Valeric acid
Synonym(s):n-Valeric acid;Pentanoic acid;Valeric acid;Valproic acid impurity A (PhEur)
- CAS NO.:109-52-4
- Empirical Formula: C5H10O2
- Molecular Weight: 102.13
- MDL number: MFCD00004413
- EINECS: 203-677-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:07:02
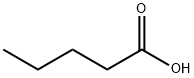
What is Valeric acid?
Description
Valeric acid, or pentanoic acid, is a straight - chain alkyl carboxylic acid with the chemical formula C5H10O2. Like other lowmolecular- weight carboxylic acids, it has a very unpleasant odor. It is found naturally in the perennial flowering plant valerian (Valeriana officinalis), from which it gets its name. Its primary use is in the synthesis of its esters. Volatile esters of valeric acid tend to have pleasant odors and are used in perfumes and cosmetics. Ethyl valerate and pentyl valerate are used as food additives because of their fruity flavors.
Valeric acid appears similar in structure to GHB and the neurotransmitter GABA in that it is a short-chain carboxylic acid, although it lacks the alcohol and amine functional groups that contribute to the biological activities of GHB and GABA, respectively. It differs from valproic acid simply by lacking a 3- carbon side - chain.
Chemical properties
Colorless liquid; penetrating odor and taste. Soluble in water, alcohol and ether. Undergoes reactions typical of normal monobasic organic acids. Combustible.
Chemical properties
Valeric acid has an unpleasant odor and flavor, similar to butyric acid. May consist of one or a mixture of isomers of n-pentanoic acid and/or 2- or 3-methyl-butanoic acid.
Occurrence
The acid is not too common in nature; reported (as the corresponding ester) found in the essential oil of Boronia anemonifolia, in pineapple fruits and in other plants; also identified as acid or the corresponding ester in the essential oil of lemon petitgrain. Also reported found in apple, apple juice, banana, orange juice, bilberry, cranberry, strawberry, raspberry, papaya, grapes, celery, onion, baked potato, tomato, corn mint oil, breads, cheeses, milk, yogurt, butter, cheddar cheese, lean and fatty fish, fish oil, cooked meats, hop oil, beer, rum, whiskies, grape wines, cocoa, tea, roasted filberts, peanuts and pecans, honey, soybeans, coconut meat and milk, cloudberry, passion fruit, starfruit, trassi, mango, jackfruit, licorice, calamus, sake, buckwheat, watercress, laurel, peated malt, wort, kiwifruit, loquat, Bourbon vanilla, shrimps, oyster, scallop, cape gooseberry, sea buckthorn, Chinese quince and maté.
The Uses of Valeric acid
valeric acid is obtained from valerian extract, which is considered skin conditioning.
The Uses of Valeric acid
Sex attractant of the sugar beet wireworm, Limonius californicus.1
The Uses of Valeric acid
Valeric acid, is used as a sex attractant of the sugar beet wireworm, Limonius californicus. It is used predominantly as an intermediate in the manufacture of flavors and perfumes, ester type lubricants, plasticizers and vinyl stabilizesrs. It is a food additive used as a synthetic flavoring substance dan adjuvant. It is an inert ingredient in controlling pest.
Definition
ChEBI: A straight-chain saturated fatty acid containing five carbon atoms.
Preparation
By oxidation of n-amyl alcohol or, together with other isomers, by distillation of valerian roots; also by reacting butyl bromide and sodium cyanide with subsequent saponification of the formed butyl nitrile.
Aroma threshold values
Detection: 940 ppb to 3 ppm
Taste threshold values
Taste characteristics at 100 ppm: acidic, dairy-like with milky and cheese nuances.
Synthesis Reference(s)
Synthetic Communications, 26, p. 165, 1996 DOI: 10.1080/00397919608003877
Tetrahedron Letters, 31, p. 1257, 1990 DOI: 10.1016/S0040-4039(00)88779-1
Tetrahedron, 40, p. 3635, 1984 DOI: 10.1016/S0040-4020(01)88794-9
General Description
A colorless liquid with a penetrating unpleasant odor. Density 0.94 g / cm3. Freezing point -93.2°F (-34°C). Boiling point 365.7°F (185.4°C). Flash point 192°F (88.9°F). Corrosive to metals and tissue.
Air & Water Reactions
Water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
Valeric acid is a carboxylic acid. Exothermically neutralizes bases, both organic and inorganic, producing water and a salt. Can react with active metals to form gaseous hydrogen and a metal salt. Reacts with cyanide salts to generate gaseous hydrogen cyanide. Flammable and/or toxic gases and heat are generated by reaction with diazo compounds, dithiocarbamates, isocyanates, mercaptans, nitrides, and sulfides. Reacts with sulfites, nitrites, thiosulfates and dithionites to generate flammable and/or toxic gases and heat. Reacts with carbonates and bicarbonates to generate a harmless gas (carbon dioxide) but still heat. Can be oxidized by strong oxidizing agents and reduced by strong reducing agents. These reactions generate heat. May initiate polymerization reactions. May catalyze (increase the rate of) chemical reactions.
Health Hazard
Corrosive. Very destructive to tissues of the mucous membranes, upper respiratory tract, eyes, and skin. Symptoms may include burning sensation, coughing, wheezing, laryngitis, shortness of breath, nausea and vomiting. Extremely destructive to skin. May be absorbed through the skin.
Fire Hazard
Special Hazards of Combustion Products: Irritating vapors and toxic gases, such as carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide, may be formed when involved in fire.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by ingestion, intravenous, and subcutaneous routes. Mildly toxic by inhalation. A corrosive irritant to skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. Combustible liquid. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes. Used in perfumes.
Purification Methods
Water is removed from the acid by distillation using a Vigreux column (p 11), until the boiling point reaches 183o. A few crystals of KMnO4 are added, and after refluxing, the distillation is continued. [Andrews & Keefer J Am Chem Soc 83 3708 1961, Beilstein 2 H 299, 2 I 130, 2 II 263, 2 III 663, 2 IV 868.]
Properties of Valeric acid
| Melting point: | −20-−18 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 110-111 °C10 mm Hg(lit.) |
| Density | 0.939 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor density | 3.5 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 0.15 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
| FEMA | 3101 | VALERIC ACID |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 192 °F |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | 40g/l |
| form | Liquid |
| pka | 4.84(at 25℃) |
| color | Clear colorless to pale yellow |
| PH | 3.95(1 mM solution);3.43(10 mM solution);2.92(100 mM solution); |
| Odor | at 1.00 % in propylene glycol. sickening putrid acidic sweaty rancid |
| Odor Threshold | 0.000037ppm |
| explosive limit | 1.8-7.3%(V) |
| Water Solubility | 40 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,9904 |
| JECFA Number | 90 |
| BRN | 969454 |
| Dielectric constant | 2.7(20℃) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 109-52-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Pentanoic acid(109-52-4) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Valeric acid (109-52-4) |
Safety information for Valeric acid
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H314:Skin corrosion/irritation H412:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P330+P331:IF SWALLOWED: Rinse mouth. Do NOT induce vomiting. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Valeric acid
Valeric acid manufacturer
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Pentanoic acid CAS 109-52-4View Details
Pentanoic acid CAS 109-52-4View Details
109-52-4 -
 Valeric acid CAS 109-52-4View Details
Valeric acid CAS 109-52-4View Details
109-52-4 -
 N Valeric Acid CASView Details
N Valeric Acid CASView Details -
 Pentanoic acid 99% CAS 109-52-4View Details
Pentanoic acid 99% CAS 109-52-4View Details
109-52-4 -
 Valeric acid CAS 109-52-4View Details
Valeric acid CAS 109-52-4View Details
109-52-4 -
 Valeric Acid CAS 109-52-4View Details
Valeric Acid CAS 109-52-4View Details
109-52-4 -
 Valeric acid 98% (GC) CAS 109-52-4View Details
Valeric acid 98% (GC) CAS 109-52-4View Details
109-52-4 -
 Valeric acid 95.00% CAS 109-52-4View Details
Valeric acid 95.00% CAS 109-52-4View Details
109-52-4