Titanium
- CAS NO.:7440-32-6
- Empirical Formula: Ti
- Molecular Weight: 47.87
- MDL number: MFCD00011264
- EINECS: 231-142-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
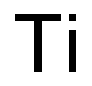
What is Titanium?
Description
Titanium was discovered by the Reverend William Gregor in 1791, and is named after the ‘Titans’ of Greek mythology. The metal was not isolated in a pure state until 1910, and useful quantities were not available for industrial applications until 1946, when an economical purification process was developed.
Chemical properties
Titanium is a silvery metal or dry, dark-gray amorphous, lustrous powder.
Physical properties
Positioned at the top of group 4 (IVB), titanium heads up a group of metals sometimesreferred to as the “titanium group.” Members of this group have some similar properties.Titanium’s density is 4.5 g/cm3, which makes it heavier than aluminum but not as heavy asiron. Its melting point is high at 1,660°C, and its boiling point is even higher at 3287°C.Titanium metal is harder than steel but much lighter and does not corrode in seawater,which makes it an excellent alloy metal for use in most environmental conditions. It is alsoparamagnetic, which means that it is not responsive to magnetic fields. It is not a very goodconductor of heat or electricity.
Isotopes
There are 23 known isotopes of titanium. All but five are radioactive, rangingfrom Ti-38 to Ti-61, and have half-lives varying from a few nanoseconds to a few hours.The percentages of the five stable isotopes found in nature are as follows: 46Ti = 8.25%,47Ti = 7.44%, 48Ti = 73.72%, 49Ti = 5.41%, and 50Ti = 5.18%.
Origin of Name
It was named after “Titans,” meaning the first sons of the Earth as stated in Greek mythology.
Occurrence
Titanium is the ninth most abundant element found in the Earth’s crust, but not in pureform. It is found in two minerals: rutile, which is titanium dioxide (TiO2), and ilmenite(FeTiO3). It is also found in some iron ores and in the slag resulting from the productionof iron. The mineral rutile is the major source of titanium production in the United States.Although titanium is widely spread over the crust of the Earth, high concentrations of itsminerals are scarce. In the past it was separated from it ores by an expensive process ofchemical reduction that actually limited the amount of metal produced. A two-step processinvolves heating rutile with carbon and chlorine to produce titanium tetrachloride—TiO2+ C + 2Cl2 ?→ TiCl4 + CO2—which is followed by heating the titanium tetrachloridewith magnesium in an inert atmosphere: TiCl4 + 2Mg ?→ Ti + 2 MgCl2. As recently as theyear 2000, a method of electrolysis was developed using titanium tetrachloride in a bath ofrare-earth salts. This process can be used on a commercial scale that makes the productionof titanium much less expensive. Titanium was, and still is, a difficult element to extractfrom its ore.Titanium is found throughout the universe and in the stars, the sun, the moon, and themeteorites that land on Earth.
Characteristics
As the first element in group 4, titanium has characteristics similar to those of the othermembers of this group: Zr, Hf, and Rf. Titanium is a shiny, gray, malleable, and ductile metalcapable of being worked into various forms and drawn into wires.
History
In 1791 Reverend William Gregor (1761–1817), an amateur mineralogist, discoveredan odd black sandy substance in his neighborhood. Because it was somewhat magnetic, hecalculated that it was almost 50% magnetite (a form of iron ore). Most of the remainder ofthe sample was a reddish-brown powder he dissolved in acid to produce a yellow substance.Thinking he had discovered a new mineral, he named it “menachanite,” after the Menachanregion in Cornwall where he lived. During this period, Franz Joseph Muller (1740–1825) alsoproduced a similar substance that he could not identify. In 1793 Martin Heinrich Klaproth(1743–1817), who discovered several new elements and is considered the father of modernanalytical chemistry, identified the substance that Gregor called a mineral as a new element.Klaproth named it “titanium,” which means “Earth” in Latin.
The Uses of Titanium
As alloy with copper and iron in titanium bronze; as addition to steel to impart great tensile strength; to aluminum to impart resistance to attack by salt solutions and by organic acids; to remove traces of oxygen and nitrogen from incandescent lamps. Surgical aid (fracture fixation).
The Uses of Titanium
Titanium is added to steel and aluminumto enhance their tensile strength and acidresistance. It is alloyed with copper and ironin titanium bronze.
The Uses of Titanium
Given titanium’s lightness, strength, and resistance to corrosion and high temperatures, itsmost common use is in alloys with other metals for constructing aircraft, jet engines, and missiles. Its alloys also make excellent armor plates for tanks and warships. It is the major metalused for constructing the stealth aircraft that are difficult to detect by radar.Titanium’s noncorrosive and lightweight properties make it useful in the manufacture oflaboratory and medical equipment that will withstand acid and halogen salt corrosion. Thesesame properties make it an excellent metal for surgical pins and screws in the repair of brokenbones and joints.It has many other uses as an abrasive, as an ingredient of cements, and as a paint pigmentin the oxide form and in the paper and ink industries, in batteries for space vehicles, andwherever a metal is needed to resist chlorine (seawater) corrosion.
Definition
A silvery transition metal that occurs in various ores as titanium(IV) oxide and also in combination with iron and oxygen. It is extracted by conversion of titanium(IV) oxide to the chloride, which is reduced to the metal by heating with sodium. Titanium is reactive at high temperatures. It is used in the aerospace industry as it is strong, resistant to corrosion, and has a low density. It forms compounds with oxidation states +4, +3, and +2, the +4 state being the most stable. Symbol: Ti; m.p. 1660°C; b.p. 3287°C; r.d. 4.54 (20°C); p.n. 22; r.a.m. 47.867.
Production Methods
Titanium is the ninth most abundant element and accounts for about 0.63% of the Earth’s crust. Analyses of rock samples from the moon indicate that titanium is far more abundant there; some lunar rocks consist of 12% titanium by weight. World production of titanium sponge metal was estimated at 69,000 metric tons in 1991. The most important titaniumbearing minerals are ilmenite, rutile, and leucoxene. Ilmenite (FeTiO3) is found in beach sands (Australia, India, and Florida) and in rock deposits associated with iron (Norway and Finland). Ilmenite accounts for about 91%of the world’s consumption of titanium minerals and world resources of anatase, ilmenite, and rutile total more than 2 billion tons. Rutile (a form ofTiO2) is less abundant; its chief source is certain Australian beach sands. Two other less prominent forms of TiO2 exist, anatase and brookite. The ores vary around the world in TiO2 content from 39% to 96%. Anatase is used as a food color.
General Description
TITANIUM is a gray lustrous powder. TITANIUM can be easily ignited and burns with an intense flame. The very finely powdered material may be ignited by sparks.
Air & Water Reactions
Highly flammable. Pyrophoric in dust form [Bretherick 1979, p. 104]. Titanium is water-reactive at 700C, releasing hydrogen, which may cause an explosion [Subref: Mellor, 1941, vol. 7, 19].
Reactivity Profile
TITANIUM reacts violently with cupric oxide and lead oxide when heated. When titanium is heated with potassium chlorate, potassium nitrate, or potassium permanganate, an explosion occurs [Mellor 7:20. 1946-47]. The residue from the reaction of titanium with red fuming nitric acid exploded violently when the flask was touched [Allison 1969]. Liquid oxygen gives a detonable mixture when combined with powdered titanium, [Kirchenbaum 1956].
Hazard
Almost all of titanium’s compounds, as well as the pure metal when in powder form, areextremely flammable and explosive. Titanium metal will ignite in air at 1200°C and willburn in an atmosphere of nitrogen. Titanium fires cannot be extinguished by using water orcarbon dioxide extinguishers. Sand, dirt, or special foams must be used to extinguish burningtitanium.
Health Hazard
Fire will produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Inhalation of decomposition products may cause severe injury or death. Contact with substance may cause severe burns to skin and eyes. Runoff from fire control may cause pollution.
Health Hazard
Inhalation of metal powder may cause coughing,irritation of the respiratory tract, anddyspnea. Intramuscular administration of titaniumin rats caused tumors in blood. Animalcarcinogenicity is not fully established.Human carcinogenicity is not known.
Fire Hazard
Flammable/combustible material. May ignite on contact with moist air or moisture. May burn rapidly with flare-burning effect. Some react vigorously or explosively on contact with water. Some may decompose explosively when heated or involved in a fire. May re-ignite after fire is extinguished. Runoff may create fire or explosion hazard. Containers may explode when heated.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Safety Profile
Questionable carcinogen with experimental tumorigenic data. Experimental reproductive effects. The dust may ignite spontaneously in air. Flammable when exposed to heat or flame or by chemical reaction. Titanium can burn in an atmosphere of carbon dioxide, nitrogen, or air. Also reacts violently with BrF3, CuO, PbOx (Ni + KClO3), metaloxy salts, halocarbons, halogens, CO2, metal carbonates, Al, water, AgF, O2 , nitryl fluoride, HNO3,O2, KClO3, KNO3 , KMnO4, steam @ 704°, trichloroethylene, trichlorotrifluoroethane. Ordinary extinguishers are often ineffective against titanium fires. Such fires require special extinguishers designed for metal fires. In airtight enclosures, titanium fires can be controlled by the use of argon or helium. Titanium, in the absence of moisture, burns slowly, but evolves much heat. The application of water to burning titanium can cause an explosion. Finely dwided titanium dust and powders, like most metal powders, are potential explosion hazards when exposed to sparks, open flame, or high-heat sources. See also TITANIUM COMPOUNDS, POWDERED METALS, and MAGNESIUM.
Potential Exposure
Titanium metal, because of its low weight, high strength, and heat resistance, is used in the aerospace and aircraft industry as tubing, fittings, fire walls; cowlings, skin sections; jet compressors; and it is also used in surgical appliances. It is used, too, as controlwire casings in nuclear reactors, as a protective coating for mixers in the pulp-paper industry and in other situations in which protection against chlorides or acids is required; in vacuum lamp bulbs and X-ray tubes; as an addition to carbon and tungsten in electrodes and lamp filaments; and to the powder in the pyrotechnics industry. It forms alloys with iron, aluminum, tin, and vanadium, of which ferrotitanium is especially important in the steel industry. Other titanium compounds are utilized in smoke screens, as mordants in dyeing; in the manufacture of cemented metal carbides; as thermal insulators; and in heat resistant surface coatings in paints and plastics.
Environmental Fate
Titanium is poorly absorbed by plants and animals and is
retained to only a certain extent. High levels of titanium in food
products can be detects, however, when soil is contaminated by
fly-ash fallout or titanium-containing sewage residues and
when titanium dioxide is used as a food whitener. Food, which
is considered to be the most important source of exposure to
titanium, contributes >99% of the daily intake of the element.
There are no relevant tolerable intakes for titanium against
which to compare estimated dietary intake. Typical diets may
contain approximately 0.3–0.5 mg titanium.
Titanium content of soil generally ranges from 0.3 to 6%,
high levels of which are found in the vicinity of power plants
because of combustion of coal.
Titanium concentrations in the atmosphere are comparatively
low. Annual average concentrations in urban air are
mostly <0.1 mgm-3 and they are lower still in rural air. Air
concentrations up to 0.5 mgm-3 have been reported in urban
and industrialized areas.
Shipping
UN2546 Titanium powder, dry, Hazard Class: 4.2; Labels: 4.2-Spontaneously combustible material.
Toxicity evaluation
Many data indicate that titanium is absorbed poorly from the gastrointestinal tract in human beings. It is likely that transferrin may act as a specific carrier of titanium ions and may play a central role during the transport and biodistribution of soluble titanium species throughout the organism. Titanium concentrations found generally in urine suggest an absorption of <5%, assuming a daily intake of at least 300 mg.
Incompatibilities
Powder and dust may ignite spontaneously in air. Violent reactions occur on contact with water, steam, halocarbons, halogens, and aluminum. The dry powder is a strong reducing agent; Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause firesor explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides.
Properties of Titanium
| Melting point: | 1660 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 3287 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 4.5 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| Flash point: | 0°C |
| storage temp. | no restrictions. |
| form | wire |
| color | Silver-gray |
| Specific Gravity | 4.5 |
| Resistivity | 42.0 μΩ-cm, 20°C |
| Water Solubility | Insoluble in water. |
| Merck | 13,9547 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 2.5 mg/m3 NIOSH: IDLH 250 mg/m3 |
| Stability: | Stable. Dust is thought to be spontaneously flammable, and may form an explosive mixture with air. Flammable solid. Incompatible with mineral acids, halogens, carbon dioxide, strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7440-32-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Titanium (7440-32-6) |
Safety information for Titanium
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H228:Flammable solids |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P240:Ground/bond container and receiving equipment. P241:Use explosion-proof electrical/ventilating/lighting/…/equipment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P370+P378:In case of fire: Use … for extinction. |
Computed Descriptors for Titanium
| InChIKey | RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Titanium manufacturer
New Products
(R)-1-Boc-3-hydroxypyrrolidine Methyl (R)-1-Boc-4,4-difluoropyrrolidine-2-carboxylate 2,2-Difluoropropylamine hydrochloride tert-butyl 3-bromoazetidine-1-carboxylate DIFLUOROACETIC ANHYDRIDE 2,2-Difluoropropionic acid Diallylamine, 99% Calcium hydroxide, 95% Aluminum oxide, basic 2-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 97% L-tert-Leucine,97% N-Hydroxy-2-methylpropanimidamide 4-(3,4-Dichlorophenyl)-3,4-Dihydro-N-Methyl-1-(2H)-Naphthalenimine (Schiff Base) 2-AMINO-3,5-DIBROMO BENZALDEHYDE [ADBA] L-Glutamic Acid Dimethyl Ester Hcl 10-Methoxy-5H-dibenz[b,f]azepine 5-Cyanophthalide N, N-Carbonyldiimidazole (CDI) Dibenzoyl Peroxide Titanium Dioxide 2-(Methylthio) Benzonitrile Sodium Acetate Anhydrous Allopurinol 1,5-DibromopentaneRelated products of tetrahydrofuran






You may like
-
 Titanium, Ti 1000μg/mL CAS 7440-32-6View Details
Titanium, Ti 1000μg/mL CAS 7440-32-6View Details
7440-32-6 -
 Titanium, Ti 1000μg/mL CAS 7440-32-6View Details
Titanium, Ti 1000μg/mL CAS 7440-32-6View Details
7440-32-6 -
 Titanium, Ti 1000μg/mL CAS 7440-32-6View Details
Titanium, Ti 1000μg/mL CAS 7440-32-6View Details
7440-32-6 -
 Titanium slug, 9.5mm (0.37 in.) dia. x 9.5mm (0.37 in.) length CAS 7440-32-6View Details
Titanium slug, 9.5mm (0.37 in.) dia. x 9.5mm (0.37 in.) length CAS 7440-32-6View Details
7440-32-6 -
 Titanium powder CAS 7440-32-6View Details
Titanium powder CAS 7440-32-6View Details
7440-32-6 -
 Titanium, Annealed CAS 7440-32-6View Details
Titanium, Annealed CAS 7440-32-6View Details
7440-32-6 -
 Titanium, Annealed CAS 7440-32-6View Details
Titanium, Annealed CAS 7440-32-6View Details
7440-32-6 -
 Titanium alloy CASView Details
Titanium alloy CASView Details
