Methylglyoxal
Synonym(s):Acetylformaldehyde;Methylglyoxal solution;Pyruvaldehyde;Pyruvic aldehyde
- CAS NO.:78-98-8
- Empirical Formula: C3H4O2
- Molecular Weight: 72.06
- MDL number: MFCD00006960
- EINECS: 201-164-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:07:02
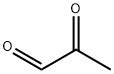
What is Methylglyoxal?
Description
Methylglyoxal (MG) is a highly reactive a-dicarbonyl compound that is primarily generated endogenously during glycolytic pathways (glucose and fructose metabolism) in cells and exogenously due to autoxidation of sugar, degradation of lipids, and fermentation during food and drink processing. Methylglyoxal polymerizes readily; it is hygroscopic and incompatible with strong oxidizing agents and bases. Methylglyoxal may be present as a free molecule in the diet or bound to biological materials, such as proteins, and as advanced glycation end products (AGEs), which are poorly absorbed. Methylglyoxal has been indicated in pathological events associated with hyperglycemia in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes and in other diabetic complications as either a direct toxin or as a precursor for AGEs. In animal studies, MG has been shown to induce tumorigenesis, but has also been reported as a tumoristatic agent. Methylglyoxal has been identified as the dominant antibacterial constituent of manuka honey.
Chemical properties
clear yellow to yellow-brown solution
Chemical properties
Pyruvaldehyde has a characteristic, pungent, stinging odor with a pungent, caramellic, sweet flavor.
Occurrence
Reported found in the dry distillate of Manilla copal. Also reported found in apple juice, orange juice, celery root, rutabaga, tomato, wheaten bread, white bread, roasted and raw turkey, cognac, roasted barley, beer, cocoa, coffee and roasted pecans.
The Uses of Methylglyoxal
Methylglyoxal solution has been used:
- to assess glyoxalase 1 (GLO1) enzymatic activity
- as an advanced glycation end (AGE) forming agent for the preparation of albumin in vitro
- to regulate anxiety like behavior in mice
- to induce peritoneal fibrosis in rats
- to study the chromatographic retention characteristics of organic chemicals and metal DNA adducts
- for intraplantar injection in mice to investigate peripheral and central components of methylglyoxal (MG)-transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 (TRPA1)-adenylyl cyclase 1 isoform (AC1) pathway
The Uses of Methylglyoxal
Organic synthesis, as of complex chemical com- pounds such as pyrethrins, tanning leather, flavor- ing.
The Uses of Methylglyoxal
Used in organic synthesis, as a flavoring agent, and in tanning leather. Commercial formulation is available as a 30% aqueous solution. No safety concern at current levels of intake when used as a flavoring agent.
Definition
ChEBI: A 2-oxo aldehyde derived from propanal.
Preparation
By distilling a dilute solution of dihydroxyacetone from calcium carbonate; by oxidation of acetone with selenium dioxide; by heating dihydroxy acetone with phosphorus pentoxide; by warming isonitroso acetone with diluted H2SO4.
Taste threshold values
Taste characteristics at 0.1%: sweet, caramellic with a dairy creamy nuance
General Description
Clear yellow slightly viscous liquid with a pungent odor. Yellowish-green vapors. Faintly acidic to litmus.
Air & Water Reactions
Water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
Methylglyoxal polymerizes readily. Methylglyoxal is hygroscopic. Methylglyoxal is incompatible with strong oxidizing agents and bases. Methylglyoxal is an aldehyde. Aldehydes are frequently involved in self-condensation or polymerization reactions. These reactions are exothermic; they are often catalyzed by acid. Aldehydes are readily oxidized to give carboxylic acids. Flammable and/or toxic gases are generated by the combination of aldehydes with azo, diazo compounds, dithiocarbamates, nitrides, and strong reducing agents. Aldehydes can react with air to give first peroxo acids, and ultimately carboxylic acids. These autoxidation reactions are activated by light, catalyzed by salts of transition metals, and are autocatalytic (catalyzed by the products of the reaction). The addition of stabilizers (antioxidants) to shipments of aldehydes retards autoxidation.
Fire Hazard
Literature sources indicate that Methylglyoxal is nonflammable.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Environmental Fate
Methylglyoxal production and use as a chemical intermediate
and flavoring agent may result in its release to the environment
through various waste streams. If released into water, MG is not
expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based on
the estimated Koc. Volatilization from water surfaces is not
expected to be an important fate process based upon the estimated
Henry’s Law constant. If released to soil, MG is expected
to have very high mobility based upon an estimated Koc of 1
determined from the structure estimation method. Hydrolysis
is not expected to be an important environmental fate process
since this compound lacks functional groups that hydrolyze
under environmental conditions.
Methylglyoxal serves as a substrate for the isozymes E1, E2,
and E3 of human aldehyde dehydrogenase. Oxidation of MG
by these isozymes generated pyruvate. Methylglyoxal is
a partially oxidized compound obtained from the tropospheric
oxidation of numerous hydrocarbons, of both biogenic and
anthropogenic origin. If released to the air, an estimated vapor
pressure of 27 mm Hg at 25 ℃ indicates MG will exist solely as
a vapor in the atmosphere. Vapor-phase MG will be degraded
in the atmosphere by reaction with photochemically produced
hydroxyl radicals; the half-life for this reaction in air is estimated
to be 30 h. Methylglyoxal absorbs light at wavelengths
>290 nm and, therefore, is susceptible to direct photolysis by
sunlight; half-lives of 2–4 h have been reported.
Purification Methods
Commercial 30% (w/v) aqueous solution is diluted to about 10% and distilled twice, taking the fraction boiling below 50o/20mm Hg. (This treatment does not remove lactic acid). [Beilstein 1 IV 3631.]
Toxicity evaluation
Endogenously formed MG modifies arginine and lysine residues in proteins that form AGEs, which have been associated with diabetic complications and some neurodegenerative diseases. In different cell lines, MG treatment has been shown to induce apoptosis as measured by nuclear fragmentation and apoptotic body formation, indicating an increase in apoptosis. At the mitochondrial level, exogenous MG is highly toxic as it promotes proliferation, swelling, and membrane derangement. In both in vitro and in vivo studies, MG treatment has been shown to significantly reduce antioxidant enzymes and elevate reactive oxygen species that lead to oxidative stress-mediated cell death. Genotoxicity has been observed in both in vivo and in vitro studies, as MG is capable of binding to cellular macromolecules and forming DNA adducts.
Properties of Methylglyoxal
| Melting point: | 25 °C |
| Boiling point: | 72 °C |
| Density | 1.19 g/mL at 20 °C |
| vapor pressure | 25.09hPa at 20℃ |
| refractive index | n |
| RTECS | UZ0700000 |
| FEMA | 2969 | PYRUVALDEHYDE |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly), Water (Soluble) |
| form | Solution |
| color | Clear yellow to yellow-brown |
| Odor | at 1.00 % in propylene glycol. sweet acidic ethereal brown rum |
| Water Solubility | >=10 g/100 mL at 17 ºC |
| Sensitive | Air Sensitive |
| JECFA Number | 937 |
| Merck | 14,6081 |
| BRN | 906750 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 78-98-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 3 (Vol. 51) 1991 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Propanal, 2-oxo-(78-98-8) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Methylglyoxal (78-98-8) |
Safety information for Methylglyoxal
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H290:Corrosive to Metals H317:Sensitisation, Skin H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H341:Germ cell mutagenicity |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P234:Keep only in original container. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Methylglyoxal
| InChIKey | AIJULSRZWUXGPQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Methyl glyoxal, 40% solution CAS 78-98-8View Details
Methyl glyoxal, 40% solution CAS 78-98-8View Details
78-98-8 -
 Pyruvaldehyde CAS 78-98-8View Details
Pyruvaldehyde CAS 78-98-8View Details
78-98-8 -
 PYRUVICALDEHYDE 40%AQ.SOL. CAS 78-98-8View Details
PYRUVICALDEHYDE 40%AQ.SOL. CAS 78-98-8View Details
78-98-8 -
 Methylglyoxal solution CAS 78-98-8View Details
Methylglyoxal solution CAS 78-98-8View Details
78-98-8 -
 Methylglyoxal solution CAS 78-98-8View Details
Methylglyoxal solution CAS 78-98-8View Details
78-98-8 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1