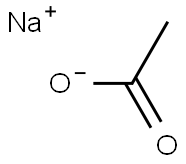
Sodium chlorite
Synonym(s):Scentrex DTS 1.20 sachet;Sodium chlorite
- CAS NO.:7758-19-2
- Empirical Formula: ClNaO2
- Molecular Weight: 90.44
- MDL number: MFCD00003478
- EINECS: 231-836-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:50:35
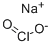
What is Sodium chlorite?
Chemical properties
It is a white crystalline powder or flakes that is readily soluble in water. It is slightly hygroscopic.
The Uses of Sodium chlorite
Sodium chlorite is used in the in situ generation of chlorine dioxide for stripping of textiles, bleaching, pulp and paper industries. It acts as a disinfectant in water treatment plant and as a preservative in eye drops. It is also used in contact lens cleaning solution and for sanitizing air ducts. It is associated with zinc chloride and used as a component in therapeutic rinses, toothpastes, mouth sprays and gels. It is utilized for the synthesis of 4-oxo-2-alkenoic acids from alkyl furans. Further, it is involved as a reagent in Pinnick oxidation reaction to prepare carboxylic acid from aldehydes.
The Uses of Sodium chlorite

A fresh solution of sodium phosphate buffer (40 mL, pH ~6.5) consisting of a 1:1 solution of NaH2PO4 (20 mL, 0.67 M) and Na2HPO4 (20 mL, 0.67 M) was prepared. A mixture of the SM (2.1 g, 8.64 mmol), TEMPO (0.094 g, 0.604 mmol), and sodium phosphate buffer (32.2 mL, 21.59 mmol, 0.67 M) in ACN (30 mL) heated to 35 C. Solutions of NaClO2 (3.91 g, 34.5 mmol) in H2O (4.5 mL) and bleach (4.3 mL, 6% wt) were added simultaneously over 40 min. The reaction was monitored by HPLC. After 2 h, ~30% SM remained. After 6 h, ~10% SM remained. Additional bleach (100 uL) was added, and the reaction was left at RT overnight. Additional bleach (100 uL) was added. The resulting mixture was stirred at 35 C for 2 h, after which time HPLC indicated a complete conversion. The reaction mixture was quenched by the slow addition of solution of Na2SO3 (2.07 mL, 43.2 mmol) in H2O (90 mL) at 0 C, resulting in the disappearance of the brown reaction color. The solvent was removed in vacuo, and the remaining aq residue was extracted with EtOAc (3 x 40 mL). The organics were combined, washed with H2O (8 mL), brine (8 mL), dried (Na2SO4), and concentrated to provide the product as a pale yellow solid. [2.2 g, 99%]
The Uses of Sodium chlorite
Sodium chlorite may be used in the synthesis of chlorine dioxide and as a hydroxylating agent for the hydroxylation of androstenedione (steroid).
What are the applications of Application
Sodium chlorite is an oxidative reagent
Definition
ChEBI: Sodium chlorite is an inorganic sodium salt in which chlorite is the counterion. It has a role as an oxidising agent. It is an inorganic sodium salt and a chlorite salt.
General Description
Sodium chlorite appears as a white crystalline solid. Difficult to burn, but accelerates the burning of organic substances. Forms explosive mixtures with certain combustible materials. May explode under prolonged exposure to heat or fire. Used in water purification, to bleach wood pulp, textile, fats, oils; and for many other uses.
Air & Water Reactions
Soluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
SODIUM CHLORITE SOLUTION is an oxidizing agent. Can react with acids to form spontaneously explosive chlorine dioxide gas (ClO2). Reacts with ammonia to produce ammonium chlorite, which is shock-sensitive. Finely divided metallic or organic substances in dry mixture with chlorites are highly flammable and may be ignited on friction (Lab. Gov. Chemist 1965). A mixture of organic matter and solid sodium chlorite can be extremely sensitive to heat, impact, or friction (Diox Process 1949). Sodium chlorite reacts very violently with organic materials containing divalent sulfur or with free sulfur (may ignite).
Hazard
Flammable, strong oxidizing agent, dan- gerous fire and moderate explosion risk. (Solution) Strong irritant to skin and tissue.
Health Hazard
TOXIC; inhalation, ingestion or skin contact with material may cause severe injury or death. Contact with molten substance may cause severe burns to skin and eyes. Avoid any skin contact. Effects of contact or inhalation may be delayed. Fire may produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may be corrosive and/or toxic and cause pollution.
Fire Hazard
Non-combustible, substance itself does not burn but may decompose upon heating to produce corrosive and/or toxic fumes. Some are oxidizers and may ignite combustibles (wood, paper, oil, clothing, etc.). Contact with metals may evolve flammable hydrogen gas. Containers may explode when heated.
Agricultural Uses
Chlorite is a group of greenish clay minerals of variable composition (similar to mica in structure), which crystallizes in the monoclinic system. The term chlorite is derived from 'chloros', the Greek word for green.
Chlorites are composed of complex silicates of aluminum, magnesium and iron in combination with water.
These are often called 2:2 type clays because they are similar to the unit lattice of vermiculite. But strictly speaking, they are 2:1:1 type clays. A layer of chlorite has 2 silicate tetrahedral units, one alumina octahedral unit and one magnesium octahedral sheet. It has a low cation exchange capacity. Chlorites are most commonly found in low-grade metamorphic rocks. They also occur as secondary minerals in igneous rocks as alteration products of pyroxenes, amphiboles and micas.
Chlorites are infrequent in soils and when present, make up a small fraction of clay minerals. Chlorites are primary minerals and form vermiculites and smectites. Chlorites do not swell on wetting.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion. An experimental teratogen. Experimental reproductive effects. Questionable carcinogen with experimental carcinogenic data. Mutation data reported. May act as an irritant due to its oxidizing power. A powerful oxidzing agent; ignited by friction, heat, or shock. An explosive sensitive to impact or heating to 200'. Potentially explosive reaction with acids, oils, organic matter, oxahc acid + water, zinc. Violent reaction or iption with carbon (above 60'), ethylene glycol (at loo'), phosphorus (above SO0), sodum dithionate, sulfur-containing materials. Can react vigorously on contact with reducing materials. When heated to decomposition it emits highly toxic fumes of Cland NazO. Used as a bleachmg agent. See also CHLORITES.
Purification Methods
Crystallise the chlorite from hot water and store it in a cool place. It has also been crystallised from MeOH by counter-current extraction with liquid ammonia [Curti & Locchi Anal Chem 29 534 1957]. A major impurity is chloride ion which can be removed by recrystallisation from 0.001M NaOH. [Schmeisser in Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry (Ed. Brauer) Academic Press Vol I p 312 1963.]
Properties of Sodium chlorite
| Melting point: | 190 °C (dec.) |
| Density | 2.5 g/cm3 |
| vapor pressure | 0Pa at 25℃ |
| solubility | Methanol (Slightly), Water (Slightly) |
| appearance | White solid |
| form | Powder |
| color | White |
| Odor | odorless |
| PH Range | 10 - 11 |
| explosive limit | 7% |
| Water Solubility | 39 g/100 mL (17 ºC) |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| Merck | 14,8600 |
| Dielectric constant | 6.1(Ambient) |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with phosphorus, sulphur, zinc, ammonia, finely powdered metals, strong reducing agents, acids, organic materials. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7758-19-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 3 (Vol. 52) 1991 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Sodium chlorite (7758-19-2) |
Safety information for Sodium chlorite
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Over Circle Oxidizers GHS03  Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H271:Oxidising liquids;Oxidising solids H302:Acute toxicity,oral H310:Acute toxicity,dermal H314:Skin corrosion/irritation H373:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H400:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, acute hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Sodium chlorite
Sodium chlorite manufacturer
Hunny Dye Chem
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Sodium chlorite CAS 7758-19-2View Details
Sodium chlorite CAS 7758-19-2View Details
7758-19-2 -
 Sodium chlorite CAS 7758-19-2View Details
Sodium chlorite CAS 7758-19-2View Details
7758-19-2 -
 Sodium chlorite CAS 7758-19-2View Details
Sodium chlorite CAS 7758-19-2View Details
7758-19-2 -
 Sodium chlorite CASView Details
Sodium chlorite CASView Details -
 Sodium Chlorite .View Details
Sodium Chlorite .View Details
7758-19-2 -
 Sodium Chlorite 22% Powder, 80%View Details
Sodium Chlorite 22% Powder, 80%View Details
7758-19-2 -
 Industrial Grade Sodium Chlorite 25% Liquid, CAS No.: 7758-19-2, 50 Kg DRUMView Details
Industrial Grade Sodium Chlorite 25% Liquid, CAS No.: 7758-19-2, 50 Kg DRUMView Details
7758-19-2 -
 Sodium Chlorite 31% DisinfectantView Details
Sodium Chlorite 31% DisinfectantView Details
7758-19-2
