Valeronitrile
Synonym(s):Butyl cyanide;Butyl cyanide, Valeronitrile;Pentanenitrile;Pentanonitrile;Valeronitrile
- CAS NO.:110-59-8
- Empirical Formula: C5H9N
- Molecular Weight: 83.13
- MDL number: MFCD00001974
- EINECS: 203-781-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-09-25 17:15:13
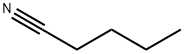
What is Valeronitrile?
Chemical properties
Clear liquid
The Uses of Valeronitrile
Valeronitrile is used in the preparation of valeric acid. It is also used to enhance the nitrilase activity in many strains.
The Uses of Valeronitrile
Valeronitrile is used as building block in organic synthesis. Product Data Sheet
The Uses of Valeronitrile
Solvent.
Production Methods
Valeronitrile can be synthesized by dehydration of valeronamide. The nitrile is also found in nature and is a constituent of coal gasification and oil shale processing waste water, sewage wastewater and tobacco smoke.
Definition
ChEBI: Pentanenitrile is a nitrile.
General Description
Clear colorless to yellow liquid.
Air & Water Reactions
Slightly soluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Nitriles, such as Valeronitrile, may polymerize in the presence of metals and some metal compounds. They are incompatible with acids; mixing nitriles with strong oxidizing acids can lead to extremely violent reactions. Nitriles are generally incompatible with other oxidizing agents such as peroxides and epoxides. The combination of bases and nitriles can produce hydrogen cyanide. Nitriles are hydrolyzed in both aqueous acid and base to give carboxylic acids (or salts of carboxylic acids). These reactions generate heat. Peroxides convert nitriles to amides. Nitriles can react vigorously with reducing agents. Acetonitrile and propionitrile are soluble in water, but nitriles higher than propionitrile have low aqueous solubility. They are also insoluble in aqueous acids. Valeronitrile is incompatible with strong acids, strong bases, strong oxidizing agents and strong reducing agents. .
Health Hazard
Valeronitrile is an irritant and may be harmful by inhalation, ingestion or skin absorption .
Fire Hazard
Valeronitrile is combustible.
Industrial uses
Valeronitrile is used as an industrial solvent and as a chemical intermediate.
Toxicology
Pentanenitrile is toxic to animals, and produces its action by the liberation of cyanide by cytochrome P450. The cyanide is detoxified and excreted in urine as thiocyanate.
Metabolism
As with other aliphatic nitriles, valeronitrile is metabolized in vivo resulting in the liberation of cyanide ion which is responsible for much of the observed toxicity of this compound . Biotransformation of valeronitrile presumably proceeds in a manner similar to that of other aliphatic nitriles with an initial cytochrome P-450 catalyzed oxidation of the nitrile to the cyanohydrin followed by release of the cyanide group from the activated molecule. Cyanide formation was significantly reduced when valeronitrile was incubated with mouse hepatic microsomes in the presence of SKF-525A or carbon monoxide or when microsomes from mice pretreated with chloroform were used . Ethanol pretreatment of mice markedly increases the in vivo and in vitro microsomal oxidation of valeronitrile presumably as a result of increased levels of an ethanol inducible cytochrome P-450 . As with other nitriles, the cyanide released upon biotransformation of valeronitrile is readily converted to thiocyanate in vivo and the latter ion was the major urinary excretion product observed with valero-nitrile in rats . From 18 to 31% of a daily 175 mg/kg dose of valeronitrile was eliminated in the urine as thiocyanate during a 24 h period. In another study , 43.2 and 27.5%, respectively, of an oral or i.p. dose of 0.75 mmol/kg valeronitrile was excreted as thiocyanate in the urine of male Sprague-Dawley rats over a 24 h period.
Purification Methods
Wash the nitrile with half its volume of conc HCl (twice), then with saturated aqueous NaHCO3, dry it with MgSO4 and fractionally distil it from P2O5. [Beilstein 2 H 301, 2 I 131, 2 II 267, 2 III 675, 2 IV 875.]
Structure and conformation
The valeronitrile molecule is flexible and can adopt a number of different conformers, so that it will naturally be a mixture. These conformers are called anti-anti (30%), anti-gauche (46%), gauche-anti, gauche-gauche-cis, and gauche-gauche-trans.
Properties of Valeronitrile
| Melting point: | −96 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 139-141 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 0.795 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor pressure | 7.0 hPa (20 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 105 °F |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | 10.0g/l |
| form | Liquid |
| color | Clear colorless |
| Water Solubility | 0.1-0.5 g/100 mL at 22.5 ºC |
| Merck | 14,9905 |
| BRN | 1736706 |
| Exposure limits | NIOSH: IDLH 25 mg/m3 |
| Dielectric constant | 17.4(21℃) |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong acids, strong bases, strong oxidizing agents, strong reducing agents. Flammable. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 110-59-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Pentanenitrile(110-59-8) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Valeronitrile (110-59-8) |
Safety information for Valeronitrile
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H226:Flammable liquids H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P233:Keep container tightly closed. P240:Ground/bond container and receiving equipment. P241:Use explosion-proof electrical/ventilating/lighting/…/equipment. P242:Use only non-sparking tools. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. |
Computed Descriptors for Valeronitrile
| InChIKey | RFFFKMOABOFIDF-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Valeronitrile manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Valeronitrile 99%View Details
Valeronitrile 99%View Details -
 Valeronitrile 98%View Details
Valeronitrile 98%View Details -
 Valeronitrile CAS 110-59-8View Details
Valeronitrile CAS 110-59-8View Details
110-59-8 -
 Valeronitrile CAS 110-59-8View Details
Valeronitrile CAS 110-59-8View Details
110-59-8 -
 VALERONITRILE For Synthesis CAS 110-59-8View Details
VALERONITRILE For Synthesis CAS 110-59-8View Details
110-59-8 -
 Valeronitrile, For IndustrialView Details
Valeronitrile, For IndustrialView Details
110-59-8 -
 ValeronitrileView Details
ValeronitrileView Details
110-59-8 -
 Valeronitrile Cas 110 59 8View Details
Valeronitrile Cas 110 59 8View Details
110-59-8