Tungsten carbide
Synonym(s):Tungsten carbide;Tungsten monocarbide;W 526010;Wolfram carbide
- CAS NO.:12070-12-1
- Empirical Formula: CW
- Molecular Weight: 195.85
- MDL number: MFCD00011464
- EINECS: 235-123-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-09-25 17:15:13
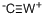
What is Tungsten carbide?
Chemical properties
Gray powder. Mohs hardness of 9+ in solid form. Insoluble in water but readily attacked by a nitric acid– hydrofluoric acidmixture. Stable to 400C with chlorine, burns in fluorine at room temperature, oxidizes on heating in air.
Physical properties
Gray powder, dissolved by HF=HNO3 mixture. Cutting tools, wear-resistant semiconductor film. Corroded by molten metals Mg, Al, V, Cr, Mn, Ni, Cu, Zn, Nb, and Mo. Corrosion resistant to molten Sn and Ta.
The Uses of Tungsten carbide
Tungsten Carbide/Carbon (WC/C) is a black-gray colored coating of hard tungsten carbide particles in a soft amorphous carbon matrix. It is used for precision components with abrasive and adhesive wear, seizure problems (poor lubrication) and for dry machining applications.
The Uses of Tungsten carbide
Tungsten carbide is extremely hard and are excellent cutting materials. It is used extensivly in the tool and die industry for drilling and cutting tools, sand blasting nozzels, armor-piercing bullets, and studs to increase traction of tires.
Besides, it is used in dental burs, surgical instruments, wear-resistant coatings; in manufacture of cemented carbide; Substitute for noble metals in catalysis.
The Uses of Tungsten carbide
Tungsten carbide is extensively used as a cutting tool for machining and in armor-piercing ammunition. It is also used in farriery, the shoeing of horses as well as to improve traction on slippery surfaces like roads or ice. It finds application in nuclear reactors as an effective neutron reflector. It is also used for making surgical instruments meant for open surgery such as scissors, forceps, hemostats, blade-handles and in laparoscopic surgery instruments such as graspers, cutter, needle holder and cautery. Further, it also used to make the rotating ball in the tips of ballpoint pens, bridal jewelry, and gauge blocks, which is useful for producing precision lengths in dimensional metrology.
Definition
A ditungsten carbide, W2C, with similar physical properties is also known. WC is said to be the strongest of all structural materials.
Definition
A black powder,WC, made by heating powderedtungsten metal with lamp black at1600°C. It is extremely hard (9.5 onMohs’ scale) and is used in dies andcutting tools. A ditungsten carbide,W2C, also exists.
Hazard
Toxic by inhalation.
Flammability and Explosibility
Not classified
Industrial uses
Tungsten carbide with a 3 to 20% matrix ofcobalt is the most common structural RHM. Thelow-cobalt grades are used for applicationsrequiring wear resistance; the high-cobalt gradesserve where impact resistance is required.
Safety Profile
Chronic inhalation causes lung damage in humans. Ignites at 600°C in nitrogen oxide atmospheres. Violent reaction with F2, ClF3, NOx, IF5, PbO2, NO2, N20. See also TUNGSTEN COMPOUNDS.
Properties of Tungsten carbide
| Melting point: | 2870°C |
| Boiling point: | 6000°C |
| Density | 15,63 g/cm3 |
| solubility | insoluble in H2O; soluble in HNO3/HF |
| form | powder |
| color | Gray |
| Specific Gravity | 15.63 |
| Resistivity | 19.2 (ρ/μΩ.cm) |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in nitric acid and hydrofluroic acid. Insoluble in water. |
| Crystal Structure | Hexagonal |
| Merck | 14,9815 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 3 mg/m3 NIOSH: TWA 5 mg/m3; STEL 10 mg/m3 |
| IARC | 2A (Vol. 86) 2006 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Tungsten monocarbide (12070-12-1) |
Safety information for Tungsten carbide
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H228:Flammable solids |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P240:Ground/bond container and receiving equipment. P241:Use explosion-proof electrical/ventilating/lighting/…/equipment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for Tungsten carbide
Tungsten carbide manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Tungsten carbide CASView Details
Tungsten carbide CASView Details -
 Tungsten carbide CASView Details
Tungsten carbide CASView Details -
 Tungsten carbide CASView Details
Tungsten carbide CASView Details -
 Tungsten carbide CASView Details
Tungsten carbide CASView Details -
 Tungsten carbide CASView Details
Tungsten carbide CASView Details -
 Tungsten carbide CASView Details
Tungsten carbide CASView Details -
 Tungsten carbide CASView Details
Tungsten carbide CASView Details -
 Tungsten carbide CASView Details
Tungsten carbide CASView Details
