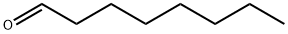
Valeraldehyde
Synonym(s):Pentanal;Valeraldehyde, Amylaldehyde
- CAS NO.:110-62-3
- Empirical Formula: C5H10O
- Molecular Weight: 86.13
- MDL number: MFCD00007026
- EINECS: 203-784-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
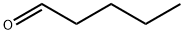
What is Valeraldehyde?
Description
Valeraldehyde is one of the key volatile flavor compounds identified in cooked rice, beef fish meat and uncured ham. Its smell is described as fermented, bready, fruity, nutty, berry.It is an alkyl aldehyde used in flavoring Compounds, resin chemistry, rubber accelerators.
Chemical properties
Valeraldehyde is a colorless flammable liquid with a strong acrid, pungent odor. At low levels, the taste is warm, slightly fruity and nut-like.The odor threshold is 0.028 ppm. Slightly soluble in water; soluble in alcohol and ether.
Occurrence
Valeraldehyde is naturally occurring (e.g., plant volatile). Reported found among the constituents of several essential oils: Brazilian sassafras, Bulgarian rose, Bulgarian clary sage and others. Also in the distillates from leaves of various Eucalyptus species: E. cinereea, E. globulus, E. dives, E. maideni and E. hemilampra. Also reported found in fresh apple, banana, sweet cherry, black currant berries, fresh blackberry, Bantu beer, plum brandy, cardamom, coriander leaf, unprocessed rice, Bourbon vanilla, cooked shrimp, scallop, hog plum and clary sage.
The Uses of Valeraldehyde
Valeraldehyde is mainly used for hydrogenation to Isoamyl alcohol and oxidation to valeric acid. It can also be used as a raw material for fragrances, resin chemistry, and rubber accelerators.
What are the applications of Application
Valeraldehyde is Used in flavorings, resin chemistry, and rubber accelerators
Definition
ChEBI: Valeraldehyde is a saturated fatty aldehyde composed from five carbons in a straight chain. It has a role as a plant metabolite.
Preparation
Valeraldehyde can be prepared by oxidation of the corresponding alcohol, 1-pentanol or by reduction of n-valeric acid (Opdyke, 1979; Lewis, 1993). Valeraldehyde is one of a number of aliphatic aldehydes industrially prepared by the oxo process, which involves the reaction of olefins with carbon monoxide and hydrogen in the presence of a catalyst. Use of a cobalt carbonyl complex as catalyst required high pressure in an older process, which has been largely replaced by a low-pressure process based on rhodium complex catalysts, such as a tris (alkyldiarylphosphine) rhodium carbonyl hydride.
What are the applications of Application
Valeraldehyde is used as a gaseous standard in the study of the sorptive loss pattern for volatile compounds.
Valeraldehyde has been used to study its time-weighted average sampling using solid-phase microextraction (SPME) device.
Valeraldehyde is used in flavoring compounds and as a rubber accelerator.
Valeraldehyde is also used extensively as a natural and synthetic flavoring agent. It is used as a top note for flavor to give identity (fruity, nutty) on first impression and is a component of rose oil used to flavor foods, beverages and chewing tobacco (Furia, 1972; Rogers, 1981; NLM, 1996).
Valeraldehyde is mainly used as a chemical intermediate. As a starting material in industrial organic synthesis, it is hydrogenated to 1-pentanol, oxidized to valeric acid, and aminated to 1-aminopentane (Falbe et al., 1985; NLM, 1996).
Aroma threshold values
Detection: 12 to 100 ppb
Taste threshold values
Taste characteristics at 25 ppm: winey, fermented, bready and cocoa chocolate notes.
General Description
A colorless liquid. Slightly soluble in water and less dense than water. Flash point 54°F. Vapors heavier than air. Used to make artificial flavorings and rubber.
Air & Water Reactions
Highly flammable. Slightly soluble in water. Valeraldehyde may be sensitive to prolonged exposure to air.
Reactivity Profile
Valeraldehyde is an aldehyde. Aldehydes are frequently involved in self-condensation or polymerization reactions. These reactions are exothermic; they are often catalyzed by acid. Aldehydes are readily oxidized to give carboxylic acids. Flammable and/or toxic gases are generated by the combination of aldehydes with azo, diazo compounds, dithiocarbamates, nitrides, and strong reducing agents. Aldehydes can react with air to give first peroxo acids, and ultimately carboxylic acids. These autoxidation reactions are activated by light, catalyzed by salts of transition metals, and are autocatalytic (catalyzed by the products of the reaction). The addition of stabilizers (antioxidants) to shipments of aldehydes retards autoxidation. Valeraldehyde is incompatible with oxidizing agents, strong bases and strong reducing agents.
Health Hazard
n-Valeraldehyde is a moderate skin andeye irritant. At a high concentration theirritation may be severe; 100 mg/day wasseverely irritating on rabbits’ eyes. Pure liquidcaused severe irritation to guinea pigskin. The systemic toxicity of valeraldehydeis very low.
LD50 value, skin (rabbits): 4857 mg/kg
LD50 value, oral (rats): 3200 mg/kg
Inhalation toxicity is very low. Exposure to4000 ppm for air was lethal to rats.
Fire Hazard
HIGHLY FLAMMABLE: Will be easily ignited by heat, sparks or flames. Vapors may form explosive mixtures with air. Vapors may travel to source of ignition and flash back. Most vapors are heavier than air. They will spread along ground and collect in low or confined areas (sewers, basements, tanks). Vapor explosion hazard indoors, outdoors or in sewers. Runoff to sewer may create fire or explosion hazard. Containers may explode when heated. Many liquids are lighter than water.
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by ingestion. Mddly toxic by inhalation and s h contact. A severe eye and skin irritant. A very dangerous fire hazard when exposed to heat or flame. %%en heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes. See also ALDEHYDES.
Potential Exposure
Valeraldehyde is used in food flavorings; in resin chemistry. It is also used in the acceleration of rubber vulcanization.
Carcinogenicity
n-Valeraldehyde caused chromosomal and DNA effects in mammalian cells in culture but was not mutagenic in an Ames bacterial test.
Shipping
UN2058 Valeraldehyde, Hazard Class: 3; Labels: 3-Flammable liquid.
Purification Methods
Purify pentanal via the bisulfite derivative (see 2-butanone above for the preparation and decomposition of the bisulfite derivative). [Birrell & Trotman-Dickinson J Chem Soc 2059 1960, Beilstein 1 H 676, 1 IV 3268.] The 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazone [2057-84-3] M 266.3 has m 103-105o (from EtOH). [Beilstein 15 III/IV 429.]
Incompatibilities
Vapor may form explosive mixture with air. Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides, caustics, amines.
Waste Disposal
Dissolve or mix the material with a combustible solvent and burn in a chemical incinerator equipped with an afterburner and scrubber. All federal, state, and local environmental regulations must be observed.
Properties of Valeraldehyde
| Melting point: | -92 °C |
| Boiling point: | 103 °C |
| Density | 0.81 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor pressure | 36 hPa (20 °C) |
| FEMA | 3098 | VALERALDEHYDE |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 54 °F |
| storage temp. | Store at +2°C to +8°C. |
| solubility | soluble in ethyl alcohol, ethyl ether, and other common organic solvents. |
| form | neat |
| color | Colorless to Light yellow |
| Odor | at 1.00 % in dipropylene glycol. fermented bready fruity nutty berry |
| Odor Threshold | 0.00041ppm |
| explosive limit | 1.7-6.8%(V) |
| Water Solubility | 14 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Sensitive | Air Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,9902 |
| JECFA Number | 89 |
| BRN | 1616304 |
| Exposure limits | TLV-TWA 175 mg/m3 (50 ppm) (ACGIH
and OSHA). |
| Dielectric constant | 13.9(Ambient) |
| Stability: | Stable. Highly flammable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, acids, strong alkalies, strong reducing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 110-62-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Pentanal(110-62-3) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Pentanal (110-62-3) |
Safety information for Valeraldehyde
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H225:Flammable liquids H317:Sensitisation, Skin H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H332:Acute toxicity,inhalation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P233:Keep container tightly closed. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Valeraldehyde
New Products
Tetrabutylammonium iodide (3,3-DIFLUOROCYCLOBUTYL)METHANOL 4,4-DIFLUOROCYCLOHEXANAMINE Cyclobutylamine (S)-3-Fluoro-pyrrolidine hydrochloride 3-Oxocyclobutanecarboxylic acid N-Hydroxy-2-methylpropanimidamide L-tert-Leucine,97% 2-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 97% Aluminum oxide, basic Calcium hydroxide, 95% Diallylamine, 99% 2-Iodobenzoic Acid 3-Methoxybenzonitrile Pentachlorobenzonitrile Chloral Dibenzoyl Peroxide Titanium Dioxide O-Benzylhydroxylamine Hydrochloride 2-Nitrobenzaldehyde 2-Picolylamine (2-Aminomethylpyridine) 2-Venylpyridine Ethyl-2-Chloroacetoacetate 4-Dimethylamine PyridineRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Valeraldehyde 95% CAS 110-62-3View Details
Valeraldehyde 95% CAS 110-62-3View Details
110-62-3 -
 Valeraldehyde pure (Pentanal) CAS 110-62-3View Details
Valeraldehyde pure (Pentanal) CAS 110-62-3View Details
110-62-3 -
 n-Valeraldehyde CAS 110-62-3View Details
n-Valeraldehyde CAS 110-62-3View Details
110-62-3 -
 Valeraldehyde CAS 110-62-3View Details
Valeraldehyde CAS 110-62-3View Details
110-62-3 -
 Valeraldehyde CAS 110-62-3View Details
Valeraldehyde CAS 110-62-3View Details
110-62-3 -
 Valeraldehyde 110-62-3 98%View Details
Valeraldehyde 110-62-3 98%View Details
110-62-3 -
 TETRABUTYLAMMONIUM CYANIDE 10442-39-4 98+View Details
TETRABUTYLAMMONIUM CYANIDE 10442-39-4 98+View Details
10442-39-4 -
 19752-84-2 TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 98+View Details
19752-84-2 TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 98+View Details
19752-84-2