with certain medications, including :
Blood-pressure-lowering medications: enalapril (Vasotec), losartan (Cozaar), amlodipine (Norvasc), furosemide (Lasix), etc.
Erectile dysfunction medications: sildenafil citrate (Viagra), tadalafil (Cialis), etc.
Blood-thinning medications: clopidogrel (Plavix), enoxaparin (Lovenox), heparin, warfarin (Coumadin), etc.
Antidiabetic medications: insulin, pioglitazone (Actos), glipizide (Glucotrol), etc.
Medications that increase blood flow: nitroglycerin (Nitro-Dur, Nitro-Bid, Nitrostat), isosorbide ( Sorbitrate, Imdur, Isordil), etc.
Diuretic medications: amiloride (Midamor), and triamterene (Dyrenium), spironolactone (Aldactone), etc.
Metabolism
Not Available
Purification Methods
S-Arginine crystallises from H2O as the dihydrate and as plates from EtOH. It also crystallises from 66% EtOH. Its solubility in H2O is 15% at 21o. Its isoelectric point is at pH 10.76. [Greenstein & Winitz The Chemistry of the Amino Acids J. Wiley, Vol 3 p 1841 1961, Beilstein 4 IV 817.]
Properties of L(+)-Arginine
| Melting point: | 222 °C (dec.) (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 305.18°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | 27.1 º (c=8, 6N HCl) |
| Density | 1.2297 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 27 ° (C=8, 6mol/L HCl) |
| FEMA | 3819 | L-ARGININE |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | H2O: 100 mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| appearance | white crystals or powder |
| pka | 1.82, 8.99, 12.5(at 25℃) |
| color | white |
| PH Range | 10.5 - 12 |
| Odor | Faint |
| PH | 10.5-12.0 (25℃, 0.5M in H2O) |
| optical activity | [α]20/D +27°, c = 8 in 6 M HCl |
| Water Solubility | 148.7 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Sensitive | Air Sensitive |
| λmax | λ: 260 nm Amax: ≤0.2 λ: 280 nm Amax: ≤0.1 |
| JECFA Number | 1438 |
| Merck | 14,780 |
| BRN | 1725413 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 74-79-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | L-Arginine(74-79-3) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | L-Arginine (74-79-3) |
Safety information for L(+)-Arginine
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P337+P313:IF eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/attention. P403:Store in a well-ventilated place. |
Computed Descriptors for L(+)-Arginine
| InChIKey | ODKSFYDXXFIFQN-BYPYZUCNSA-N |
L(+)-Arginine manufacturer
Oxford Lab Fine Chem LLP
Aditya Molecules
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 L(+)-Arginine 99%View Details
L(+)-Arginine 99%View Details -
 L-Arginine (free base) extrapure CHR CAS 74-79-3View Details
L-Arginine (free base) extrapure CHR CAS 74-79-3View Details
74-79-3 -
 L-Arginine 98% (HPLC) for Tissue Culture CAS 74-79-3View Details
L-Arginine 98% (HPLC) for Tissue Culture CAS 74-79-3View Details
74-79-3 -
 L-Arginine (free base) CAS 74-79-3View Details
L-Arginine (free base) CAS 74-79-3View Details
74-79-3 -
 L- Arginine Powder, Bionique PharmaView Details
L- Arginine Powder, Bionique PharmaView Details
7200-25-1 -
 L-Arginine (CAS NO.74-79-3), Packaging Type: Small Container, Packaging Size: 25kgView Details
L-Arginine (CAS NO.74-79-3), Packaging Type: Small Container, Packaging Size: 25kgView Details
74-79-3 -
 L Arginine PowderView Details
L Arginine PowderView Details
74-79-3 -
 L-ARGININE 99% (For Biochemistry), Packaging Type: Bottles,DrumsView Details
L-ARGININE 99% (For Biochemistry), Packaging Type: Bottles,DrumsView Details
74-79-3
