Pazopanib Hydrochloride
Synonym(s):5-[[4-[(2,3-Dimethyl-2H-indazol-6-yl)(methyl)amino]pyrimidin-2-yl]amino]-2-methylbenzenesulfonamide hydrochloride;5-[[4-[(2,3-Dimethyl-2H-indazol-6-yl)methylamino]-2-pyrimidinyl]amino]-2-methylbenzenesulfonamide, hydrochloride;
- CAS NO.:635702-64-6
- Empirical Formula: C21H24ClN7O2S
- Molecular Weight: 473.98
- MDL number: MFCD12546138
- EINECS: 619-728-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-03-21 11:08:55
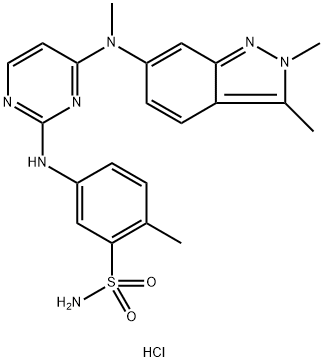
What is Pazopanib Hydrochloride?
Description
The growth of solid tumors is dependent on angiogenesis, the process
wherein new capillaries are formed from existing blood vessels. VEGF is
one of the most important inducers of angiogenesis and expressed at high
levels by most tumors. Hence, the inhibition of VEGF or its receptor
signaling system is an attractive target for cancer therapeutics. The most
studied and developed inhibitors are monoclonal antibodies that neutralize VEGF (e.g., bevacizumab), anti-VEGF ribozymes (e.g., angiozyme),
and small-molecule VEGFR kinase inhibitors (e.g., sunitinib, sorafenib).
Pazopanib is the latest VEGFR kinase inhibitor to reach the market. It is
indicated for the oral treatment of advanced RCC. The biological functions of the VEGF family are mediated by activation of three structurally
homologous tyrosine kinase receptors, VEGFR-1, VEGFR-2, and VEGFR3. In vitro, pazopanib inhibits VEGFR-1, VEGFR-2, and VEGFR-3 with
IC50 values of 10, 30, and 47 nM, respectively.
In addition, it inhibits
several of the closely related tyrosine receptor kinases, including platelet-derived growth-factor receptor β(PDGFR-β), c-kit, and fibroblast
growth factor receptor-1 (FGFR1) with IC50 values of 84, 74, and
140 nM, respectively. In human umbilical vein endothelial cells
(HUVEC), pazopanib inhibits VEGF-induced proliferation more potently
than basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF)-stimulated proliferation
(IC50 = 21 nM vs. 721 nM) and concentration-dependently inhibits
VEGF-induced VEGFR-2 phosphorylation (IC50 = 7 nM). It also potently
inhibits angiogenesis in Matrigel plug and corneal micropocket assays.
The most common adverse events associated with pazopanib
were diarrhea, hypertension, hair depigmentation, nausea, anorexia,
and vomiting.
Description
Pazopanib Hydrochloride is the hydrochloride salt of a small molecule inhibitor of multiple protein tyrosine kinases with potential antineoplastic activity. It is an oral second-generation multitarget TKI developed by GSK and approved for marketing by the FDA in 2009 and the EMA in 2010. It targets the VEGFR, platelet-derived growth factor receptor, and c-kit, key proteins responsible for tumor growth and survival. It is used to treat patients with advanced RCC and advanced soft tissue sarcoma who have experienced chemotherapy. Pazopanib Hydrochloride has a role as an antineoplastic agent, a vascular endothelial growth factor receptor antagonist, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor, and an angiogenesis-modulating agent.
Originator
GlaxoSmithKline (US)
The Uses of Pazopanib Hydrochloride
Pazopanib Hydrochloride (GW786034, Votrient, Armala) is a novel multi-target inhibitor of VEGFR1, VEGFR2, VEGFR3, PDGFR, FGFR, c-Kit and c-Fms with IC50 of 10 nM, 30 nM, 47 nM, 84 nM, 74 nM, 140 nM and 146 nM, respectively.
The Uses of Pazopanib Hydrochloride
Pazopanib (GW786034) is a novel multi-target inhibitor of VEGFR1, VEGFR2, VEGFR3, PDGFR, FGFR, c-Kit and c-Fms with IC50 of 10 nM, 30 nM, 47 nM, 84 nM, 74 nM, 140 nM and 146 nM, respectively - See more at: http://www.selleckchem.com/products/Pazopanib-Hyd
The Uses of Pazopanib Hydrochloride
The Hydrochloride salt of Pazopanib (P210925) a oral angiogenesis inhibitor targeting VEGFR and PDGFR.
What are the applications of Application
Pazopanib Hydrochloride is a multi-targeted inhibitor
Definition
ChEBI: A hydrochloride salt prepared from equimolar amounts of pazopanib and hydrochloric acid. Used for treatment of kidney cancer.
Definition
The growth of solid tumors is dependent on angiogenesis, the process wherein new capillaries are formed from existing blood vessels. VEGF is one of the most important inducers of angiogenesis and expressed at high levels by most tumors. Hence, the inhibition of VEGF or its receptor signaling system is an attractive target for cancer therapeutics. The most studied and developed inhibitors are monoclonal antibodies that neutralize VEGF (e.g., bevacizumab), anti-VEGF ribozymes (e.g., angiozyme), and small-molecule VEGFR kinase inhibitors (e.g., sunitinib, sorafenib). Pazopanib is the latest VEGFR kinase inhibitor to reach the market. It is indicated for the oral treatment of advanced RCC. The biological functions of the VEGF family are mediated by activation of three structurally homologous tyrosine kinase receptors, VEGFR-1, VEGFR-2, and VEGFR3. In vitro, pazopanib inhibits VEGFR-1, VEGFR-2, and VEGFR-3 with IC50 values of 10, 30, and 47 nM, respectively. In addition, it inhibits several of the closely related tyrosine receptor kinases, including platelet-derived growth-factor receptor β(PDGFR-β), c-kit, and fibroblast growth factor receptor-1 (FGFR1) with IC50 values of 84, 74, and 140 nM, respectively. In human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC), pazopanib inhibits VEGF-induced proliferation more potently than basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF)-stimulated proliferation (IC50 = 21 nM vs. 721 nM) and concentration-dependently inhibits VEGF-induced VEGFR-2 phosphorylation (IC50 = 7 nM). It also potently inhibits angiogenesis in Matrigel plug and corneal micropocket assays. The most common adverse events associated with pazopanib were diarrhea, hypertension, hair depigmentation, nausea, anorexia, and vomiting.
brand name
Votrient
Clinical Use
Pazopanib is a potent and selective multi-targeted receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor of VEGFR-1, VEGFR-2, VEGFR-3, PDGFR-a/b, and c-kit that blocks tumor growth and inhibits angiogenesis. It was approved for renal cell carcinoma by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 2009 and is marketed under the trade name Votrient by the drug’s manufacturer, GlaxoSmithKline.
Side Effects
Pazopanib is synthesized in five chemical steps starting from 3-methyl-6-nitroindazole, which is converted to the corresponding 2,3-dimethylindazole analog via N-methylation with trimethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate. Subsequent reduction of the nitro group to the amino group using tin chloride followed by condensation with 2,4dichloropyrimidine yields a chloropyrimidinylaminoindazole intermediate. The final two steps leading up to pazopanib consist of an N-methylation reaction using iodomethane and cesium carbonate followed by condensation with 5-amino-2-methylbenzenesulfonamide.
Synthesis
The synthesis of pazopanib begins with methylation of 3-methyl-6- nitroindazole (82) with trimethyl orthoformate in the presence of BF3?¤OEt to give indazole 83 in 65% yield. Reduction of the nitro group was achieved via transfer hydrogenation to give 84 in 97% yield, and this was followed by coupling the aniline with 2,4-dichloropyrimidine in a THF-ethanol mixture at elevated temperature to provide diarylamine 85 in 90% yield. The aniline nitrogen was then methylated using methyl iodide to give 86 in 83% yield prior to coupling with 5-amino-2-methylbenzenesulfonamide (87) and salt formation using an alcoholic solution of HCl to furnish pazopanib hydrochloride (XIV) in 81% yield.

References
[1] Sodeifian, G. et al. “Solubility of pazopanib hydrochloride (PZH, anticancer drug) in supercritical CO2: Experimental and thermodynamic modeling.” The Journal of Supercritical Fluids 55 1 (2022): 0.
[2] “Stability Indicating HPTLC Method Development and Validation for the Estimation of Pazopanib Hydrochloride in Bulk and its Dosage Form.” International Journal of Pharmaceutical Research 18 1 (2020).
[3] K. Kawasaki . “Retrospective Safety Analysis in Advanced Soft Tissue Sarcoma Patients of Pazopanib Hydrochloride.” Annals of Oncology 24 (2013): Page ix38.
[4] Gupta, Amit and Rashmi Dahima. “Application of Simplex Lattice Mixture design and desirability function in the development and Optimization of SEDDS for protein kinase inhibitor-Pazopanib Hydrochloride.” Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology 83 1 (2023): 0.
Properties of Pazopanib Hydrochloride
| Melting point: | >290°C (dec.) |
| storage temp. | Hygroscopic, Refrigerator, under inert atmosphere |
| solubility | Acetonitrile (Slightly), DMSO (Slightly) |
| form | Yellow powder. |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
Safety information for Pazopanib Hydrochloride
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H332:Acute toxicity,inhalation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Pazopanib Hydrochloride
New Products
Methyl (R)-1-Boc-4,4-difluoropyrrolidine-2-carboxylate 2,2-Difluoropropylamine hydrochloride tert-butyl 3-bromoazetidine-1-carboxylate (R)-1-Boc-3-hydroxypyrrolidine DIFLUOROACETIC ANHYDRIDE 2,2-Difluoropropionic acid Diallylamine, 99% Calcium hydroxide, 95% Aluminum oxide, basic 2-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 97% L-tert-Leucine,97% N-Hydroxy-2-methylpropanimidamide 4-(3,4-Dichlorophenyl)-3,4-Dihydro-N-Methyl-1-(2H)-Naphthalenimine (Schiff Base) 2-AMINO-3,5-DIBROMO BENZALDEHYDE [ADBA] L-Glutamic Acid Dimethyl Ester Hcl 10-Methoxy-5H-dibenz[b,f]azepine 5-Cyanophthalide N, N-Carbonyldiimidazole (CDI) Dibenzoyl Peroxide Titanium Dioxide 2-(Methylthio) Benzonitrile Sodium Acetate Anhydrous Allopurinol 1,5-DibromopentaneRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

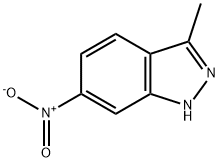

You may like
-
 Pazopanib HCL 97%View Details
Pazopanib HCL 97%View Details -
 Pazopanib Hydrochloride 99%View Details
Pazopanib Hydrochloride 99%View Details -
 Pazopanib hydrochloride 99%View Details
Pazopanib hydrochloride 99%View Details
635702-64-6 -
 Pazopanib hydrochloride 635702-64-6 99%View Details
Pazopanib hydrochloride 635702-64-6 99%View Details
635702-64-6 -
 Pazopanib hydrochloride 635702-64-6 98%View Details
Pazopanib hydrochloride 635702-64-6 98%View Details
635702-64-6 -
 635702-64-6 Pazopanib hydrochloride 98%View Details
635702-64-6 Pazopanib hydrochloride 98%View Details
635702-64-6 -
 Pazopanib hydrochloride 98% CAS 635702-64-6View Details
Pazopanib hydrochloride 98% CAS 635702-64-6View Details
635702-64-6 -
 Pazopanib hydrochloride 98% (HPLC) CAS 635702-64-6View Details
Pazopanib hydrochloride 98% (HPLC) CAS 635702-64-6View Details
635702-64-6
