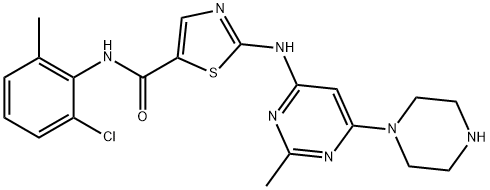
Dasatinib
Synonym(s):BMS 354825;BMS354825;BMS-354825;N-(2-Chloro-6-methylphenyl)-2-[[6-[4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazinyl]-2-methyl-4-pyrimidinyl]amino]-5-thiazolecarboxamide
- CAS NO.:302962-49-8
- Empirical Formula: C22H26ClN7O2S
- Molecular Weight: 488.01
- MDL number: MFCD11046566
- EINECS: 801-607-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-26 16:58:18
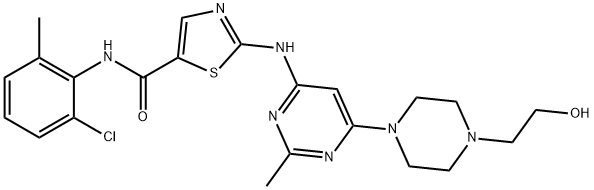
What is Dasatinib?
Absorption
Dasatinib has a dose-proportional pharmacokinetic profile and a linear elimination between 15 mg/day (0.15 times the lowest approved recommended dose) and 240 mg/day (1.7 times the highest approved recommended dose). At 100 mg once a day, dasatinib has a Cmax and AUC of 82.2 ng/mL and 397 ng/mL*hr, respectively. In healthy adult subjects given dasatinib as dispersed tablets in juice, the adjusted geometric mean ratio compared to intact tablets was 0.97 for Cmax, and 0.84 for AUC. The Tmax of dasatinib is between 0.5 and 6 hours following oral administration. Following a single dose of 100 mg, a high-fat meal increases the AUC of dasatinib by 14%.
Toxicity
Overdose cases with dasatinib occurred in isolated cases during clinical studies. Patients that received 280 mg of dasatinib per day for 1 week developed severe myelosuppression and bleeding. Since dasatinib is associated with severe myelosuppression, patients that ingest more than the recommended dosage should be monitored closely for myelosuppression and receive appropriate supportive treatment.
Acute overdose in animals was associated with cardiotoxicity. In rodents, ventricular necrosis and valvular/ventricular/atrial hemorrhage were detected at single doses higher than or equal to 100 mg/kg (600 mg/m2). In monkeys receiving single doses higher than or equal to 10 mg/kg (120 mg/m2), there was a tendency for increased systolic and diastolic blood pressure. In rats, the oral LD50 of dasatinib is 50-100 mg/kg, and in monkeys, it is 25-45 mg/kg.
Description
Dasatinib, developed and marketed by Bristol Myers, is the first approved oral tyrosine kinase inhibitor which binds to multiple conformations of ABL kinase for the treatment of two leukemia indications: chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) and Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia (Ph+ ALL). Dasatinib is a highly potent, ATPcompetitive ATPcompetitive kinase inhibitor which, at nanomolar concentrations, inhibits BCR-ABL, SRC family, c-KIT, EPHA2 and PDGFR-B.
Chemical properties
Pale-Yellow Solid
Class: non-receptor tyrosine kinase
Treatment: CML, ALL
Oral bioavailability = 14–34%
Elimination half-life = 3–5 h
Protein binding = 96%
Originator
Bristol–Myers Squibb (US)
The Uses of Dasatinib
Dasatinib is a novel, potent and multi-targeted inhibitor that targets Abl, Src and c-Kit, with IC50 of <1 nM, 0.8 nM and 79 nM, respectively.
Background
Dasatinib is an orally available multikinase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of Philadelphia chromosome (Ph)-positive leukemias. Ph is a chromosomal abnormality found in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) and acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL), where the ABL tyrosine kinase and the breakpoint cluster region (BCR) gene transcribe the chimeric protein BCR-ABL. BCR-ABL is associated with the uncontrolled activity of the ABL tyrosine kinase and is involved in the pathogenesis of CML and 15-30% of ALL cases. Dasatinib also inhibits a spectrum of kinases involved in cancer, including several SRC-family kinases.
Unlike imatinib, another tyrosine kinase used for the treatment of CML and Ph-positive ALL, dasatinib inhibits the active and inactive conformations of the ABL kinase domain. Also, mutations in the kinase domain of BCR-ABL may lead to relapse during imatinib treatment. Since dasatinib does not interact with some of the residues involved in those mutations, the use of this drug represents a therapeutic alternative for patients with cancers that have developed imatinib-resistance. The use of dasatinib was first approved by the FDA in 2006.
Indications
Dasatinib is indicated for the treatment of newly diagnosed adults with Philadelphia chromosome-positive (Ph+) chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) in chronic phase, as well as adults with chronic, accelerated, or myeloid or lymphoid blast phase Ph+ CML with resistance or intolerance to prior therapy including imatinib, and adults with Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia (Ph+ ALL) with resistance or intolerance to prior therapy. Dasatinib is also indicated for the treatment of pediatric patients 1 year of age and older with Ph+ CML in chronic phase or newly diagnosed Ph+ ALL in combination with chemotherapy.
What are the applications of Application
Dasatinib is potent inhibitor, effective at sub-nanomolar concentrations, of the non-receptor tyrosine kinases Abl and Src as well as other members of the Src family.
Definition
ChEBI: Dasatinib (anhydrous) is an aminopyrimidine that is 2-methylpyrimidine which is substituted at position 4 by the primary amino group of 2-amino-1,3-thiazole-5-carboxylic acid and at position 6 by a 4-(2-hydroxyethyl)piperazin-1-yl group, and in which the carboxylic acid group has been formally condensed with 2-chloro-6-methylaniline to afford the corresponding amide. A multi-targeted kinase inhibitor, it is used, particularly as the monohydrate, for the treatment of chronic, accelerated, or myeloid or lymphoid blast phase chronic myeloid leukemia. Note that the name 'dasatinib' is used to refer to the monohydrate (USAN) as well as to anhydrous dasatinib (INN). It has a role as a tyrosine kinase inhibitor, an anticoronaviral agent and an antineoplastic agent. It is a secondary amino compound, a tertiary amino compound, an organochlorine compound, an aminopyrimidine, a member of 1,3-thiazoles, a monocarboxylic acid amide, a N-arylpiperazine and a N-(2-hydroxyethyl)piperazine. It is a conjugate base of a dasatinib(1+).
brand name
Sprycel (Bristol-Myers Squibb).
General Description
Dasatinib is available in 20-, 50-, and 70-mg tablets fororal administration in the treatment of CML and ALL thatare Ph1 positive. Although dasatinib is more potent thanimatinib, bioavailability is much lower with values rangingbetween 14% to 34%. The agent is extensively metabolizedwith as many as 29 metabolites seen as result of oxidationby primarily CYP3A4 and phase II conjugation.The agent may act as an inhibitor of CYP3A4 andCYP2C8. Metabolism does give an active metabolite, but this accounts for only 5% of the total and is not believed tobe important for the overall activity of the agent. Dasatinibis 95% protein bound with a terminal half-life of 3 to5 hours. The majority of the drug and metabolites are eliminatedin the feces. The most common side effects are skinrash, nausea, diarrhea, and fatigue. Serious side effects includemyelosuppression appearing as neutropenia andthrombocytopenia, bleeding of the brain and GI tract, andfluid retention.
Synthesis
A concise and efficient route was developed for the synthesis of dasatinib. Reaction of 2-chlorothioa-zole (18) with n-butyllithium at low temperature followed by addition of 2-chloro-6-methylphenyl isocyanate (19) gave anilide 20 in 86% yield. The amide 20 was protected as corresponding 4-methoxy benzyl (PMB) anilide 22 in 95% yield which was subsequently reacted with 4- amino-6-chloro-2-methylpyrimidine (23) in the presence of sodium hydride in hot THF to give compound 24 in 83% yield. The PMB protecting group was then removed with triflic acid to give compound 25 in 99% yield. Compound 25 was reacted with 1-(2-hydroxyethyl)piperazine (26) in refluxing dioxane to give dasatinib (III) in 91% yield.

Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Antacids: absorption possibly reduced by antacids,
give at least 2 hours apart.
Antibacterials: metabolism accelerated by rifampicin
- avoid.
Antipsychotics: avoid with clozapine, increased risk
of agranulocytosis.
Antivirals: avoid with boceprevir.
Ulcer healing drugs: avoid with histamine H2
antagonists; concentration reduced by proton pump
inhibitors.
Mechanism of action
Dasatinib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor with several targets. At nanomolar concentrations, it inhibits BCR-ABL, SRC family (SRC, LCK, YES, FYN), c-KIT, EPHA2, and PDGFRβ. In patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), the tyrosine kinase activity of BCR-ABL is deregulated, leading to the growth, proliferation and survival of cancerous hematopoietic cells. Dasatinib binds to the active and inactive conformation of the ABL kinase domain with a higher affinity than imatinib. In chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) and acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) cell lines overexpressing BCR-ABL, dasatinib inhibits cell growth. Also, dasatinib has in vitro activity against leukemic cell lines that are either sensitive or resistant to imatinib. It has been suggested that dasatinib is able to overcome imatinib resistance caused by BCR-ABL kinase domain mutations because it does not require interaction with some of the residues involved in those mutations.
Metabolism
In humans, dasatinib is mainly metabolized by CYP3A4, although flavin-containing monooxygenase 3 (FMO3) and uridine diphosphate-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) enzymes are also involved in the formation of dasatinib metabolites. Five pharmacologically active dasatinib metabolites have been identified: M4, M5, M6, M20 and M24. M4, M20, and M24 are mainly generated by CYP3A4, M5 is generated by FMO3, and M6 is generated by a cytosolic oxidoreductase. M4 is equipotent to dasatinib and represents approximately 5% of the AUC. However, it is unlikely to play a major role in the observed pharmacology of dasatinib. M5 and M6 are more than 10 times less active than dasatinib and are considered minor circulating metabolites.
Metabolism
Dasatinib is extensively metabolised, mainly via the
cytochrome P450 isoenzyme CYP3A4, forming an active
metabolite.
Elimination is predominantly in the faeces, mostly as
metabolites. Following a single oral dose of [14C]-labelled
dasatinib, approximately 89% of the dose was eliminated
within 10 days, with 4% and 85% of the radioactivity
recovered in the urine and faeces, respectively. Unchanged
dasatinib accounted for 0.1% and 19% of the dose in
urine and faeces, respectively, with the remainder of the
dose as metabolites.
Side Effects
Dasatinib is an orally available small-molecule multikinase inhibitor. During clinical trials, less than 1% of patients treated with dasatinib had QTc prolongation as an adverse reaction, and 1% experienced a QTcF higher than 500 ms. The use of dasatinib is also associated with myelosuppression, bleeding-related events, fluid retention, cardiovascular toxicity, pulmonary arterial hypertension, severe dermatologic reactions, tumour lysis syndrome and hepatotoxicity. It may also cause embryo-fetal toxicity and lead to adverse reactions associated with bone growth and development in pediatric patients.
Storage
Store at -20°C
References
1) Lombardo et al. (2004), Discovery of N-2-chloro-6-methyl-phenyl)-2-(6-(4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-piperazin-1-yl)-2-methylpyrimidin-4-ylamino)thiazole-5-carboxamide (BMS-354825), a duel Src/Abl kinase inhibitor with potent antitumor activity in preclinical assays; J. Med. Chem., 47 6658 2) Nam et al. (2005), Action of the Src family kinase inhibitor dasatinib (BMS-354825), on human prostate cancer cells; Cancer Res., 65 9185 3) Johnson et al. (2005), Dasatinib (BMS-354825) tyrosine kinase inhibitor suppresses invasion and induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and non-small cell lung cancer cells; Clin. Cancer Res., 11 6924
Properties of Dasatinib
| Melting point: | 275-286°C |
| Density | 1.408±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Store in freezer, under -20°C |
| solubility | Soluble in DMSO (up to 200 mg/ml). |
| form | White powder. |
| pka | 10.94±0.70(Predicted) |
| color | White or off-white |
| Stability: | Stable for 1 year from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions in DMSO may be stored at -20° for up to 2 months. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 302962-49-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Dasatinib
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H351:Carcinogenicity H372:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Dasatinib
Dasatinib manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 Dasatinib 99%View Details
Dasatinib 99%View Details -
 Dasatinib 99%View Details
Dasatinib 99%View Details -
 Dasatinib 98% (HPLC) CAS 302962-49-8View Details
Dasatinib 98% (HPLC) CAS 302962-49-8View Details
302962-49-8 -
 Dasatinib IHSView Details
Dasatinib IHSView Details
302962-49-8 -
 Dasakast 70 DASATINIB, Prescription, Treatment: Blood CancerView Details
Dasakast 70 DASATINIB, Prescription, Treatment: Blood CancerView Details
302962-49-8 -
 Dasatinib - API, PrescriptionView Details
Dasatinib - API, PrescriptionView Details
302962-49-8 -
 Dasakast 50mg Dasatinib TabletsView Details
Dasakast 50mg Dasatinib TabletsView Details
302962-49-8 -
 Dasakast 70mg Dasatinib TabletsView Details
Dasakast 70mg Dasatinib TabletsView Details
302962-49-8
