Ammonium oxalate monohydrate
Synonym(s):Oxalic acid diammonium salt
- CAS NO.:6009-70-7
- Empirical Formula: C2H10N2O5
- Molecular Weight: 142.11
- MDL number: MFCD00149694
- EINECS: 611-933-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-09-25 17:15:13
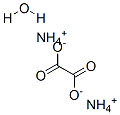
What is Ammonium oxalate monohydrate?
Chemical properties
Ammonium oxalate (NH4)2C204, is a white solid soluble, formed by reaction of NH40H and oxalic acid, and then evaporating. Used as a source of oxalate; ammonium binoxalate NH4HC204·H20.
Chemical properties
Ammonium oxalate is an odorless, colorless crystalline material or powder.
The Uses of Ammonium oxalate monohydrate
Ammonium oxalate monohydrate can be used to study chelators, biological buffers and biochemicals and reagents. It has been used for the detection and determination of calcium, lead, fluoride, and rare earth metals. It is employed as chelators and forms complexes with metals. It acts as reducing agent in gold extraction and is an active ingredient of ferrous metal surface polishing fluid. It is a promoting agent in production of cobalt oxide and nickel oxide. It has been used in an analysis of the effective segregation coefficient keff of different impurities, which suggested that the dehydration energies of cations mainly determine the capability of capture of impurity species by the growing crystal. It is widely utilized as a buffering reagent and a dispersant to determine the surface interaction of platelets. Ammonium oxalate monohydrate is also a buffering reagent and a dispersant to determine the surface interaction of platelets and to investigate the formation of oxalate monoalkylamide in the human lens. Ammonium oxalate monohydrate has also been used to study its acute poisoning effect on sheep, and surely has many additional uses.
The Uses of Ammonium oxalate monohydrate
Used for the detection of calcium, lead, fluoride and a buffering agent
The Uses of Ammonium oxalate monohydrate
Ammonium oxalate monohydrate is widely utilized as a buffering reagent and a dispersant to determine the surface interaction of platelets. It finds an application to study its acute poisoning effect on sheep and to investigate the formation of oxalate monoalkylamide in the human lens. It is also used in the detection and determination of calcium, lead, fluoride and rare earth metals. It is employed as chelators and forms complexes with metals. It acts as reducing agent in gold extraction and is an active ingredient of ferrous metal surface polishing fluid. It is a promoting agent in production of cobalt oxide and nickel oxide.
What are the applications of Application
Ammonium oxalate monohydrate is used for the detection of calcium, lead, fluoride and a buffering agent
General Description
Ammonium oxalate monohydrate is a diammonium salt of oxalic acid. Its refined crystal structure has been investigated by three-dimensional diffraction studies. Influence of bivalent [Mn(II), Co(II), Ni(II)] and trivalent cations [Fe(III), Cr(III)] impurities on the growth rates of ammonium oxalate monohydrate crystals has been described. Its space group and unit cell parameters have been analyzed by neutron diffraction studies. Its IR spectra have been compared with that of isolated coal-solubilizing agent (CSA).
Potential Exposure
It is used in chemical analysis and to make blueprint paper, explosives; a rust-removal ingredient in metal polishes.
Shipping
UN2811 Toxic solids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required. UN1759 Corrosive solids, n.o.s., Hazard class: 8; Labels: 8-Corrosive material, Technical Name Required.
Purification Methods
Crystallise it from water (10mL/g) at 50o. [Beilstein 2 IV 1846.]
Incompatibilities
Ammonium oxalate is a reducing agent and also reacts as a base to neutralize acids and reacts with oxidizers generating carbon dioxide. Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, hypochlorite solutions, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides.
Properties of Ammonium oxalate monohydrate
| Melting point: | 133 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 259.65°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.5 |
| refractive index | 1.4500 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Store at +5°C to +30°C. |
| solubility | H2O: 0.1 M at 20 °C, clear, colorless |
| form | Solid |
| color | White |
| Specific Gravity | 1.5 |
| PH Range | 6.4 (0.1 molar solution) |
| Odor | Odorless |
| PH | 6.0-7.0 (25℃, 0.1M in H2O) |
| Water Solubility | 45 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,537 |
| BRN | 3759830 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong acids. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 6009-70-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Diammonium oxalate monohydrate (6009-70-7) |
Safety information for Ammonium oxalate monohydrate
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Ammonium oxalate monohydrate
Ammonium oxalate monohydrate manufacturer
Buradon Inc.
Suvchem
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Ammonium Oxalate 97%View Details
Ammonium Oxalate 97%View Details
6009-70-7 -
 Ammonium oxalate monohydrate 98%View Details
Ammonium oxalate monohydrate 98%View Details -
 Ammonium oxalate, Monohydrate CAS 6009-70-7View Details
Ammonium oxalate, Monohydrate CAS 6009-70-7View Details
6009-70-7 -
 Ammonium Oxalate Monohydrate, Monohydrate CAS 6009-70-7View Details
Ammonium Oxalate Monohydrate, Monohydrate CAS 6009-70-7View Details
6009-70-7 -
 Ammonium oxalate monohydrate, Monohydrate CAS 6009-70-7View Details
Ammonium oxalate monohydrate, Monohydrate CAS 6009-70-7View Details
6009-70-7 -
 Ammonium Oxalate Monohydrate extrapure AR CAS 6009-70-7View Details
Ammonium Oxalate Monohydrate extrapure AR CAS 6009-70-7View Details
6009-70-7 -
 Ammonium Oxalate Monohydrate extrapure CAS 6009-70-7View Details
Ammonium Oxalate Monohydrate extrapure CAS 6009-70-7View Details
6009-70-7 -
 Ammonium Oxalate Monohydrate, Grade Standard: Bio-Tech GradeView Details
Ammonium Oxalate Monohydrate, Grade Standard: Bio-Tech GradeView Details
6009-70-7
