Ammonium chloride
Synonym(s):Ammonium chloride;Ammonium chloride solution;Sal ammoniac;Salmiac;NH?Cl
- CAS NO.:12125-02-9
- Empirical Formula: ClH4N
- Molecular Weight: 53.49
- MDL number: MFCD00011420
- EINECS: 235-186-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-23 08:32:17
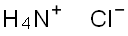
What is Ammonium chloride ?
Absorption
Completely absorbed within 3–6 h. In healthy persons, absorption of ammonium chloride given by mouth was practically complete. Only 1 to 3% of the dose was recovered in the feces.
Toxicity
LD50 "Rat" after oral administration is: 1650 mg/kg.
Overdosage of Ammonium Chloride has resulted in a serious degree of metabolic acidosis, disorientation, confusion and coma. If metabolic acidosis occur following overdosage, the administration of an alkalinizing solution such as sodium bicarbonate or sodium lactate will serve to correct the acidosis.
Patients administering Ammonium chloride should be watched to the signs of ammonia toxicity including (pallor, sweating, irregular breathing, bradycardia, cardiac arrhythmias, local and general twitching, tonic convulsions and coma).
It should be used with caution in patients with high total CO2 and buffer base secondary to primary respiratory acidosis.
Intravenous administration should be slow to avoid local irritation and toxic effects.
Description
Ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) is a solid that is often used as a source of ammonia (NH3) for reactions such as amide couplings. NH4Cl solutions are mildly acidic. Solutions of saturated aqueous ammonium chloride (sat aq NH4Cl) are very common in organic chemistry labs. Sat aq NH4Cl is typically used to quench reaction mixtures.
Chemical properties
Ammonium chloride is a white crystalline solid. It is soluble in water, aqueous solutionsof ammonia, and is slightly soluble in methyl alcohol. Ammonium chloride is found in natureas a sublimation productof volcanic activity, or is produced by neutralizing HCI(either in liquid or gaseousphase) with NH3 gas or liquid NH40H then evaporating the excess H20. The salt decomposes at350℃ and sublimes under controlled conditions at 520℃.
Physical properties
Colorless cubic crystals or white granular powder; saline taste; odorless; hygroscopic; does not melt but sublimes on heating at 340°C; vapor pressure 48.75 torr at 250°C and 251.2 torr at 300°C; density 1.5274 g/cm3 at 25°C; refractive index 1.642; readily dissolves in water, solubility: 229 g and 271 g/L solution at O°C and 20°C, respectively; solubility lowered by alkali metal chlorides and HCl; dissolution lowers the temperature of the solution; sparingly soluble in alcohols (6 g/L at 19°C) and soluble in liquid NH3; insoluble in acetone and ether.
Occurrence
Ammonium chloride occurs in nature in crevices near volcanoes. Also, it is found in smoke when burning dry camel or donkey dung as fuel. Important applications of this compound include the manufacture of dry cells for batteries; as a metal cleaner in soldering; as a flux in tin coating and galvanizing; in fertilizers; in pharmaceutical applications as a diuretic, or diaphoretic expectorant; and as an analytical standard in ammonia analysis. Also, it is used in freezing mixtures; washing powders; lustering cotton; in safety explosives and in dyeing and tanning.
The Uses of Ammonium chloride
Ammonium chloride is widely used in coatings, batteries, welding, medicine, and agriculture. Its primary applications are as a nitrogen supply in fertilizers and as an electrolyte in dry cell batteries. It is also widely used as a component of galvanizing, tinning, and soldering fluxes to remove oxide coatings from metals, thereby improving solder adhesion. In medicine, it is an intravenous acidifier used to treat metabolic alkalosis and low chloride levels (hypochloremia). It is also a component of cold and cough remedies.
What are the applications of Application
Ammonium Chloride is a compound used in the lysis of red blood cells and protein isolation techniques
Background
Ammonium chloride is an inorganic compound with the formula NH4Cl. It is highly soluble in water producing mildly acidic solutions.
Indications
Expectorant in cough syrups. The body's ammonium ion (NH4+) plays a vital role in maintaining acid-base balance. The kidney uses ammonium (NH4+) instead of sodium (Na+) to combine with fixed anions to maintain acid-base balance, especially as a homeostatic compensatory mechanism in metabolic acidosis. The therapeutic effects of Ammonium Chloride depend upon the ability of the kidney to utilize ammonia in the excretion of an excess of fixed anions and the conversion of ammonia to urea by the liver, thereby liberating hydrogen (H+) and chloride (Cl–) ions into the extracellular fluid. Ammonium Chloride Injection, USP, after dilution in isotonic sodium chloride injection, may be indicated in treating patients with (1) hypochloremic states and (2) metabolic alkalosis.
Definition
ChEBI: Ammonium chloride is an inorganic chloride having ammonium as the counterion. It has a role as a ferroptosis inhibitor. It is an inorganic chloride and an ammonium salt.
Preparation
Ammonium chloride is prepared commercially by reacting ammonia with hydrochloric acid. It may be prepared by fractional crystallization from a solution containing ammonium sulphate and sodium chloride or ammonium carbonate and calcium chloride. Because of it sease of preparation it can be manufacture dindustrially along side any plant that uses or produces ammonia. Ammonium chloride is used in dry cells, metal finishing, and in the preparation of cotton for dyeing and printing.
General Description
Ammonium chloride is a white crystalline solid. Ammonium chloride is soluble in water(37%). The primary hazard is the threat posed to the environment. Immediate steps should be taken to limit its spread to the environment. Ammonium chloride is used to make other ammonium compounds, as a soldering flux, as a fertilizer, and for many other uses.
Air & Water Reactions
Soluble in water. Slowly releases hydrogen chloride [USCG, 1999].
Reactivity Profile
Acidic salts, such as Ammonium chloride , are generally soluble in water. The resulting solutions contain moderate concentrations of hydrogen ions and have pH's of less than 7.0. They react as acids to neutralize bases. These neutralizations generate heat, but less or far less than is generated by neutralization of inorganic acids, inorganic oxoacids, and carboxylic acid. They usually do not react as either oxidizing agents or reducing agents but such behavior is not impossible. Many of these compounds catalyze organic reactions.
Hazard
Eye and upper respiratory tract irritant.
Health Hazard
Inhalation of fumes irritates respiratory passages. Ingestion irritates mouth and stomach. Fumes are irritating to eyes. Contact with skin may cause irritation.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Agricultural Uses
Ammonium chloride, like all other ammonium salts, is used as a fertilizer. It contains 24 to 26% nitrogen and is available as white crystals or granules. A coarse form of this fertilizer is preferred to the powdered form for direct application. It is used either directly for fertilization or in a variety of compound fertilizers, such as ammonium phosphate chloride or ammonium potassium chloride or in combination with urea or ammonium sulphate.
As a fertilizer, ammonium chloride has an advantage in that it contains 26% nitrogen, which is higher than that found in ammonium sulphate (20.5%). In terms of per unit cost of nitrogen, ammonium chloride is relatively cheaper than ammonium sulphate and has some agronomic advantages for rice. Nitrification of ammonium chloride is less rapid than that of urea or ammonium sulphate. Therefore, nitrogen losses are lower and yields, higher. It is a good source of nitrogen for cotton, rice, wheat, barley, maize, sorghum, sugar cane and fiber crops.
However, ammonium chloride is a highly acid forming fertilizer and the amount of calcium carbonate required to neutralize the acidity is more than the fertilizer itself, Further, it has a lower nitrogen content and a higher chloride content compared to urea and ammonium nitrate, making it harmful to some plants. It is not ideal for grapes, chilies, potatoes and tobacco as the added chlorine affects the quality and storability of these crops.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Ammonium chloride is one of the three principal components of the nitrogen cycle. Ammonium chloride administration promotes creatinine and urea clearance andinduces metabolic acidosis in mice. Excess of ammonium chloride inhibits Kreb′s pathway in brain and depletes ATP in astrocytes. Ammonium chloride inhibits acidification in the endosome-lysosome system. Ammonium chloride is a hemolysing agent used for the lysis of erythrocytes.
Safety
Ammonium chloride is used in oral pharmaceutical formulations.
The pure form of ammonium chloride is toxic by SC, IV, and IM
routes, and moderately toxic by other routes. Potential symptoms of
overexposure to fumes are irritation of eyes, skin, respiratory
system: cough, dyspnea, and pulmonary sensitization. Ammonium
salts are an irritant to the gastric mucosa and may induce
nausea and vomiting.
LD50 (mouse, IP): 1.44 g/kg
LD50 (mouse, oral): 1.3 g/kg
LD50 (rat, IM): 0.03 g/kg
LD50 (rat, oral): 1.65 g/kg
Potential Exposure
Ammonium chloride is used as an industrial chemical, pharmaceutical, and veterinary drug; to make dry batteries; in galvanizing; as a soldering flux.
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
The veterinary indications for ammonium chloride are as a urinary
acidifying agent to help prevent and dissolve certain types of uroliths
(e.g., struvite), to enhance renal excretion of some types of toxins
(e.g., strontium, strychnine) or drugs (e.g., quinidine), or to enhance
the efficacy of certain
antimicrobials (e.g., chlortetracycline, methenamine
mandelate, nitrofurantoin, oxytetracycline, penicillin G or
tetracycline) when treating urinary tract infections. Ammonium
chloride has also been used intravenously for the rapid correction
of metabolic alkalosis.
Because of changes in feline diets to restrict struvite and as struvite
therapeutic diets (e.g., s/d) cause aciduria, ammonium chloride
is not commonly recommended for struvite uroliths in cats.
Metabolism
Ammonium chloride is a systemic acidifier. In the liver, ammonium chloride is converted into urea with the liberation of hydrogen ions ( which lowers the pH) and chloride; chloride ion replaces bicarbonate.
Storage
Ammonium chloride is chemically stable. It decomposes completely at 3388℃ to form ammonia and hydrochloric acid. Store in airtight containers in a cool, dry place.
Shipping
UN3077 Environmentally hazardous substances, solid, n.o.s., Hazard class: 9; Labels: 9-Miscellaneous hazardous material, Technical Name Required.
Purification Methods
Crystallise it several times from conductivity water (1.5mL/g) between 90o and 0o. It sublimes. After one crystallisation, ACS grade has: metal(ppm) As (1.2), K (1), Sb (7.2), V (10.2). [Becher in Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry (Ed. Brauer) Academic Press Vol I p 812 1963.]
Incompatibilities
Ammonium chloride is incompatible with strong acids and strong bases. It reacts violently with ammonium nitrate and potassium chlorate, causing fire and explosion hazards. It also attacks copper and its compounds.
Waste Disposal
Pretreatment involves addition of sodium hydroxide to liberate ammonia and form the soluble sodium salt. The liberated ammonia can be recovered and sold. After dilution to the permitted provisional limit, the sodium salt can be discharged into a stream or sewer.
Regulatory Status
GRAS listed. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (oral syrup, tablets). Accepted for use as a food additive in Europe. Included in medicines licensed in the UK (eye drops; oral syrup).
Properties of Ammonium chloride
| Melting point: | 340 °C (subl.) (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 100 °C750 mm Hg |
| Density | 1.52 |
| vapor density | 1.9 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 1 mm Hg ( 160.4 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.642 |
| FEMA | 4494 | AMMONIA (ALSO INCLUDES AMMONIUM CHLORIDE) |
| storage temp. | Store at +5°C to +30°C. |
| solubility | H2O: 1 M at 20 °C, clear, colorless |
| form | Solid |
| appearance | White crystalline solid |
| pka | 9.25[at 20 ℃] |
| Specific Gravity | 1.53 |
| color | White |
| PH | 4.7 (200g/l, H2O, 25℃)(External MSDS) |
| Odor | odorless |
| Water Solubility | soluble |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| λmax | λ: 260 nm Amax: ≤0.021 λ: 280 nm Amax: ≤0.019 |
| Merck | 14,509 |
| BRN | 4371014 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 10 mg/m3; STEL 20 mg/m3 NIOSH: TWA 10 mg/m3; STEL 20 mg/m3 |
| Dielectric constant | 7(0.0℃) |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong acids, strong bases. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 12125-02-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Ammonium chloride(12125-02-9) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Ammonium chloride (12125-02-9) |
Safety information for Ammonium chloride
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P337+P313:IF eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Ammonium chloride
Ammonium chloride manufacturer
Ambica Dhatu Pvt Ltd
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
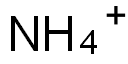
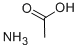
You may like
-
 AMMONIUM CHLORIDE CASView Details
AMMONIUM CHLORIDE CASView Details -
 Ammonium Standard Solution CASView Details
Ammonium Standard Solution CASView Details -
 Ammonium standard solution CASView Details
Ammonium standard solution CASView Details -
 Ammonium Standard Solution CASView Details
Ammonium Standard Solution CASView Details -
 Ammonium Standard Solution CASView Details
Ammonium Standard Solution CASView Details -
 Ammonium Standard Solution CASView Details
Ammonium Standard Solution CASView Details -
 Ammonium Standard Solution CASView Details
Ammonium Standard Solution CASView Details -
 Ammonium Standard Solution CASView Details
Ammonium Standard Solution CASView Details
