Calcium nitrite
Synonym(s):Calcium dinitrite;Calcium nitrite;Calcium nitrite (Ca(NO2 )2 )
- CAS NO.:13780-06-8
- Empirical Formula: CaN2O4
- Molecular Weight: 132.09
- MDL number: MFCD00049399
- EINECS: 237-424-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-07-04 14:22:53
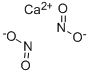
What is Calcium nitrite?
Description
Calcium nitrite has the formula of Ca(NO2)2 and the
molecular weight of 132.0894 g/mol. It can be made by
the usual double decomposition reaction of sodium
nitrite and CaCl2. It forms a tetrahydrate that is isomorphous
with the strontium and barium salts:
2Na2NO2 (aq) + CaCl2 ? Ca(NO2)2 (aq) + 4NaCl (aq)
Chemical properties
white or yellowish deliquescent, hexagonal crystal(s); prepared from nitric oxide and a mixture consisting of calcium ferrate and calcium nitrate; used to inhibit corrosion in lubricants and concrete [MER06]
Physical properties
Calcium nitrite, Ca(NO2)2, has the CAS number of
13780-06-8 and occurs as yellow-white crystals. It is
very hygroscopic. Its density is 2.23 g/cm3 and it
decomposes at 392°C to form nitrogen oxides and
CaO. It is slightly soluble in alcohol. Ca(NO2)2·4H2O
loses two waters of hydration at about 80°C and one
at 105°C to form the monohydrate. It loses the other at
about 155°C. The anhydrate, if further heated, is
unstable and oxidizes to the nitrate in air above 220°C:
Ca(NO2)2 + O2 + heat?Ca(NO3)2
The Uses of Calcium nitrite
Calcium nitrite has several industrial uses:
1. Calcium nitrite has high solubility, so can be used as
a solution or powder in concrete as an “anti-freeze”
during winter months as needed. Using this
antifreeze at negative temperature can promote
the hydration of minerals in cement, and the
freezing point of operative temperature can be
reduced to –25°C.
2. This salt is a steel rust inhibitor: calcium nitrite can
clean steel and protect it from rust, and can protect
steel material in concrete used to construct buildings
and structures, to extend the useful life of concrete in
buildings.
3. In concrete, Ca(NO2)2 acts as a coagulator: calcium
nitrite is free of chlorine and alkali, capable to reduce
alkali aggregation of concrete and improve its early
strength and compressive resistance. The calcium
nitrite protects steel reenforcing bars from chlorideinduced
corrosion. One advantage to calcium nitrite
is that its protection mechanism is well defined. Data
are known that show the levels of chloride to which
given levels of calcium nitrite will protect. Once corrosion initiates, the rates are lower with calcium
nitrite present. These results have been used to
produce reinforced concrete structures with
durability in excess of 50–100 years.
4. Calcium nitrite can be used as corrosion inhibitor
when added to lubricating agents.
5. Calcium nitrite can also be used in pharmaceutical,
dyes and metallurgy industries, as a mild reducing
agent.
The Uses of Calcium nitrite
Corrosion inhibitor in lubricants, concrete.
What are the applications of Application
Calcium nitrite solution is an inorganic compound
Preparation
Industrially, calcium nitrite is manufactured by reacting
“NOX” gas with “lime”:
Ca(OH)2 + NO +NO2?Ca(NO2)2 +H2O
By carefully controlling calciumnitrite conditions, the
selectivity on converted lime, on a molar basis, is over
95% pure. It is soluble in water (98.2 g/100 ml at
20 °C) and the solution must be evaporated at low
temperature to obtain the tetrahydrate. If heated with
NO2 gas, it also form the nitrate:
Ca(NO2)2 + NO2?Ca(NO3)2 + NO
Anhydrous calcium nitrite is unstable and slowly
oxidizes in air to form the nitrate. It is also soluble in
alcohol at 0.97 g/100 ml at 20 °C.
General Description
Calcium nitrite solution (Ca(NO2)2) is widely utilized as a corrosion inhibitor. It protects the metal surface against chloride attack and increases the threshold level and improves the overall life of the concrete. Ca(NO2)2 does not change the mechanical properties of the cement.
Flammability and Explosibility
Not classified
Purification Methods
Crystallise it from hot water (1.4mL/g) by adding ethanol and cooling to give the hydrate. It is deliquescent. [Ray & Ogg J Am Chem Soc 79 265 1957.]
Properties of Calcium nitrite
| Melting point: | 390 °C |
| Density | 2.23 |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 110 °C |
| solubility | slightly soluble in ethanol |
| form | white-yellow hexagonal crystals |
| color | white-yellow hexagonal, hexane crystals, crystalline;
hygroscopic |
| Water Solubility | slightly soluble alcohol [MER06]; g/100g solution H2O: 38.3 (0°C), 43.0 (18.5°C), 71.2 (91°C); solid phase Ca(NO2)2 · 4H2O (0°C, 18.5°C), Ca(NO2)2 ·2H2O (91°C) [KRU93] |
| Merck | 13,1688 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 13780-06-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Calcium nitrite (13780-06-8) |
Safety information for Calcium nitrite
Computed Descriptors for Calcium nitrite
Calcium nitrite manufacturer
Sonu Chem
Destiny Chemicals
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Calcium nitrite solution 30 wt. % in H2O CAS 13780-06-8View Details
Calcium nitrite solution 30 wt. % in H2O CAS 13780-06-8View Details
13780-06-8 -
 Calcium Nitrite CASView Details
Calcium Nitrite CASView Details -
 Industrial Grade 25 kg Calcium Nitrite PowderView Details
Industrial Grade 25 kg Calcium Nitrite PowderView Details
13780-06-8 -
 Calcium Nitrite Corrosion Inhibitor For Steel Bar Rod,ConstructionView Details
Calcium Nitrite Corrosion Inhibitor For Steel Bar Rod,ConstructionView Details
13780-06-8 -
 Technical Grade 25kg Calcium Nitrite, 100%View Details
Technical Grade 25kg Calcium Nitrite, 100%View Details
13780-06-8 -
 Calcium NitriteView Details
Calcium NitriteView Details
13780-06-8 -
 Calcium NitriteView Details
Calcium NitriteView Details
13780-06-8 -
 Calcium NitriteView Details
Calcium NitriteView Details
13780-06-8
