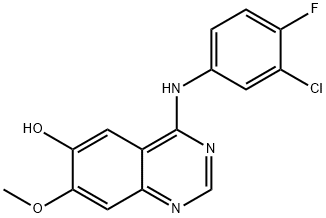
Gefitinib
Synonym(s):N-(3-Chloro-4-fluoro-phenyl)-7-methoxy-6-(3-morpholin-4-ylpropoxy)quinazolin-4-amine;ZD1839
- CAS NO.:184475-35-2
- Empirical Formula: C22H24ClFN4O3
- Molecular Weight: 446.9
- MDL number: MFCD04307832
- EINECS: 643-034-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 20:33:22
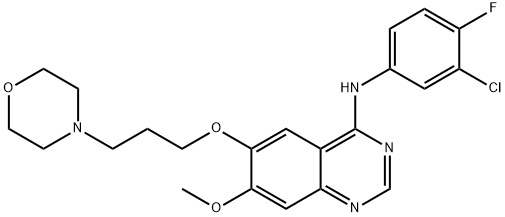
What is Gefitinib?
Absorption
Absorbed slowly after oral administration with a mean bioavailability of 60%. Peak plasma levels occurs 3-7 hours post-administration. Food does not affect the bioavailability of gefitinib.
Toxicity
The acute toxicity of gefitinib up to 500 mg in clinical studies has been low. In non-clinical studies, a single dose of 12,000 mg/m2 (about 80 times the recommended clinical dose on a mg/m2 basis) was lethal to rats. Half this dose caused no mortality in mice. Symptoms of overdose include diarrhea and skin rash.
Description
Gefitinib was introduced in Japan as a daily oral monotherapy for the treatment of inoperable or recurrent non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLC). This anilinoquinazoline derivative can be synthesized in 6 steps starting from 6,7-dimethoxyquinazolin-4(3H)-one by successive monodemethylationlacetylation of the 6-hydroxy-group followed by chlorination and reaction with 3-chloro-4-fluoroaniline, finally deacetylation and alkylation with 3-(4-morpholinyl)propylbromide complete the synthesis. Gefitinib reversibly inhibits the activity of the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase (EGRF TK). This inhibits autophosphorylation of EGRF and blocks the cascade of intracellular events which have been implicated in the proliferation, survival and metastasis of cancer cells. Gefitinib diplays good selectivity for the EGRF TK relative to other growth factors in human umbilical endothelial cells. It is similarly selective relative to other kinases, for example cerB2. Data from two large phase II studies in patients with pretreated NSCLC have shown that gefitinib induces a response rate approaching 20% in patients receiving the agent as a second line therapy and approximately 10% in those pretreated with more lines of chemotherapy. Gefitinib has good bioavailability and is metabolized in the liver via the cytochrome P450 3A4 enzyme system with a mean elimination half life of 28 h. Gefitinib has been generally well tolerated in cancer patients with predominant side effects being acne-like skin-rash, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting and mild to moderate myelosuppression. .
Chemical properties
Light-Yellow Crystalline Powder
Originator
Astra Zeneca (UK)
The Uses of Gefitinib
Gefitinib (Iressa, ZD-1839) is an EGFR inhibitor for Tyr1173, Tyr992, Tyr1173 and Tyr992 in the NR6wtEGFR and NR6W cells with IC50 of 37 nM, 37nM, 26 nM and 57 nM, respectively.
The Uses of Gefitinib
Gefitinib is an antineoplastic.
The Uses of Gefitinib
Gefitinib has been used :
- To study its effective use in endometrial cancer therapy
- Cell proliferation, cell cycle and apoptosis assays
- Cell viability assay and colony formation assay
Background
Gefitinib (originally coded ZD1839) is a drug used in the treatment of certain types of cancer. Acting in a similar manner to erlotinib (marketed as Tarceva), gefitinib selectively targets the mutant proteins in malignant cells. It is marketed by AstraZeneca under the trade name Iressa.
Indications
For the continued treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer after failure of either platinum-based or docetaxel chemotherapies.
What are the applications of Application
Gefitinib is an EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitor
Indications
The EGFR or ErbB1 inhibitor gefitinib (Iressa(R), AstraZeneca) was originally approved by the US FDA in 2003 under accelerated regulations for the treatment of locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) after progression on docetaxel- and platinum-based chemotherapy. AstraZeneca voluntarily withdrew gefitinib from the market in 2005, owing to failed verification of clinical benefit during post-approval studies. In July 2015, FDA reinstated the approval of gefitinib for a different group of patients (i.e., NSCLC patients with EGFR mutations).
Other approved kinase inhibitors targeting the ErbB family, which includes ErbB1/EGFR, ErbB2/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (Her2), ErbB3/ Her3, and ErbB4/Her4, are erlotinib (Tarceva(R), OSI Pharm.), lapatinib (Tykerb(R), GlaxoSmithKline), vandetanib (Caprelsa(R), AstraZeneca), afatinib (Gilotrif(R), Boehringer Ingelheim) , and osimertinib (Tagrisso(R), AstraZeneca). All approved EGFR family inhibitors share a common quinazoline scaffold with the exception of osimertinib, which has a pyrimidinylphenylamine scaffold that resembles that of imatinib and nilotinib. Gefitinib and vandetanib adopt the type I binding mode with “DFG-in” and αC-helix “in” conformation, while erlotinib and lapatinib bind to“DFG-in”with the αC-helix adopting an “out” conformation. Afatinib and osimertinib are covalent inhibitors with an electrophilic enone moiety.
Indications
Iressa (ZD1839) is an orally active tyrosine kinase inhibitor selective for the epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor tyrosine kinase. Iressa is undergoing clinical trials in the treatment of various solid tumors, including head and neck cancer, breast cancer and non-small cell lung cancer. Its antitumor activity is derived from the fact that the EGF receptor and EGF signaling are frequently overactivated in sensitive tumors. The major side effects include diarrhea and skin rash. Bone marrow toxicity has not been a dose-limiting problem.
Definition
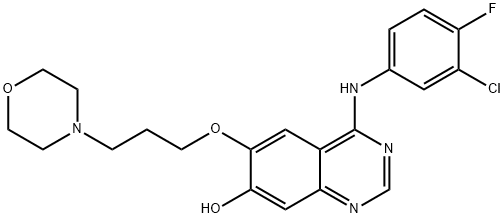
ChEBI: Gefitinib is a member of the class of quinazolines that is quinazoline which is substituted by a (3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)nitrilo group, 3-(morpholin-4-yl)propoxy group and a methoxy group at positions 4,6 and 7, respectively. An EGFR kinase inhibitor used for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. It has a role as an epidermal growth factor receptor antagonist and an antineoplastic agent. It is an aromatic ether, a member of monochlorobenzenes, a member of monofluorobenzenes, a secondary amino compound, a tertiary amino compound, a member of quinazolines and a member of morpholines.
Synthesis
The synthesis of gefitinib started with 7-methoxy-4-oxo-3,4-dihydroquinazolin-6-yl-acetate 41 which underwent chlorination by phosphorus oxychloride to give 42, as shown in Scheme 6. The produced 4-chloroquinazoline 42 was reacted with 3-chloro-4-fluoroaniline 43 in isopropanol alcohol (i-ProOH) to give 44. Hydrolysis of the ester group in 44 afforded quinazolin-6-ol 45, which gave gefitinib on the reaction with 4-(3-chloropropyl)morpholine 46.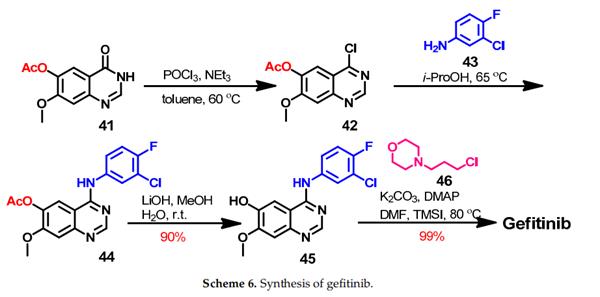
brand name
Iressa (AstraZeneca).
General Description
Geftinib is available as 250-mg tablets for oral administrationin the treatment of NSCLC for those patients who have failedto respond to platinum-based therapies and docetaxel and hasalso been used against squamous cell cancers of the head andneck. The agent is an inhibitor of the TK of EGF-R and possiblyother TKs as well. Gefitinib is both a substrate and inhibitorof Pgp and BCRP. The agent is absorbed slowly afterbeing administered orally with 60% bioavailability.Metabolism occurs in the liver and is mediated primarily byCYP3A4 to give eight identified metabolites resulting fromdefluorination of the phenyl ring, oxidative-O-demethylation,and multiple products arising as a result of oxidation of themorpholine ring. The O-demethylated product represents thepredominate metabolite and is 14-fold less active comparedwith the parent. The parent and metabolites are eliminated inthe feces with a terminal elimination half-life of 48 hours.The drug appears to be well tolerated with the most commonlyreported side effects being rash and diarrhea. It mayalso cause elevations in blood pressure especially in those patientswith preexisting hypertension, elevation of transaminaselevels, and mild nausea and mucositits.
General Description
Class: receptor tyrosine kinase
Treatment: NSCLC
Oral bioavailability = 60%
Elimination half-life = 48 h
Protein binding = 97%
Biological Activity
Orally active, selective inhibitor of EGFR tyrosine kinase (IC 50 = 23-79 nM). Shows minimal activity against ErbB2, KDR, c-flt, PKC, MEK and ERK-2. Blocks EGFR autophosphorylation and inhibits tumor growth in mice bearing a range of human xenografts.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Gefitinib is a selective epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase (EGFR TK) inhibitor. Gefitinib has antineoplastic activity, and has been approved for the treatment on non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).Gefitinib has a higher affinity for ATP (adenosine triphosphate) binding site in the EGFR tyrosine kinase domain than ATP. Hence, gefitinib is known to inhibit the progression of endometrial cancer.
Pharmacokinetics
Gefitinib inhibits the intracellular phosphorylation of numerous tyrosine kinases associated with transmembrane cell surface receptors, including the tyrosine kinases associated with the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR-TK). EGFR is expressed on the cell surface of many normal cells and cancer cells.
Clinical Use
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors:
Treatment of non-small cell lung cancer
Synthesis
A mixture of 4,5-dimethoxyanthranilic acid (133) and formamide was heated to generate the cyclized quinazoline 134. The quinazoline was selectively monodemethylated with methionine in refluxing methanesulfonic acid to afford 135 in 47% yield. Compound 135 was acylated to give acetate 136, which was treated with refluxing thionyl chloride to yield chloropyrimidine 137. Chloride 137 was condensed with 3-chloro-4-fluoroaniline (138) in refluxing IPA to yield anilinoquinazoline 139 in 56% yield from 136. The acetate protecting group in compound 139 was hydrolyzed with ammonium hydroxide in methanol, and the free phenol was alkylated with 3-(4- morpholinyl)propyl chloride (140) to give gefitinib (13) in 55% yield.

Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Antibacterials: Avoid with rifampicin (reduced
gefitinib concentration).
Anticoagulants: possibly enhanced anticoagulant
effect with warfarin
Antipsychotics: avoid with clozapine (increased risk
of agranulocytosis).
Antivirals: avoid with boceprevir.
Ulcer-healing drugs: concentration reduced by
ranitidine.
Avoid concomitant use with other inhibitors or
inducers of CYP3A4. Dose alterations may be
required.
Metabolism
Primarily hepatic via CYP3A4. Three sites of biotransformation have been identified: metabolism of the N-propoxymorpholino-group, demethylation of the methoxy-substituent on the quinazoline, and oxidative defluorination of the halogenated phenyl group. Wang et al. investigated the metabolism of gefitinib in NSCLC patients. Eighteen metabolites were tentatively identified in human plasma. Among these metabolites, M7 (Figure 1) was proposed to be formed through the removal of the 3-chloro-4-fluoroaniline moiety. In addition, dechlorination, and defluorination metabolism were proposed to give the M1-u, and M5 metabolites. The conjugation of M1-u with taurine was also proposed to produce the M1 metabolite. The conjugation of the phenolic metabolite M5 with sulfate gave the sulfate conjugate M4, while the demethylation of gefitinib was proposed to produce the phenolic M12 metabolite, which could undergo glucuronidation, yielding M8.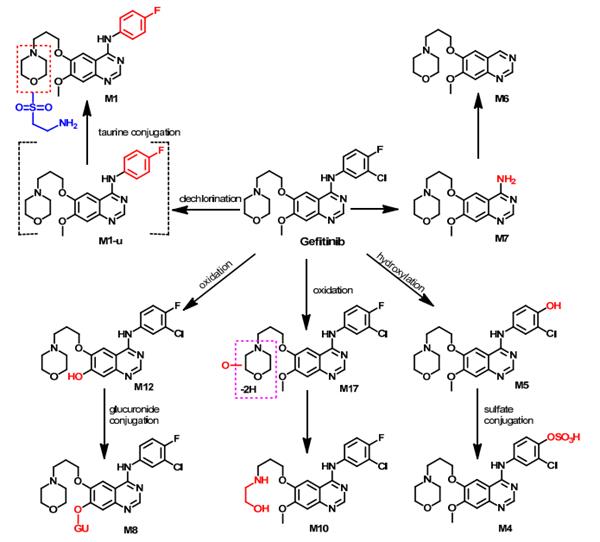
Metabolism
Extensively metabolised in the liver, mainly by the
cytochrome P450 isoenzymes CYP3A4 and CYP2D6;
the major metabolite is O-desmethylgefitinib, which is
much less potent than gefitinib, and unlikely to contribute
to its clinical activity.
Gefitinib is excreted mainly as metabolites via the faeces
(86%); renal elimination of gefitinib and its metabolites
accounts for <4% of the dose.
storage
Store at RT
References
1) Baselga et al. (2000), ZD1839 (‘Iressa’) as an anticancer agent; Drugs, 60 33 2) McKillop et al. (2005), Tumor penetration of gefitinib (Iressa), an epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor; Mol. Cancer Ther., 4 641 3) Sirotnak et al. (2000), Efficacy of cytotoxic agents against human tumor xenografts is markedly enhanced by coadministration of ZD1839 (Iressa), an inhibitor of EGFR tyrosine kinase; Clin. Cancer Res., 6 4885 4) Ciaradiello et al. (2001), Inhibition of growth factor production and angiogenesis in human cancer cells by ZD1839 (Iressa), a selective epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor; Clin. Cancer Res., 7 1459
Properties of Gefitinib
| Melting point: | 119-1200C |
| Boiling point: | 586.8±50.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.322±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | room temp |
| solubility | Soluble in DMSO (up to 40 mg/ml) or in Ethanol (up to 4 mg/ml). |
| form | powder |
| pka | 7.00±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | white to beige |
| Stability: | Stable for 2 years from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions in DMSO or ethanol may be stored at -20°C for up to 1 month. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 184475-35-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Gefitinib
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Gefitinib
Gefitinib manufacturer
Zyphars Biopharmaceuticals Pvt. Ltd
Basil Drugs AND Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
NATCO Pharma Limited
Raising Sun Pharma
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Gefitinib 97%View Details
Gefitinib 97%View Details -
 Gefitinib 99%View Details
Gefitinib 99%View Details -
 Gefitinib 97% CAS 184475-35-2View Details
Gefitinib 97% CAS 184475-35-2View Details
184475-35-2 -
 GEFTINIB 184475-35-2 95-99%View Details
GEFTINIB 184475-35-2 95-99%View Details
184475-35-2 -
 Gefitinib CAS 184475-35-2View Details
Gefitinib CAS 184475-35-2View Details
184475-35-2 -
 Gefitinib 184475-35-2 99%View Details
Gefitinib 184475-35-2 99%View Details
184475-35-2 -
 Gefitinib 95.00% CAS 184475-35-2View Details
Gefitinib 95.00% CAS 184475-35-2View Details
184475-35-2 -
 Gefitinib >98% (HPLC) CAS 184475-35-2View Details
Gefitinib >98% (HPLC) CAS 184475-35-2View Details
184475-35-2