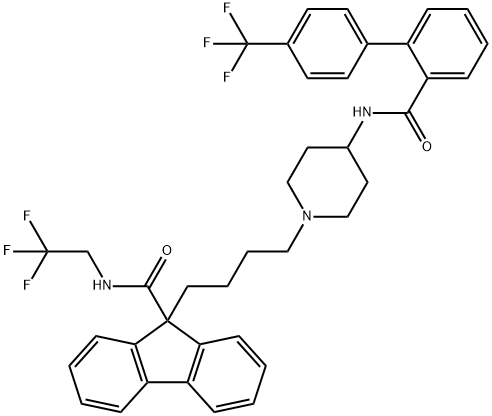
Lomitapide
Synonym(s):AEGR-733;BMS-201038;N-(2,2,2-Trifluoroethyl)-9-[4-[4-[[[4′-(trifluoromethyl)[1,1′-biphenyl]2-yl]carbonyl]amino]-1-piperidinyl]butyl]9H-fluoren-9-carboxamde
- CAS NO.:182431-12-5
- Empirical Formula: C39H37F6N3O2
- Molecular Weight: 693.72
- MDL number: MFCD16620494
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
What is Lomitapide?
Absorption
In healthy patients, time to maximum lomitapide concentration is about 6 hours with a single dose of 60 mg. Lomitapide has an approximate absolute bioavailability of 7%.
Toxicity
Contra-indicated in pregnancy, and moderate to severe hepatic insufficiency (Child-Pugh category B or C). Severe GI adverse reactions may occur.
Description
Lomitapide was approved by the US FDA in December 2012 for the treatment of patients with familial hypercholesteremia (referred to as HoFH) in conjunction with a low-fat diet andother lipid-lowering treatments. Lomitapide was discovered from a high-through put screen that identified several structurally distinct MTP inhibitors. Combination of key structural features from two structurally distinct HTS hits provided potent MTP inhibitors. Parallel analog synthesis led to lomitapide as an optimized structure. Lomitapide was synthesized via alkylation of 9-fluorenylcarboxylic acid with 1,4-dibromobutane which, after trifluoroethylamide formation, provided a bromide intermediate that was displaced by Boc-4-aminopiperidine. Introduction of the 4'-trifluoromethylbiphenylcarboxamide gave lomitapide, which was found to inhibit MTP with an IC50 of 0.5 nM and to exhibit good cholesterol-lowering efficacy in Sprague–Dawley rats (intravenous and oral ED50~0.2 mg/kg).
Description
The drug lomitapide was originally developed to reduce low-density lipids (“bad” cholesterol) but failed in Phase I clinical trials.?M. Beer and colleagues at Aegerion Pharmaceuticals (Cambridge, MA), however, “rescued” lomitapide?by developing it as a treatment for the orphan disease homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HoFH), a genetic disorder that affects the liver and often causes heart failure. Lomitapide inhibits the microsomal triglyceride transfer protein needed for the assembly of bad cholesterol and its secretion in the liver. Aegerion and its pharmaceutical services partner, Aptuit (Greenwich, CT), rushed lomitapide through trials; and the US FDA approved as an HoFH drug.
Originator
Bristol-Myers Squibb (United States)
The Uses of Lomitapide
Lomitapide has been used as a microsomal triglyceride transfer protein (MTP) inhibitor to study its effects on very-low-density lipoproteins (VLDL) export in mouse hepatocytes.
Indications
Used in homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HoFH) patients to reduce low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), total cholesterol (TC), apolipoprotein B (apo B), and non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (non-HDL-C).
Background
Lomitapide is a microsomal triglyceride transfer protein (MTP) inhibitor used in homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HoFH) patients. It is marketed under the name Juxtapid (R).
Definition
ChEBI: Lomitapide is a member of the class of benzamides obtained by formal condensation of the carboxy group of 4'-(trifluoromethyl)biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid with the primary amino group of 9-[4-(4-aminopiperidin-1-yl)butyl]-N-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-9H-fluorene-9-carboxamide. Used (as its mesylate salt) as a complement to a low-fat diet and other lipid-lowering treatments in patients with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. It has a role as an anticholesteremic drug and a MTP inhibitor. It is a member of piperidines, a member of fluorenes, a member of benzamides and a member of (trifluoromethyl)benzenes. It is a conjugate base of a lomitapide(1+).
brand name
Juxtapid
Biochem/physiol Actions
Lomitapide is an inhibitor of microsomal triglyceride transfer protein (MTP). Lomitapide has been shown to be highly effective in reducing LDL-cholesterol and triglycerides, and has been aproved for treatment of homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia.
Pharmacokinetics
Lomitapide directly inhibits microsomal triglyceride transfer protein (MTP).
Metabolism
Lomitapide is mainly metabolized by CYP3A4 to it's inactive metabolites, M1 and M3. CYP enzymes that metabolize lomitapide to a minor extent include CYP 1A2,2B6,2C8,2C19.
Properties of Lomitapide
| Melting point: | 142°C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 778.2±60.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.34±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| pka | 12.66±0.20(Predicted) |
| form | powder |
| color | white to beige |
Safety information for Lomitapide
Computed Descriptors for Lomitapide
Lomitapide manufacturer
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 182431-12-5 Lomitapide 98%View Details
182431-12-5 Lomitapide 98%View Details
182431-12-5 -
 182431-12-5 98%View Details
182431-12-5 98%View Details
182431-12-5 -
 Lomitapide CAS 182431-12-5View Details
Lomitapide CAS 182431-12-5View Details
182431-12-5 -
 Lomitapide CAS 182431-12-5View Details
Lomitapide CAS 182431-12-5View Details
182431-12-5 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8