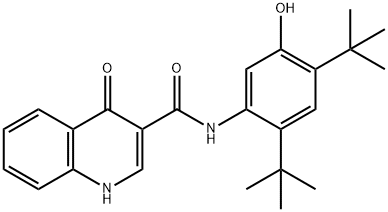
Ivacaftor
Synonym(s):CFTR Potentiator, VX-770 - CAS 873054-44-5 - Calbiochem;N-(5-Hydroxy-2,4- bis(2-methyl-2-propanyl)phenyl]-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-3-quinolinecarboxamide, Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator Potentiator, VX 770, Ivacaftor, Kalydeco;N-(5-Hydroxy-2,4-bis(2-methyl-2-propanyl)phenyl]-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-3-quinolinecarboxamide, Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator Potentiator, VX 770, Ivacaftor, Kalydeco
- CAS NO.:873054-44-5
- Empirical Formula: C24H28N2O3
- Molecular Weight: 392.49
- MDL number: MFCD17171361
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
What is Ivacaftor?
Absorption
Ivacaftor is well absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract. Following administration of ivacaftor with fat-containing foods, peak plasma concentrations were reached at 4 hours (Tmax) with a maximum concentration (Cmax) of 768 ng/mL and AUC of 10600 ng * hr/mL. It is recommended that ivacaftor is taken with fat-containing foods as they increase absorption by approximately 2.5- to 4-fold.
Toxicity
LD50 information is not readily available. There have been no reports of overdose with ivacaftor, but when given with tezacaftor, the highest clinical dose lead to diarrhea and dizziness. Provide supportive measures in cases of a suspected overdose. No antidote is available at this time.
Description
In January 2012, the US FDA approved ivacaftor for the treatment of cystic fibrosis (CF) in patients who have the G551D mutation of the CF transmembrane regulator (CFTR) and are at least 6 years old. Ivacaftor (also known as VX-770) is a CFTR potentiator that increases the open probability of CFTR, thus increasing chloride secretion particularly in the 5% of CF patients with the G551D/F508 gating/ processing mutation. Ivacaftor was discovered by medicinal chemistry optimization of a lead scaffold identified through high-throughput screening of a 228,000 compound collection. In cultured bronchial epithelial cells from a CF patient with F508del, ivacaftor increased chloride secretion (EC50=81 nM). Preparation of ivacaftor is accomplished via a multistep synthesis oftwointermediates, 4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid and 5-amino-di-tert-butylphenyl methyl carbonate, which are coupled using propane phosphonic acid anhydride (T3P) to afford the amide; deprotection of the phenol then provides ivacaftor.
Originator
Vertex Pharmaceuticals (United States)
The Uses of Ivacaftor
Ivacaftor (VX-770, Kalydeco) is a potentiator of CFTR targeting G551D-CFTR and F508del-CFTR with EC50 of 100 nM and 25 nM, respectively
The Uses of Ivacaftor
Ivacaftor is used in the treatment of cystic fibrosis.
Indications
When used as monotherapy as the product Kalydeco, ivacaftor is indicated for the treatment of cystic fibrosis (CF) in patients aged one month and older who have one mutation in the CFTR gene that is responsive to ivacaftor potentiation based on clinical and/or in vitro assay data.
When used in combination with the drug lumacaftor as the product Orkambi, ivacaftor is indicated for the management of CF in patients aged one year and older who are homozygous for the F508del mutation in the CFTR gene. If the patient’s genotype is unknown, an FDA-cleared CF mutation test should be used to detect the presence of the F508del mutation on both alleles of the CFTR gene.
When used in combination with tezacaftor in the product Symdeko, it is used to manage CF in patients 12 years and older who have at least one mutation in the CFTR gene or patients aged 12 or older who are shown to be homozygous for the F508del mutation.
When used in combination with tezacaftor and elexacaftor in the product Trikafta, it is indicated for the treatment of cystic fibrosis in patients 12 years of age and older who have at least one F508del mutation in the CFTR gene.
Background
Ivacaftor (also known as Kalydeco or VX-770) is a drug used for the management of Cystic Fibrosis (CF). It is manufactured and distributed by Vertex Pharmaceuticals. It was approved by the Food and Drug Administration on January 31, 2012, and by Health Canada in late 2012. Ivacaftor is administered as a monotherapy and also administered in combination with other drugs for the management of CF.
Cystic Fibrosis is an autosomal recessive disorder caused by one of several different mutations in the gene for the Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator (CFTR) protein, an ion channel involved in the transport of chloride and sodium ions across cell membranes. CFTR is active in epithelial cells of organs such as of the lungs, pancreas, liver, digestive system, and reproductive tract. Alterations in the CFTR gene result in altered production, misfolding, or function of the protein and consequently abnormal fluid and ion transport across cell membranes. As a result, CF patients produce thick, sticky mucus that clogs the ducts of organs where it is produced making patients more susceptible to complications such as infections, lung damage, pancreatic insufficiency, and malnutrition.
Prior to the development of ivacaftor, management of CF primarily involved therapies for the control of infections, nutritional support, clearance of mucus, and management of symptoms rather than improvements in the underlying disease process or lung function (FEV1). Notably, ivacaftor was the first medication approved for the management of the underlying causes of CF (abnormalities in CFTR protein function) rather than control of symptoms.
What are the applications of Application
Ivacaftor is is a CFTR activator
Definition
ChEBI: An aromatic amide obtained by formal condensation of the carboxy group of 4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid with the amino group of 5-amino-2,4-di-tert-butylphenol. Used for the treatment of cystic fibrosis.
brand name
Kalydeco
Pharmacokinetics
The use of Ivacaftor has been shown to both improve CF symptoms and modulate underlying disease pathology. This is achieved by potentiating the channel opening probability (or gating) of CFTR protein in patients with impaired gating mechanisms. This is in contrast to Lumacaftor, another CF medication, that functions by preventing misfolding of the CFTR protein and thereby results in increased processing and trafficking of mature protein to the cell surface.
Results from clinical trials indicated that treatment with ivacaftor results in improved lung function, reduced chance of experiencing a pulmonary exacerbation, reduced sweat chloride, increased weight gain, and improvements in CF symptoms and quality of life. When combined with tezacaftor, significant improvements in lung function have been observed in clinical studies. Ivacaftor was not found to increase the QTc interval in a clinically significant manner.
Although ivacaftor given alone has not shown any significant improvements in patients with the delta-F508 mutation, it has shown significant improvements (>10% increase in FEV1 from baseline) in lung function for the following mutations: E56K, P67L, R74W, D110E, D110H, R117C, R117H, G178R, E193K, L206W, R347H, R352Q, A455E, S549N, S549R, G551D, G551S, D579G, S945L, S977F, F1052V, K1060T, A1067T, G1069R, R1070Q, R1070W, F1074L, D1152H, G1244E, S1251N, S1255P, D1270N, and G1349. This list was expanded by the FDA in May 2017 from 10 to 33 to accommodate more rare mutations.
It is important to note that this drug may cause an increase in liver transaminases (ALT, AST). Ensure to assess liver transaminases before the initiation of treatment, every 3 months during the first year of administration, followed by every year thereafter.
Clinical Use
Vertex’s ivacaftor was granted breakthrough therapy designation by the FDA in January 2012 for cystic fibrosis (CF) patients who bear the G551D mutation in the Cycstic Fibrosis Transmembrane Regulator (CFTR) gene. This CFTR mutation occurs in roughly 4% of the 30,000 people living with CF in the United States. While the compound has been identified as a potentiator in cell-based assays, its mechanism of action is as yet unknown.
Synthesis
Several patents describe a synthesis of ivacaftor, only one demonstrates the synthesis on scale and includes yields, which is depicted in the scheme. Beginning with treatment of commercial di-tert-butylphenol derivative 91 with ethyl chloroformate, the synthesis of carbonate 92 was achieved in quantitative yield. Nitration of 92 provided the desired nitroarene regioisomer 93 in 57% yield which was isolated by recrystallization. Reduction of the newlyinstalled nitro group and subsequent amide bond formation via reaction with commercially available acid chloride 94 produced amide 95 in 53% yield over the two step sequence. Finally, cleavage of the carbonate unmasked the phenol to furnish ivacaftor (XV) in 96% yield.

Metabolism
Ivacaftor is extensively metabolized in humans. In vitro and clinical studies indicate that ivacaftor is primarily metabolized by CYP3A. From this metabolism, the major formed metabolites are M1 and M6. M1 is considered pharmacologically active even though it just presents approximately one-sixth the effect of the parent compound ivacaftor. On the other hand, M6 is not considered pharmacologically active as it represents less than one-fiftieth of the effect of the parent compound.
References
1. van goor f1, hadida s, grootenhuis pd, burton b, cao d, neuberger t, turnbull a, singh a, joubran j, hazlewood a, zhou j, mccartney j,arumugam v, decker c, yang j, young c, olson er, wine jj, frizzell ra, ashlock m, negulescu p. rescue of cf airway epithelial cell function in vitro by a cftr potentiator, vx-770. proc natl acad sci u s a. 2009 nov 3;106(44):18825-30. 2. vachel l1, norez c, becq f, vandebrouck c. effect of vx-770 (ivacaftor) and oag on ca2+ influx and cftr activity in g551d and f508del-cftr expressing cells. j cyst fibros. 2013 dec;12(6):584-91
Properties of Ivacaftor
| Melting point: | 212-215°C |
| Boiling point: | 550.4±50.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.187 |
| storage temp. | Refrigerator |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Ethyl Acetate (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 11.08±0.23(Predicted) |
| color | White to Light Brown |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C24H28N2O3/c1-23(2,3)16-11-17(24(4,5)6)20(27)12-19(16)26-22(29)15-13-25-18-10-8-7-9-14(18)21(15)28/h7-13,27H,1-6H3,(H,25,28)(H,26,29) |
Safety information for Ivacaftor
Computed Descriptors for Ivacaftor
| InChIKey | PURKAOJPTOLRMP-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | N1C2=C(C=CC=C2)C(=O)C(C(NC2=CC(O)=C(C(C)(C)C)C=C2C(C)(C)C)=O)=C1 |
Ivacaftor manufacturer
Vidgas science and technologies Pvt Ltd
SOLFYN INTERNATIONAL LLP
Ralington Pharma
ShreeGen Pharma Ltd (part of Rumit Group of Companies)
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 873054-44-5 Ivacaftor 98%View Details
873054-44-5 Ivacaftor 98%View Details
873054-44-5 -
 Ivacaftor 98%View Details
Ivacaftor 98%View Details
873054-44-5 -
 Ivacaftor 98% CAS 873054-44-5View Details
Ivacaftor 98% CAS 873054-44-5View Details
873054-44-5 -
 Ivacaftor API 99%View Details
Ivacaftor API 99%View Details
873054-44-5 -
 Ivacaftor 873054-44-5 98%View Details
Ivacaftor 873054-44-5 98%View Details
873054-44-5 -
 873054-44-5 Ivacaftor 98%View Details
873054-44-5 Ivacaftor 98%View Details
873054-44-5 -
 Ivacaftor (VX-770) 99% (HPLC) CAS 873054-44-5View Details
Ivacaftor (VX-770) 99% (HPLC) CAS 873054-44-5View Details
873054-44-5 -
 CFTR Potentiator, VX-770 CAS 873054-44-5View Details
CFTR Potentiator, VX-770 CAS 873054-44-5View Details
873054-44-5