Propanolol
- CAS NO.:525-66-6
- Empirical Formula: C16H21NO2
- Molecular Weight: 259.34
- EINECS: 208-378-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-07-04 15:23:57
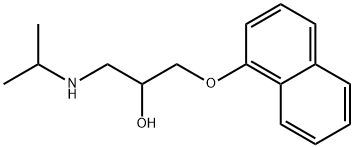
What is Propanolol?
Absorption
Patients taking doses of 40mg, 80mg, 160mg, and 320mg daily experienced Cmax values of 18±15ng/mL, 52±51ng/mL, 121±98ng/mL, and 245±110ng/mL respectively. Propranolol has a Tmax of approximately 2 hours, though this can range from 1 to 4 hours in fasting patients. Taking propranolol with food does not increase Tmax but does increase bioavailability.
Toxicity
Symptoms of overdose include hypotension, hypoglycemic seizure, restlessness, euphoria, insomnia. Patients with asthma may develop bronchospasm. In case of overdose, monitor vital signs, mental status, and blood glucose. Treat hypotension with intravenous fluids, bradycardia with atropine, and isoproterenol and aminophylline for bronchospasm. If patients do not respond to intravenous fluids, follow up with glucagon 50-150μg/kg intravenously, then 1-5mg/hour, followed by catecholamines. Dialysis will not be useful as propranolol is highly protein bound.
Description
Propranolol was responsible for sensitisation of workers in drug synthesis. In one case, epichlorhydrin was used for the production of both propranolol and oxprenolol.
Chemical properties
Colorless crystals.Soluble in water and alcohol; insoluble in benzene and ether.
The Uses of Propanolol
Cardiac depressant (anti-arrhythmic); anti-adrenergic (β-receptor).
The Uses of Propanolol
β?Adrenergic blocker. Antihypertensive; antianginal; antiarrhythmic (class II).
Background
Propranolol is a racemic mixture of 2 enantiomers where the S(-)-enantiomer has approximately 100 times the binding affinity for beta adrenergic receptors. Propranolol is used to treat a number of conditions but most commonly is used for hypertension.
Propranolol was granted FDA approval on 13 November 1967.
Indications
Propranolol is indicated to treat hypertension. Propranolol is also indicated to treat angina pectoris due to coronary atherosclerosis, atrial fibrillation, myocardial infarction, migraine, essential tremor, hypertrophic subaortic stenosis, pheochromocytoma, and proliferating infantile hemangioma.
Definition
ChEBI: A propanolamine that is propan-2-ol substituted by a propan-2-ylamino group at position 1 and a naphthalen-1-yloxy group at position 3.
Indications
Major indications of propranolol, and of many other β-blockers, include coronary heart disease, hypertension, and cardiac arrhythmias. These β-blocking agents are mainly used in arrhythmias accompanied by increased catecholamine levels, e.g., excitement, stress, or hyperthyroidism .
brand name
Inderal (Wyeth); Innopran (Reliant).
Hazard
Highly toxic.
Contact allergens
Propranolol is a beta-blocking agent that was responsible for the sensitization of workers in drug synthesis. In one case, epichlorhydrin was used for the production of drugs propranolol and oxprenolol. Crossreactivity is expected between beta-blockers.
Pharmacokinetics
Propranolol is a beta-adrenergic receptor antagonist used to treat hypertension. Propranolol has a long duration of action as it is given once or twice daily depending on the indication. When patients abruptly stop taking propranolol, they may experience exacerbations of angina and myocardial infarctions.
Metabolism
Propranolol undergoes side chain oxidation to α-naphthoxylactic acid, ring oxidation to 4’-hydroxypropranolol, or glucuronidation to propranolol glucuronide. It can also be N-desisopropylated to become N-desisopropyl propranolol. 17% of a dose undergoes glucuronidation and 42% undergoes ring oxidation.
Properties of Propanolol
| Melting point: | 163-164 °C |
| Boiling point: | 402.6°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.0280 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5500 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | -20°C Freezer, Under inert atmosphere |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 13.84±0.20(Predicted) |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Water Solubility | 80.99mg/L(25 ºC) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 525-66-6 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Propranolol(525-66-6) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 2-Propanol, 1-[(1-methylethyl)amino]-3-(1-naphthalenyloxy)- (525-66-6) |
Safety information for Propanolol
Computed Descriptors for Propanolol
Propanolol manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
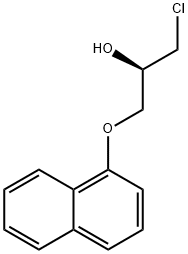
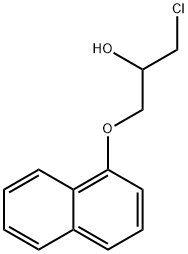
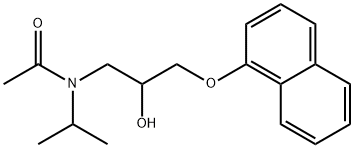
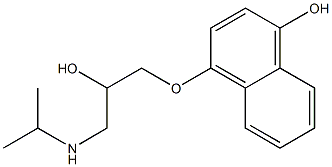
![PROPANOLOL, L-[4-3H]-](https://img.chemicalbook.in/StructureFile/ChemBookStructure2/GIF/CB4391069.gif)
You may like
-
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 1-methylindoline-2,3-dione 98%View Details
1-methylindoline-2,3-dione 98%View Details
2058-74-4 -
 614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 -
 3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
