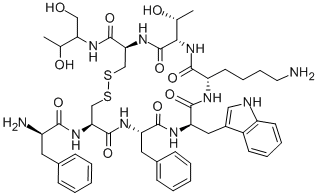
Linaclotide
- CAS NO.:851199-59-2
- Empirical Formula: C59H79N15O21S6
- Molecular Weight: 1526.74
- MDL number: MFCD20526656
- EINECS: 251-228-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33

What is Linaclotide?
Absorption
Linaclotide is minimally absorbed with negligible systemic availability following oral administration; however, systemic exposure is not of importance for the maximal effects of linaclotide, as the ligand-binding domain of the GC-C target is located on the luminal surface of intestinal epithelial cells. There is no available information regarding the area under the curve (AUC) and peak plasma concentrations (Cmax) as the concentrations of linaclotide and its active metabolite in plasma are below the limit of quantitation.
Toxicity
No information is available regarding the LD50 or overdose of linaclotide. Single linaclotide doses of 2897 mcg were administered to 22 healthy subjects; the safety profile in these subjects was consistent with that in the overall linaclotide-treated population, with diarrhea being the most commonly reported adverse reaction.
Description
In August 2012, the US FDA approved linaclotide (also referred to as MD-1100), a first-in-class, orally administered 14-amino acid peptide as a therapy for patients suffering from chronic idiopathic constipation (CIC) and irritable bowel syndrome with constipation (IBS-C). Linaclotide and its active metabolite MM-419447, which results from the cleavage of the C-terminal tyrosine residue by carboxypeptidase A, mimic the actions of the endogenous intestinal peptides guanylin (15 amino acids) and uroguanylin (16 amino acids) by activating guanylyl cyclase C (GC-C) on the intestinal epithelium. Activation of GC-C leads to increased intra- and extracellular levels of cGMP and activation of the CFTR ion channel, resulting in increased levels of HCO3-, Cl-, and water in the intestinal lumen and accelerated gastrointestinal transit. Based on an in vitro assaymeasuring the accumulation of cGMP in T84 cell exposed to an agonist, the EC50 of linaclotide at pH 7.0 was 99±17.5 nM. In preclinical studies in mice using the transit of activated charcoal as ameasure of efficacy, linaclotide at 100 μg/kg significantly accelerated transit compared to wild-type mice treated with charcoal only or GC-Cnullmice treatedwith and without linaclotide.118 Efficacy was also seen in rats treatedwith linaclotide atdoses of 5, 10, and 20 μg/kg. Linaclotide has been synthesized using conventional solid-phase peptide technology.
Originator
Ironwood Pharmaceuticals and Forest Pharmaceuticals (United States)
The Uses of Linaclotide
Linaclotide is a guanylate cyclase-C agonist currently being studied in Phase 3 trials for the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome with constipation.
Background
Linaclotide is a synthetic 14-amino acid cyclic peptide and first-in-class guanylate cyclase-C (G-CC) agonist. Linaclotide is structurally related to human guanylin and uroguanylin, paracrine peptide hormones that are endogenous activators of GC-C. It is also a homolog of a heat-stable enterotoxin derived from Escherichia coli, the first natural ligand that activates GC-C.
Linaclotide is used for the treatment of various types of constipation, including irritable bowel syndrome with constipation. Linaclotide was first approved by the FDA on August 30, 2012. It gained EMA and Health Canada approval on November 26, 2012 and December 3, 2013, respectively. Linaclotide works to improve the symptoms of constipation and gastrointestinal symptoms of conditions involving constipation.
Indications
Linaclotide is indicated for the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome with constipation in adults. This indication is approved in the US, Canada, and Europe.
In the US and Canada, it is also indicated for the treatment of chronic idiopathic constipation in adults.
In the US, it is also indicated for the treatment of functional constipation in pediatric patients 6 to 17 years of age.
Definition
ChEBI: Linaclotide is a fourteen-membered heterodetic cyclic peptide consisting of Cys, Cys, Glu, Tyr, Cys, Cys, Asn, Pro, Ala, Cys, Thr, Gly, Cys and Tyr residues joined in sequence and cyclised by three disulfide bonds: between Cys(1) and Cys(6), between Cys(2) and Cys(10), and between Cys(5) and Cys(13). Used for treatment of irritable bowel syndrome accompanied by constipation. It has a role as a guanylate cyclase 2C agonist.
brand name
Linzess
Biological Functions
Linaclotide works by increasing fluid in your intestines and helping speed up movement of food through the gut. Linaclotide may improve stool texture and lessen symptoms such as bloating, abdominal pain/discomfort, straining, and feelings of incomplete bowel movements.
Pharmacokinetics
Linaclotide is a laxative with visceral analgesic and secretory activities. In animal studies and clinical trials, linaclotide improved constipation and gastrointestinal symptoms in patients with irritable bowel syndrome with predominant constipation and chronic idiopathic constipation. In animal models, linaclotide has been shown to both accelerate gastrointestinal transit and reduce intestinal pain. In an animal model of visceral pain, linaclotide reduced abdominal muscle contraction and decreased the activity of pain-sensing nerves. Taking linaclotide with a high-fat meal results in looser stools and a higher stool frequency than taking it in the fasted state.
Linaclotide binds to its target, guanylate cyclase-C (GC-C), with high affinity and selectivity. Linaclotide and its active metabolite act locally on the luminal surface of the intestinal epithelium. As linaclotide is stable under a highly acidic pH environment, it acts in a pH-independent manner.
Side Effects
Side effects include:Diarrhea, abdominal pain, flatulence, abdominal distension, viral gastroenteritis, headache, upper respiratory tract infection, sinusitis
Metabolism
Linaclotide is metabolized in the small intestine, where it loses its C-terminal tyrosine moiety to form a principal active metabolite, MM-419447. The disulfide bonds of linaclotide and MM-419447 are reduced in the intestinal lumen, followed by proteolysis and degradation to form smaller peptides and naturally occurring amino acids which are absorbed through the intestine.
In rats in vitro, linaclotide was resistant to enzymatic hydrolysis by pepsin, trypsin, aminopeptidase or chymotrypsin.
Properties of Linaclotide
| Melting point: | 231-235°C (dec.) |
| Boiling point: | 2045.0±65.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.60 |
| storage temp. | Hygroscopic, Refrigerator, under inert atmosphere |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly, Heated), Methanol ((Slightly, Heated)), Water (Slightly, Heated) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 3.05±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | White |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
Safety information for Linaclotide
Computed Descriptors for Linaclotide
| InChIKey | KXGCNMMJRFDFNR-VRMHCMCOSA-N |
Linaclotide manufacturer
Anthem Biosciences Pvt Ltd
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 851199-59-2 Linaclotide 98%View Details
851199-59-2 Linaclotide 98%View Details
851199-59-2 -
 Linaclotide 98%View Details
Linaclotide 98%View Details -
 Linaclotide 99%View Details
Linaclotide 99%View Details
851199-59-2 -
 Linaclotide 851199-59-2 98%View Details
Linaclotide 851199-59-2 98%View Details
851199-59-2 -
 Linaclotide CAS 851199-59-2View Details
Linaclotide CAS 851199-59-2View Details
851199-59-2 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1