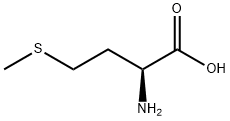
L-Methionine
Synonym(s):L-Methionine;Met;L-Methionine - CAS 63-68-3 - Calbiochem;(S)-2-Amino-4-(methylmercapto)butyric acid;L -2-Amino-4-(methylthio)butanoic acid
- CAS NO.:63-68-3
- Empirical Formula: C5H11NO2S
- Molecular Weight: 149.21
- MDL number: MFCD00063097
- EINECS: 200-562-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-06-19 18:20:17
What is L-Methionine?
Absorption
Absorbed from the lumen of the small intestine into the enterocytes by an active transport process.
Toxicity
Doses of L-methionine of up to 250 mg daily are generally well tolerated. Higher doses may cause nausea, vomiting and headache. Healthy adults taking 8 grams of L-methionine daily for four days were found to have reduced serum folate levels and leucocytosis. Healthy adults taking 13.9 grams of L-methionine daily for five days were found to have changes in serum pH and potassium and increased urinary calcium excretion. Schizophrenic patients given 10 to 20 grams of L-methionine daily for two weeks developed functional psychoses. Single doses of 8 grams precipitated encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis.
Description
Colorless or white lustrous plates, or a white crystalline powder. It has a slight, characteristic odor. It is soluble in water, in alkali solutions, and in dilute mineral acids. It is slightly soluble in alcohol and practically insoluble in ether.
Chemical properties
White crystalline powder
Chemical properties
Methionine occurs as a white or almost white, crystalline powder or colorless crystals.
Originator
Meonine ,Ives,US,1944
The Uses of L-Methionine
L-Methionine is used as an essential amino acid for human development and therapeutically acts as an antidote for acetaminophen poisoning. It serves as a chelating agent for heavy metals, as a flavoring agent and nutritional supplement for foods. It acts as a feed additive, vegetable oil enrichment and as a single cell protein. In addition to this, it is used as a hepatoprotectant and also acts as a lipotropic agent and prevents excess fat buildup in the liver.
The Uses of L-Methionine
Essential aminoacid for human development. Hepatoprotectant; antidote (acetominophen poisoning); urinary acidifier.
The Uses of L-Methionine
methionine is slows down and normalizes oil gland sebum production. Methionine is also used as a texturizer in cosmetic creams. It is an essential amino acid found in a number of proteins and obtained by means of fermentation.
Indications
Used for protein synthesis including the formation of SAMe, L-homocysteine, L-cysteine, taurine, and sulfate.
Background
A sulfur containing essential amino acid that is important in many body functions. It is a chelating agent for heavy metals.
What are the applications of Application
L-Methionine is an essential amino acid
Definition
ChEBI: The L-enantiomer of methionine.
Production Methods
Numerous methods have been described for manufacture of methionine, including hydrolysis of methionine amide )and 5-(bmethylmercaptoethyl)- hydantoin.
Preparation
The production method of choice for L-methionine is still the enzymatic resolution of racemic N-acetyl-methionine using acylase from Aspergillus oryzae. The production is carried out in a continuously operated fixed-bed or enzyme membrane reactor.
Manufacturing Process
A 3-necked flask fitted with a stirrer, thermometer, gas inlet, dropping funnel, and brine-cooled reflux condenser was charged with 53 g (1.1 mol) methyl mercaptan and 0.35 g mercuric methyl mercaptide. After admitting 56 g (1.0mol) of acrolein during the course of 15 minutes with an inside temperature of
about 10°C, the temperature was allowed to rise spontaneously to 75°C, at
which point an ice bath was applied. There was no indication of further
reaction one hour after the addition of the acrolein. Distillation of the product
gave 71 g (yield 68%) of β-methylmercaptopropionaldehyde, as described in
US Patent 2,584,496.
Then as described in US Patent 2,732,400, β-methylmercaptopropionaldehyde
(0.60 M) (56.5 g) is added to a stirred solution of sodium cyanide (0.66 M)
(32.4 g) and ammonium chloride (0.63 M) (33.7 g) in water (140 ml). The
temperature of the mixture rises to 49°C and is maintained at this point by
heat evolution for about 5 minutes when it slowly begins to fall. Methanol (50
ml) is added and the mixture is stirred for 4 hours as the temperature falls to
28°C (room temperature).
After chilling to +12°C, additional methanol (35 ml) and a concentrated
aqueous ammoniun hydroxide solution (1.4 M) (100 ml) are added and
stirring is continued for 2 hours at a temperature maintained at from +5° to
+15°C. The organic layer is separated and solvent is stripped from the
aqueous layer at water aspirator pressure at a temperature below 40°C. The
residue is extracted several times with chloroform and the chloroform extracts
are combined with the separated oil. Chloroform is removed at water aspirator
pressure at a temperature below 35°C to leave crude α-amino-γmethylmercaptobutyronitrile (methionine nitrile) in 88% yield (68 g) as a
clear, somewhat viscous oil.
The methionine nitrile (20 g) is dissolved in a solution prepared from 50 ml of
aqueous 5 N sodium hydroxide solution and 65 ml of ethanol. The solution is
then refluxed for 24 hours; ammonia is evolved. The solution is treated with
activated carbon, filtered, acidified with glacial acetic acid (17 ml), chilled to -
10°C and filtered to give crude product. This crude product is then slurried
with a solution made up of 20 ml of water and 20 ml of methanol, filtered at -
5° to +10°C and dried to give dl-methionine as white platelets.
Therapeutic Function
Lipotropic
Synthesis Reference(s)
Canadian Journal of Chemistry, 47, p. 3271, 1969 DOI: 10.1139/v69-542
Synthetic Communications, 26, p. 3619, 1996 DOI: 10.1080/00397919608003774
General Description
Minute hexagonal plates from dilute alcohol.
Air & Water Reactions
Reacts with water, steam, and/or acids to produce toxic and flammable vapors of hydrogen sulfide . Water soluble . pH of 1% aqueous solution is 5.6-6.0.
Reactivity Profile
An organosulfide and amine derivative, carboxylic acid. Look at Reactive Groups 20 (organosulfides), 7 (amines), and 3 (carboxylic acids) may give indications about reactive tendencies. L-Methionine is an amino acid essential in human nutrition.
Health Hazard
ACUTE/CHRONIC HAZARDS: L-Methionine is dangerous when heated to decomposition; it emits dangerous and highly toxic fumes.
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for L-Methionine is not available, but L-Methionine is probably combustible.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Methionine is used in oral pharmaceutical formulations as a flavoring agent.It has been included in parenteral formulations as a pH controlling agent,and it has also been used experimentally as an antioxidant with antibodies.Methionine is also used therapeutically in oral tablets
Biochem/physiol Actions
L-Methionine serves as precursor for transmethylation and transsulphuration. Methionine adenosylation results in the formation of S-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAM). SAM serves as a methyl donor to a number of substances. This methylation is significantly associated with the immune system functioning. Thus, SAM deficiency causes severe combined immunodeficiencies. L-Methionine′s metabolic product, glutathione, is known to regulate immune response and has antiviral action.
Pharmacokinetics
L-Methionine is a principle supplier of sulfur which prevents disorders of the hair, skin and nails; helps lower cholesterol levels by increasing the liver's production of lecithin; reduces liver fat and protects the kidneys; a natural chelating agent for heavy metals; regulates the formation of ammonia and creates ammonia-free urine which reduces bladder irritation; influences hair follicles and promotes hair growth. L-methionine may protect against the toxic effects of hepatotoxins, such as acetaminophen. Methionine may have antioxidant activity.
Safety Profile
Mildly toxic by ingestion and intraperitoneal routes. Human mutation data reported. An experimental teratogen. Experimental reproductive effects. An essential sulfur-containing amino acid. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of NOx and SOx.
Safety
Methionine is used in oral pharmaceutical formulations. The pure
form of methionine is mildly toxic by ingestion and by the IP route.
LD50 (rat, IP): 4.328 g/k
LD50 (rat, oral): 36 g/kg
Metabolism
Hepatic
Storage
Methionine is sensitive to light and should be stored in a cool, dark place.
Purification Methods
Crystallise L-methionine from aqueous EtOH. Also purify it by dissolving ~0.5g of amino acid in ~10mL of hot H2O, filtering, adjusting the pH to 5.8 with 5N HCl, collecting the solid after addition of ~20mL of EtOH. It is recrystallised by dissolving in H2O and adding EtOH. It sublimes at 197-208o/0.3mm with 99.8% recovery and unracemised [Gross & Gradsky J Am Chem Soc 77 1678 1955]. [Milne & Peng J Am Chem Soc 79 647 1957, Greenstein & Winitz The Chemistry of the Amino Acids J. Wiley, Vol 3 pp 2125-2152 1961, Beilstein 4 IV 3189.]
Incompatibilities
Methionine is incompatible with strong oxidizing agents.
Regulatory Status
Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (oral tablets). Included in parenteral preparations (injection solutions; powders for reconstitution) licensed in the UK.
Properties of L-Methionine
| Melting point: | 284 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 393.91°C (estimate) |
| alpha | 23.25 º (c=2, 6N HCl) |
| Density | 1,34g/cm |
| refractive index | 1.5216 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 20-25°C |
| solubility | 1 M HCl: 0.5 M at 20 °C, clear, colorless |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 2.13(at 25℃) |
| color | White |
| PH | 5-7 (10g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| Odor | Slight characteristic |
| optical activity | [α]20/D +23.7±0.5°, c = 5% in 5 M HCl |
| Water Solubility | Soluble |
| λmax | λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.40 λ: 280 nm Amax: 0.05 |
| Merck | 14,5975 |
| BRN | 1722294 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 63-68-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | L-Methionine(63-68-3) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | L-Methionine (63-68-3) |
Safety information for L-Methionine
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. |
Computed Descriptors for L-Methionine
L-Methionine manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 L-Methionine 99%View Details
L-Methionine 99%View Details -
 L-Methionine for cell culture CAS 63-68-3View Details
L-Methionine for cell culture CAS 63-68-3View Details
63-68-3 -
 L-Methionine CAS 63-68-3View Details
L-Methionine CAS 63-68-3View Details
63-68-3 -
 L-Methionine CAS 63-68-3View Details
L-Methionine CAS 63-68-3View Details
63-68-3 -
 L-Methionine CASView Details
L-Methionine CASView Details -
 L-METHIONINE For Biochemistry CAS 63-68-3View Details
L-METHIONINE For Biochemistry CAS 63-68-3View Details
63-68-3 -
 L-Methionine 98.00% CAS 63-68-3View Details
L-Methionine 98.00% CAS 63-68-3View Details
63-68-3 -
 L - Methionine, Packaging Type: DrumView Details
L - Methionine, Packaging Type: DrumView Details
63-68-3