Obeticholic Acid
Synonym(s):(3α,5β, 6α,7α)-6-ethyl-3,7-dihydroxy-cholan-24-oic acid;6a-Ethyl-Chenodeoxycholic Acid;6-ECDCA;OCA
- CAS NO.:459789-99-2
- Empirical Formula: C26H44O4
- Molecular Weight: 420.63
- MDL number: MFCD16621104
- EINECS: 810-245-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-16 16:15:04
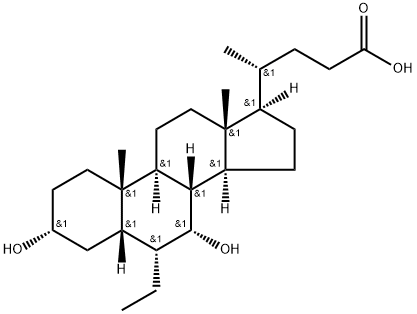
What is Obeticholic Acid?
Absorption
Obeticholic acid is absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract. The Cmax of obeticholic acid occurs at approximately 1.5 hours after an oral dose and ranges from 28.8-53.7 ng/mL at doses of 5-10mg. The median Tmax for both the conjugates of obeticholic acid is about 10 hours. One product monograph reports a Tmax of 4.5h for both 5 and 10mg doses. The AUC ranged from 236.6-568.1 ng/h/mL with 5mg to 10 mg doses.
Toxicity
LD50 information for obeticholic acid is not readily available in the literature.
The maximum documented exposure to obeticholic acid was 500 mg in healthy research volunteers. Doses of 250 mg have been administered to healthy volunteers for 12 consecutive days. Pruritus and reversible transaminase liver elevations were observed. In PBC patients who received 25mg daily to 50mg daily (2.5 to 5 times the maximum recommended dose), dose-dependent transaminase and bilirubin elevations, ascites, primary biliary cholangitis aggravation, and new-onset jaundice were reported.
In the case of an overdose with obeticholic acid, clinical monitoring and supportive care should be offered as they are required.
Description
Obeticholic acid (OCA) is a semisynthetic bile acid that is analogous to the natural acid chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA). One of the two primary bile acids produced in the human liver, CDCA is the most active physiological ligand for the farnesoid X receptor (FXR).
FXR has several biochemical functions in the liver and intestine. In response to the rise of the virulent liver disease nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), researchers have identified FXR as the one of the key targets for treating it.
Description
Obeticholic acid is a potent and selective farnesoid X receptor agonist that promotes the flow of bile in the liver. The drug was approved by the USFDA for the treatment of the rare chronic liver disease primary biliary cholangitis (PBC) in combination with ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) in adults with inadequate response to UDCA or as a single agent therapy in adults unable to tolerate UDCA. Obeticholic acid was discovered at the Università de Perugia and developed by Intercept Pharmaceuticals. Obeticholic acid has also been granted orphan drug designation for the treatment of primary sclerosing cholangitis and primary biliary cirrhosis and has received breakthrough therapy designation for the treatment of patients with nonalcohol steatohepatitis (NASH) with liver fibrosis.
The Uses of Obeticholic Acid
6-Ethylchenodeoxycholic Acid is a derivative of the bile acid Chenodeoxycholic Acid (C291900). 6-Ethylchenodeoxycholic Acid is a potent activator of the farnesoid X nuclear receptor which reduces liver fat and fibrosis in animal models of fatty liver disease.
Indications
Obeticholic acid is indicated for the treatment of primary biliary cholangitis in combination with ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) in adults with an inadequate response to UDCA. It is also used as a monotherapy in adults with PBC that are unable to tolerate UDCA.
Obeticholic acid is currently being considered for FDA approval to treat fibrosis caused by non-alcoholic liver steatohepatitis (NASH), and is likely to be approved for this indication in 2020.
Background
Primary biliary cirrhosis, or PBC, is a progressive and chronic condition that leads to hepatic injury often resulting in end-stage liver failure that requires liver transplantation.
Obeticholic acid is a farnesoid-X receptor (FXR) agonist used to treat this condition, possibly allowing for increased survival. In 2016, it was granted approval to treat primary biliary cholangitis in combination with ursodeoxycholic acid, which was previously the mainstay treatment for this condition. In May 2021, the FDA updated its prescribing information to contraindicate the use of obeticholic acid in patients with PBC and advanced cirrhosis (e.g. those with portal hypertension or hepatic decompensation) due to a risk of liver failure, in some cases requiring liver transplantation.
Definition
ChEBI: A dihydroxy-5beta-cholanic acid that is chenodeoxycholic acid carrying an additional ethyl substituent at the 6alpha-position. A semi-synthetic bile acid which acts as a farnesoid X receptor agonist and is used for treatme t of primary biliary cholangitis.
Pharmacokinetics
The activation of the FXR by obeticholic acid acts to reduce the synthesis of bile acids, inflammation, and the resulting hepatic fibrosis. This may increase the survival of patients with PBC, but to date, an association between obeticholic acid and survival in PBC has not been established.
Synthesis
The synthesis of obeticholic acid was initiated from commercial 3|á-hydroxy-7-keto-5|?-cholan-24-oic acid (138). Fischer esterification of 138 provided methyl ester 139, which was treated with trimethylsilyl chloride and triethylamine to protect the secondary alcohol. Reaction of the protected alcohol with lithium diisopropylamine and trimethylsilyl chloride gave silyl enol ether 140. Aldol condensation with acetaldehyde and boron trifluoride etherate followed by saponification of the methyl ester produced enone 141. Hydrogenation of the olefin followed by heating to reflux to epimerize the resulting ethyl group produced the |á-ethyl ketone 142 in 62% yield from compound 138. Reduction of the ketone in 142 with sodium borohydride and subsequent crystallization from phosphoric acid and water gave obeticholic acid (XIV) in 90% yield.

Enzyme inhibitor
This semisynthetic bile acid analogue (FW = 420.63 g/mol; CAS 459789- 99-2), also named INT-747, 6α-ethyl-chenodeoxycholate, and (3α,5β,6α, 7α)-6-ethyl-3,7-dihydroxycholan-24-oic acid, is an analogue of the naturally occurring bile acid (FW = 392.57 g/mol; CAS 474-25-9). The latter is synthesized in the liver, where it conjugated to form taurochenodeoxycholate and glycol-chenodeoxycholate, reducing its pKa and increasing retention in the gastrointestinal tract, until reabsorption by the ileum. Chenodeoxycholate is the most active physiological ligand known for the farnesoid X receptor, or FXR (encoded by the NR1H4 gene in humans) that translocates to the nucleus, dimerizes, and binds to hormone response elements. Obeticholic acid reduces bacterial translocation and invasion in cirrhotic rats by restoring intestinal barrier integrity (through increased expression of tight junction proteins) and by inhibiting inflammation. Obeticholate likewise up-regulated expression of the FXR-associated gene small heterodimer partner (SHP).
Metabolism
The metabolism of obeticholic acid occurs in the liver. Obeticholic acid is conjugated with glycine or taurine, followed by secretion into bile. The conjugates are then absorbed in the small intestine and then re-enter the liver via enterohepatic circulation. The intestinal microbiota in the ileum converts conjugated obeticholic acid in a deconjugated form that may be either reabsorbed or eliminated. Glycine conjugates account for 13.8% of the metabolites and taurine conjugates account for 12.3%. Another metabolite, 3-glucuronide, may also be formed, but displays little pharmacological activity.
Storage
+4°C
References
1) Fiorucci?et al.?(2005),?Protective effects of 6-ethyl chenodeoxycholic acid, a farnesoid X receptor ligand, in estrogen-induced cholestasis; J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.,?313?604 2) Rizzo?et al. (2006),?The farnesoid X receptor promotes adipocyte differentiation and regulates adipose cell function in vivo;?Mol. Pharmacol.,?70?1164 3) Maneschi?et al.?(2013),?FXR activation normalizes insulin sensitivity in visceral preadipocytes of a rabbit model of MetS; J. Endocrinol.,?218?215 4) Carr and Reid (2015),?FXR agonists as therapeutic agents for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; Curr. Atheroscler. Rep,?17?500 5) Jahn?et al. (2016),?Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis: From Pathophysiology to Novel Therapies; Dig. Dis.,?34?356 6) Hirschfield?et al. (2015),?Efficacy of obeticholic acid in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis and inadequate response to ursodeoxycholic acid; Gastroenterology,?148?751
Properties of Obeticholic Acid
| Melting point: | 108-110 °C |
| Boiling point: | 562.9±25.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.091 |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | Soluble in DMSO (up to 35 mg/ml) or in Ethanol (up to 25 mg/ml) |
| form | White solid. |
| pka | 4.76±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | White |
| Stability: | Stable for 2 years from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions in DMSO or ethanol may be stored at -20°C for up to 2 months. |
Safety information for Obeticholic Acid
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Obeticholic Acid
Obeticholic Acid manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![4-[2-(4-Amino-1,2,5-oxadiazol-3-yl)-1-ethyl-7-[(3S)-3-piperidinylmethoxy]-1H-imidazo[4,5-c]pyridin-4-yl]-2-methyl-3-butyn-2-ol](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS2/GIF/937174-76-0.gif)
You may like
-
 459789-99-2 98%View Details
459789-99-2 98%View Details
459789-99-2 -
 Obeticholic acid 99%View Details
Obeticholic acid 99%View Details -
 Obeticholic acid 459789-99-2 98%View Details
Obeticholic acid 459789-99-2 98%View Details
459789-99-2 -
 459789-99-2 98%View Details
459789-99-2 98%View Details
459789-99-2 -
 Obeticholic acid 459789-99-2 98%View Details
Obeticholic acid 459789-99-2 98%View Details
459789-99-2 -
 459789-99-2 98%View Details
459789-99-2 98%View Details
459789-99-2 -
 INT-747 98% (HPLC) CAS 459789-99-2View Details
INT-747 98% (HPLC) CAS 459789-99-2View Details
459789-99-2 -
 6-Ethylchenodeoxycholic acid CASView Details
6-Ethylchenodeoxycholic acid CASView Details
