TITANIUM NITRIDE
- CAS NO.:25583-20-4
- Empirical Formula: NTi
- Molecular Weight: 61.87
- MDL number: MFCD00049596
- EINECS: 247-117-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 13:37:16
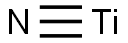
What is TITANIUM NITRIDE?
Chemical properties
gold or brown powder
Chemical properties
Tin is a soft, white, silvery metal that is insoluble in water. Tin metal is used to line cans for food, beverages, and aerosols. It is present in brass, bronze, pewter, and some soldering materials. Tin can combine with other chemicals to form various compounds. When tin is combined with chlorine, sulfur, or oxygen, it is called an inorganic tin compound. Inorganic tin compounds are found in small amounts in the earth’s crust. They are also present in toothpaste, perfumes, soaps, coloring agents, food additives, and dyes. Tin when combined with carbon forms organotin compounds. These compounds are used in making plastics, food packages, plastic pipes, pesticides, paints, wood preservatives, and rodent (rats and mice) repellants. Organic tin compounds stick to soil, sediment, and particles in water. Humans are usually exposed to tin at far less than 1 ppm in air and water. The amounts in air and water near hazardous waste sites could be higher. The most common use for tin coating is for edge retention and corrosion resistance on machine tooling, such as drill bits and milling cutters, often improving their lifetime by a factor of three or more.
Physical properties
Bronze powder. Transition temperature 4.2 K. Corrosion resistant to molten metals such as Al, Pb, Mg, Zn, Cd, and Bi. Corroded by molten Na, Rb, Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Sn, Ni, Cu, Fe, and Co. Dissolved by boiling aqua regia, decomposed by boiling alkalis evolving NH3.
The Uses of TITANIUM NITRIDE
Titanium nitride (TiN) is an extremely hard ceramic material, often used as a coating on Ti alloys, steel, carbide and Al components to improve the substrate’s surface properties. Applied as a thin coating (less than 5 μm), TiN is used to harden and protect cutting and sliding surfaces, for decorative purposes due to its gold appearance and as a non-toxic exterior for medical implants.
The Uses of TITANIUM NITRIDE
As protective coating for cutting tools; in diffusion barriers for microelectronic devices; as crucibles in metal smelting; as a gold-colored surface for jewelry. In high-performance ceramic materials. As a coating for orthopedic and dental implants.
The Uses of TITANIUM NITRIDE
Titanium Nitride (TiN), a gold-colored coating, is an excellent general purpose coating for protecting a wide variety of tools from wear. TiN coated tools are used for machining high alloy steels and low alloy steels at medium and high cutting speeds. Tool life is three to five times longer than uncoated HSS and carbide end mills.
Health Hazard
Inhalation breathing in, oral eating or drinking, or dermal exposure skin contact to some organotin compounds has been shown to cause harmful effects in humans, but the main effect will depend on the particular organotin compound. There have been reports of skin and eye irritation, respiratory irritation, gastrointestinal effects, and neurological problems in humans exposed for a short period of time to high amounts of certain organotin compounds. Some neurological problems have persisted for years after the poisoning occurred. Lethal cases have been reported following ingestion of very high amounts. Studies in animals have shown that certain organotins mainly affect the immune system, but a different type primarily affects the nervous system. Yet, there are some organotins that exhibit very low toxicity. Exposure of pregnant rats and mice to some organotin compounds has reduced fertility and caused stillbirth, but scientists are still not sure whether this occurs only with doses that are also toxic to the mother. Some animal studies also suggest that the reproductive organs of males may be affected
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Industrial uses
Titanium nitride, TiN, is a light-brown powderwith a cubic lattice crystal structure. Sinteredbars are extremely hard and brittle, with a hardnessabove Mohs 9 and a melting point of2950°C. It is not attacked by nitric, sulfuric, orhydrochloric acid, and is resistant to oxidationat high temperatures. In recent years, titaniumnitridecoatings have been used to markedlyextend the life of tool-steel cutters and formingtools. The coatings, golden in color, are depositedby chemical or physical vapor deposition.Aluminum nitride, AlN, when molded intoshapes and sintered, forms a dense, nonporousstructure with a hardness of Mohs 6. It resiststhe action of molten iron or silicon to 1704°C,and molten aluminum to 1427°C, but isattacked by oxygen and carbon dioxide at760°C. At least 1% oxygen causes AlN propertiesto deteriorate rapidly.
Properties of TITANIUM NITRIDE
| Melting point: | 2930 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 0°C |
| Density | 5.24 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| RTECS | XR2230000 |
| Flash point: | 0°C |
| solubility | it is soluble in aqua regia on boiling. |
| form | Powder |
| color | Yellow |
| Specific Gravity | 5.24 |
| Resistivity | 21.7 (ρ/μΩ.cm) |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in aqua regain. Partly soluble in water. |
| Crystal Structure | Cubic |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong acids. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 25583-20-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Titanium nitride (TiN) (25583-20-4) |
Safety information for TITANIUM NITRIDE
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H220:Flammable gases H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H336:Specific target organ toxicity,single exposure; Narcotic effects |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P405:Store locked up. |
Computed Descriptors for TITANIUM NITRIDE
| InChIKey | NRTOMJZYCJJWKI-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Titanium nitride CAS 25583-20-4View Details
Titanium nitride CAS 25583-20-4View Details
25583-20-4 -
 Titanium nitride CAS 25583-20-4View Details
Titanium nitride CAS 25583-20-4View Details
25583-20-4 -
 Titanium nitride CAS 25583-20-4View Details
Titanium nitride CAS 25583-20-4View Details
25583-20-4 -
 Titanium nitride CAS 25583-20-4View Details
Titanium nitride CAS 25583-20-4View Details
25583-20-4 -
 Titanium nitride CAS 25583-20-4View Details
Titanium nitride CAS 25583-20-4View Details
25583-20-4 -
 Titanium nitride sputtering target, 50.8mm (2.0 in.) dia. x 3.18mm (0.125 in.) thick CAS 25583-20-4View Details
Titanium nitride sputtering target, 50.8mm (2.0 in.) dia. x 3.18mm (0.125 in.) thick CAS 25583-20-4View Details
25583-20-4 -
 Titanium nitride sputtering target, 50.8mm (2.0 in.) dia. x 6.35mm (0.250 in.) thick CAS 25583-20-4View Details
Titanium nitride sputtering target, 50.8mm (2.0 in.) dia. x 6.35mm (0.250 in.) thick CAS 25583-20-4View Details
25583-20-4 -
 Titanium Nitride Nanopowder CAS 25583-20-4View Details
Titanium Nitride Nanopowder CAS 25583-20-4View Details
25583-20-4