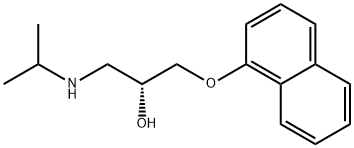
Propranolol hydrochloride
Synonym(s):(±)-1-Isopropylamino-3-(1-naphthyloxy)-2-propanol hydrochloride;(±)-Propranolol hydrochloride;DL -Propranolol hydrochloride
- CAS NO.:318-98-9
- Empirical Formula: C16H22ClNO2
- Molecular Weight: 295.8
- MDL number: MFCD00012558
- EINECS: 206-268-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-11-20 17:40:16

What is Propranolol hydrochloride?
Chemical properties
Off-White to Light-Yellow Cyrstalline Solid
The Uses of Propranolol hydrochloride
(±)-Propranolol hydrochloride has been used:
- to determine whether autonomic nervous system mediated the promotive effect on skin microcirculation in rat
- as a non-selective β- receptor blocker to reduce the arrhythmogenic events
- to study its effect on oxygen-induced retinopathy in mice
The Uses of Propranolol hydrochloride
β?Adrenergic blocker. Antihypertensive; antianginal; antiarrhythmic (class II).
The Uses of Propranolol hydrochloride
For the prophylaxis of migraine
The Uses of Propranolol hydrochloride
Propranolol, a β-adrenergic blocker, is most commonly used to reduce blood pressure; treatment of over-active thyroid and some types of tremor; prevention of migraine headaches and some heart-rhythm problems; used to decrease the number of angina attacks (pain from an inadequate oxygen supply to the heart); used after a heart attack to prevent further damage to the heart.
brand name
Inderal (Wyeth); Innopran (Reliant).
General Description
Propranolol hydrochloride is easily soluble in ethanol and water.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Propranolol hydrochloride is a β-adrenoceptor antagonist. Its action at β2 receptor results in bronchoconstriction. Due to its lipophilic nature, propranolol can penetrate to the central nervous system and has a negative effect. It serves as a 5-HT1/5-HT2 serotonin receptor antagonist. Propranolol hydrochloride is useful as an antihypertensive drug, cardiac depressant and also in the treatment of angina pectoris. It decreases the effect of stress and exercise on heart by reducing the rate of contraction and conduction of impulse. It is known to competitively block the action of catecholamines.
Clinical Use
Beta-adrenoceptor blocker:
Hypertension
Phaeochromocytoma
Angina
Arrhythmias
Anxiety
Migraine prophylaxis
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
While propranolol is used for hypertension, migraine headache prophylaxis, and angina in human patients, it is used primarily in veterinary medicine for its antiarrhythmic effects. Dysrhythmias treated with propranolol include: atrial premature complexes, ventricular premature complexes, supraventricular premature complexes and tachyarrhythmias, ventricular or atrial tachyarrhythmias secondary to digitalis, atrial tachycardia secondary to Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) with normal QRS complexes, and atrial fibrillation (generally in combination with digoxin). Propranolol reportedly improves cardiac performance in animals with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. It has been used to treat systemic hypertension and clinical signs associated with thyrotoxicosis and pheochromocytoma.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Anaesthetics: enhanced hypotensive effect; risk of
bupivacaine toxicity increased.
Analgesics: NSAIDs antagonise hypotensive effect.
Anti-arrhythmics: increased risk of myocardial
depression and bradycardia; increased risk of
bradycardia, myocardial depression and AV block
with amiodarone; concentration increased by
propafenone and possibly dronedarone; increased
risk of myocardial depression and bradycardia with
flecainide; increased risk of lidocaine toxicity.
Antibacterials: metabolism increased by rifampicin.
Antidepressants: enhanced hypotensive effect with
MAOIs; concentration increased by fluvoxamine;
concentration of imipramine increased.
Antihypertensives; enhanced hypotensive effect;
increased risk of withdrawal hypertension with
clonidine; increased risk of first dose hypotensive
effect with post-synaptic alpha-blockers such as
prazosin.
Antimalarials: increased risk of bradycardia with
mefloquine.
Antipsychotics enhanced hypotensive effect with
phenothiazines; concentration of both drugs
increased with chlorpromazine.
Calcium-channel blockers: increased risk of
bradycardia and AV block with diltiazem;
hypotension and heart failure possible with
nifedipine and nisoldipine; asystole, severe
hypotension and heart failure with verapamil.
Cytotoxics: possible increased risk of bradycardia
with crizotinib.
Diuretics: enhanced hypotensive effect.
Fingolimod: possibly increased risk of bradycardia.
Moxisylyte: possible severe postural hypotension.
Sympathomimetics: severe hypertension with
adrenaline and noradrenaline and possibly with
dobutamine.
Metabolism
Propranolol is subject to considerable hepatic-tissue
binding and first-pass metabolism. It is metabolised in the
liver to an active metabolite (4-hydroxypropranolol) and
several inactive ones.
The metabolites and small amounts of unchanged drug
are excreted in the urine.
Storage
Store at RT
Properties of Propranolol hydrochloride
| Melting point: | 163-165 °C(lit.) |
| Flash point: | 9℃ |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | H2O: 50 mg/mL, clear, colorless |
| form | powder |
| color | white |
| Water Solubility | SOLUBLE |
| Merck | 14,7840 |
| BRN | 4164259 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 318-98-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Propranolol hydrochloride (318-98-9) |
Safety information for Propranolol hydrochloride
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
Computed Descriptors for Propranolol hydrochloride
| InChIKey | ZMRUPTIKESYGQW-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Propranolol hydrochloride manufacturer
Padmavati Pharmachem
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 318-98-9 95-99 %View Details
318-98-9 95-99 %View Details
318-98-9 -
 Propranolol HCl 98% CAS 318-98-9View Details
Propranolol HCl 98% CAS 318-98-9View Details
318-98-9 -
 (±)-Propranolol hydrochloride CAS 318-98-9View Details
(±)-Propranolol hydrochloride CAS 318-98-9View Details
318-98-9 -
 Propranolol hydrochloride CAS 318-98-9View Details
Propranolol hydrochloride CAS 318-98-9View Details
318-98-9 -
 Propranolol hydrochloride CAS 318-98-9View Details
Propranolol hydrochloride CAS 318-98-9View Details
318-98-9 -
 (±)-Propranolol hydrochloride CAS 318-98-9View Details
(±)-Propranolol hydrochloride CAS 318-98-9View Details
318-98-9 -
 Propranolol hydrochloride CAS 318-98-9View Details
Propranolol hydrochloride CAS 318-98-9View Details
318-98-9 -
 Propranolol Hydrochloride (318-98-9)View Details
Propranolol Hydrochloride (318-98-9)View Details
318-98-9
