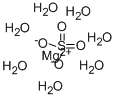
Magnesium nitrate
Synonym(s):Magnesium modifier;Magnesium nitrate – nitric acid solution
- CAS NO.:10377-60-3
- Empirical Formula: MgN2O6
- Molecular Weight: 148.3148
- MDL number: MFCD00011103
- EINECS: 233-826-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:21
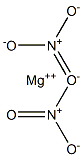
What is Magnesium nitrate?
Description
Magnesium nitrate has the molecular formula of
Mg(NO3)2 and the molecular weight of 148.3152 g/
mol.
Magnesium nitrate is prepared by the action of nitric
acid on magnesium carbonate, oxide or hydroxide:
MgCO3 + 2HNO3 ? Mg(NO3)2 + CO2 +H2O
Mg(OH)2 + 2HNO3 ? Mg(NO3)2 + 2H2O
The salt crystallizing at room temperature after
evaporation is the hexahydrate, Mg(NO3)2·6H2O. Two
stable hydrates are formed, the hexahydrate [CAS
number =13446-18-9] and the dihydrate, Mg(NO3)2·
2H2O [CAS number = 15750-45-5].
Chemical properties
White crystals.Soluble in water and alcohol; deliquescent.
Chemical properties
Magnesium nitrate is white crystalline solid.
The Uses of Magnesium nitrate
In pyrotechnics; in the concentration of nitric acid.
The Uses of Magnesium nitrate
It is used in printing, chemical, agriculture and ceramics industries. Its fertilizer grade has 10.5% nitrogen and 9.4% magnesium.
Definition
ChEBI: The inorganic nitrate salt of magnesium.
Preparation
The magnesium nitrate used in commerce has been synthesized in a variety of ways. The reaction between nitric acid and magnesium metal is one way and reaction with MgO is another. Magnesium hydroxide and ammonium nitrate also form the product but ammonia is released as a by-product:
2HNO3 + Mg Mg(NO3)2 +H2
2HNO3 + MgO Mg(NO3)2 +H2O
Mg(OH)2 + 2NH4NO3 Mg(NO3)2 + 2NH3 + 2H2O
Since magnesium nitrate has a high affinity for water, heating the hexahydrate does not result in the dehydration of the salt. Instead, it decomposes into magnesium oxide, oxygen and nitrogen oxides:
4Mg(NO3)2·6H2O + heat 4MgO + 2NO2 + 2N2O + O2 + 6H2O
Heating the hexahydrate above its melting point first forms basic nitrates, such as Mg(NO3)2·4Mg(OH)2. It is this salt that decomposes at 400 C, forming magnesium oxide and oxides of nitrogen. The absorption of these nitrogen oxides in water is one possible way to synthesize HNO3. Although it is inefficient, it does not require the use of another strong acid and the mineral, nitromagnesite, can be used in this context.
General Description
A white crystalline solid. Produces toxic oxides of nitrogen if heated to decomposition. Used in pyrotechnics.
Air & Water Reactions
Deliquescent. Water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
Mixtures of Magnesium nitrate with alkyl esters may explode owing to the formation of alkyl nitrates; mixtures with phosphorus, tin(II) chloride, or other reducing agents may react explosively [Bretherick 1979 p. 108-109]. Noncombustible but will accelerate the burning of combustible materials. If large quantities are involved in a fire or the combustible material is finely divided an explosion may result. Prolonged exposure to fire or heat may result in an explosion. Magnesium nitrate has been reported to undergo spontaneous decomposition in dimethylformamide [Bretherick 5th ed., 1995]. Magnesium nitrate tends to behave as a strong oxidizer.
Hazard
Dangerous fire and explosion risk in contact with organic materials, strong oxidizing agent.
Health Hazard
Exposure can cause mild irritation to the mucous membranes. Symptoms may include coughing and shortness of breath. Ingestion of large doses may cause dizziness, abdominal pain, vomiting, bloody diarrhea, weakness, convulsions, and collapse. Contact with skin may cause irritation, redness, and pain.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Safety Profile
Probably a severe irritant to the eyes, skin, and mucous membranes. A powerful oxidizer. Violent decomposition on contact with dmethylformamide. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx. See also NITRATES and MAGNESIUM COMPOUNDS.
Potential Exposure
Magnesium nitrate is used in fireworks and in the production of concentrated nitric acid.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and inducevomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.Note to physician: Treat for methemoglobinemia.Spectrophotometry may be required for precise determination of levels of methemoglobin in urine.
Storage
Color Code—Yellow: Reactive Hazard (strongoxidizer); Store in a location separate from other materials,especially flammables and combustibles. Prior to workingwith this chemical you should be trained on its proper handling and storage. Magnesium nitrate must be stored toavoid contact with dimethyl formamide, fuels, and strongreducing agents, since violent reactions occur. Store intightly closed containers in a cool, well-ventilated areaaway from flammable and combustible materials. Avoidstorage on wood floors. See OSHA Standard 1910.104 andNFPA 43A Code for the Storage of Liquid and SolidOxidizers for detailed handling and storage regulations.
Shipping
UN1474 Magnesium nitrate, Hazard Class: 5.1; Labels: 5.1-Oxidizer
Incompatibilities
A powerful oxidizer. Violent reaction with dimethylformamide, reducing agents; combustibles, fuels, organic and easily oxidizable matter
Properties of Magnesium nitrate
| Melting point: | 648 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 1090 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 0.889 g/mL at 25 °C |
| vapor pressure | 1 mm Hg ( 621 °C) |
| RTECS | OM3756000 |
| Flash point: | −26 °F |
| solubility | H2O: soluble |
| form | turnings |
| color | white cubic crystals, crystalline |
| Water Solubility | Freely soluble in water. Moderately soluble in ethanol and ammonia. |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| Merck | 13,5697 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 2 ppm; STEL 4 ppm OSHA: TWA 2 ppm(5 mg/m3) NIOSH: IDLH 25 ppm; TWA 2 ppm(5 mg/m3); STEL 4 ppm(10 mg/m3) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 10377-60-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Magnesium nitrate (10377-60-3) |
Safety information for Magnesium nitrate
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Over Circle Oxidizers GHS03  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H272:Oxidising liquids;Oxidising solids H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P220:Keep/Store away from clothing/…/combustible materials. P221:Take any precaution to avoid mixing with combustibles/… P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P405:Store locked up. |
Computed Descriptors for Magnesium nitrate
Magnesium nitrate manufacturer
Zama Chemical
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
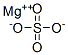
You may like
-
 Magnesium nitrate hydrate CAS 10377-60-3View Details
Magnesium nitrate hydrate CAS 10377-60-3View Details
10377-60-3 -
 Magnesium nitrate hydrate CAS 10377-60-3View Details
Magnesium nitrate hydrate CAS 10377-60-3View Details
10377-60-3 -
 Magnesium nitrate hydrate CAS 10377-60-3View Details
Magnesium nitrate hydrate CAS 10377-60-3View Details
10377-60-3 -
 Magnesium nitrate hydrate CAS 10377-60-3View Details
Magnesium nitrate hydrate CAS 10377-60-3View Details
10377-60-3 -
 Magnesium matrix modifier CASView Details
Magnesium matrix modifier CASView Details -
 Crystals Magnesium Nitrate, For Industrial, Packaging Type: PP Woven BagView Details
Crystals Magnesium Nitrate, For Industrial, Packaging Type: PP Woven BagView Details
10377-60-3 -
 Magnesium Nitrate ., Laboratory, 99%View Details
Magnesium Nitrate ., Laboratory, 99%View Details
10377-60-3 -
 Magnesium Nitrate crystals agricultural grade, 25 kg bagView Details
Magnesium Nitrate crystals agricultural grade, 25 kg bagView Details
10377-60-3
