Phosphorous acid
- CAS NO.:13598-36-2
- Empirical Formula: H3O3P
- Molecular Weight: 82
- MDL number: MFCD00137258
- EINECS: 237-066-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-10-14 12:08:39
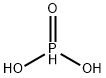
What is Phosphorous acid?
Description
Phosphorous acid, H3PO3, is diprotic (readily ionizes two protons), not triprotic as might be suggested by this formula. Phosphorous acid is as an intermediate in the preparation of other phosphorous compounds. Because preparation and uses of “phosphorous acid” actually pertain more to the major tautomer, phosphonic acid, it is more often referred to as “phosphorous acid”. Phosphorous acid has the chemical formula H3PO3, which is best expressed as HPO(OH)2 to show its diprotic character. P(OH)3 (IUPAC: phosphorous acid) has CAS number 10294-56-1. It has been shown to be a stable tautomer.
Chemical properties
Phosphorous acid is a white crystalline deliquescent solid that can be prepared by the action of water on phosphorus( III) oxide or phosphorus(III) chloride. It is a dibasic acid producing the anions H2PO3- and HPO3 2- in water. The acid and its salts are slow reducing agents. On warming, phosphonic acid decomposes to phosphine and phosphoric(V) acid. Phosphorus acid is used to prepare phosphite salts. It is usually sold as a 20% aqueous solution.
Physical properties
White crystalline mass; deliquescent; garlic-like odor; density 1.651 g/cm3 at 21°C; melts at 73.6°C; decomposes at 200°C to phosphine and phosphoric acid; soluble in water, about 310 g/100mL; K1 5.1x10-2 and K2 1.8x10-7; soluble in alcohol.
The Uses of Phosphorous acid
Phosphorous acid is used to produce the fertilizer phosphate salt like potassium phosphite, ammonium phosphite and calcium phosphite. It is actively involved in the preparation of phosphites like aminotris(methylenephosphonic acid) (ATMP), 1-hydroxyethane 1,1-diphosphonic acid (HEDP) and 2-phosphonobutane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic Acid (PBTC), which find application in water treatment as a scale or corrosive inhibitor. It is also used in chemical reactions as a reducing agent. Its salt, lead phosphite is used as PVC stabilizer. It is also used as a precursor in the preparation of phosphine and as an intermediate in the preparation of other phosphorus compounds.
Definition
ChEBI: Phosphorous acid is a phosphorus oxoacid. It is a conjugate acid of a dihydrogenphosphite. It is a tautomer of a phosphonic acid.
Preparation
Phosphorus acid can be prepared by the reaction of phosphorus trichloride with water: PCl3 + 3H2O → H3PO4 + 3HClThe reaction is violent. Addition of PCl3 should be extremely cautious and slow. The addition can be carried out safely in the presence of concentrated HCl. Alternatively, a stream of air containing PCl3 vapor is passed into icecold water and solid crystals of H3PO4 form. Alternatively, phosphorus acid can be prepared by adding phosphorus trichloride to anhydrous oxalic acid: PCl3 + 3(COOH)2 → H3PO3 + 3CO + 3CO2 + 3HCl In this reaction, all products except H3PO3 escape as gases leaving the liquid acid. Dissolution of phosphorus sesquioxide in water also forms phosphorus acid. When shaken with ice water, phosphorus acid is the only product . P4O6 + 6H2O → 4H3PO3 However, in hot water part of the phosphorus acid disproportionates to phosphoric acid and phosphorus or phosphine.
General Description
Phosphorous acid appears as a white or yellow crystalline solid (melting point 70.1 deg C) or a solution of the solid. Density 1.651 g /cm3 . Contact may severely irritate skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. Toxic by ingestion, inhalation and skin absorption.
Air & Water Reactions
Deliquescent. Absorbs oxygen from the air very readily to form phosphoric acid [Hawley]. Soluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Phosphorous acid decomposes when heated to form phosphine, a gas that usually ignites spontaneously in air. Absorbs oxygen from the air to form phosphoric acid [Hawley]. Forms yellow deposits in aqueous solution that are spontaneously flammable upon drying. Reacts exothermically with chemical bases (for example: amines and inorganic hydroxides) to form salts. These reactions can generate dangerously large amounts of heat in small spaces. Dissolution in water or dilution of a concentrated solution with additional water may generate significant heat. Reacts in the presence of moisture with active metals, including such structural metals as aluminum and iron, to release hydrogen, a flammable gas. Can initiate the polymerization of certain alkenes. Reacts with cyanide compounds to release gaseous hydrogen cyanide. May generate flammable and/or toxic gases in contact with dithiocarbamates, isocyanates, mercaptans, nitrides, nitriles, sulfides, and strong reducing agents. Additional gas-generating reactions occur with sulfites, nitrites, thiosulfates (to give H2S and SO3), dithionites (to give SO2), and carbonates (to give CO2).
Health Hazard
Phosphorous acid is toxic; inhalation, ingestion or skin contact with material may cause severe injury or death. Contact with molten substance may cause severe burns to skin and eyes. Avoid any skin contact. Effects of contact or inhalation may be delayed. Fire may produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may be corrosive and/or toxic and cause pollution.
Fire Hazard
Non-combustible, substance itself does not burn but may decompose upon heating to produce corrosive and/or toxic fumes. Some are oxidizers and may ignite combustibles (wood, paper, oil, clothing, etc.). Contact with metals may evolve flammable hydrogen gas. Containers may explode when heated.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Industrial uses
Phosphorous acid was developed recently and was used primarily as specific collector for cassiterite from ores with complex gangue composition.On the basis of the phosphonic acid, Albright and Wilson had developed a range of collectors mainly for flotation of oxidic minerals (i.e. cassiterite, ilmenite and pyrochlore). Very little is known about the performance of these collectors. Limited studies conducted with cassiterite and rutile ores showed that some of these collectors produce voluminous froth but were very selective.
Phosphorous acid application
Phosphorous acid (H3PO3, orthophosphorous acid) may be used as one of the reaction components for the synthesis of the following: α-aminomethylphosphonic acids via Mannich-Type Multicomponent Reaction 1-aminoalkanephosphonic acids via amidoalkylation followed by hydrolysis N-protected α-aminophosphonic acids (phospho-isosteres of natural amino acids) via amidoalkylation reaction
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by ingestion. When heated to decomposition at 200℃ it emits toxic fumes of POx and phosphme whch may ignite. See also PHOSPHINE.
Properties of Phosphorous acid
| Melting point: | 73 °C |
| Boiling point: | 200 °C |
| Density | 1.651 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor pressure | 0.001Pa at 20℃ |
| Flash point: | 200°C |
| storage temp. | 0-6°C |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly), Water (Sparingly) |
| pka | pK1 1.29; pK2 6.74(at 25℃) |
| form | Crystals |
| Specific Gravity | 1.651 |
| color | White |
| Water Solubility | SOLUBLE |
| Sensitive | Air Sensitive & Hygroscopic |
| Merck | 14,7346 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong bases. Hygroscopic. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 13598-36-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | (HO)2HPO(13598-36-2) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Phosphonic acid (13598-36-2) |
Safety information for Phosphorous acid
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H290:Corrosive to Metals H302:Acute toxicity,oral H314:Skin corrosion/irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P234:Keep only in original container. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Phosphorous acid
Phosphorous acid manufacturer
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Phosphorous acid CAS 13598-36-2View Details
Phosphorous acid CAS 13598-36-2View Details
13598-36-2 -
 13598-36-2 99%View Details
13598-36-2 99%View Details
13598-36-2 -
 Phosphorous Acid Crystals (Phosphonic Acid) extrapure CAS 13598-36-2View Details
Phosphorous Acid Crystals (Phosphonic Acid) extrapure CAS 13598-36-2View Details
13598-36-2 -
 Phosphonic Acid CASView Details
Phosphonic Acid CASView Details -
 Phosphorous acid CAS 13598-36-2View Details
Phosphorous acid CAS 13598-36-2View Details
13598-36-2 -
 Phosphonic Acid CASView Details
Phosphonic Acid CASView Details -
 Phosphorous acid solution CAS 13598-36-2View Details
Phosphorous acid solution CAS 13598-36-2View Details
13598-36-2 -
 Phosphorous Acid .View Details
Phosphorous Acid .View Details
13598-36-2
