Rifaximin
Synonym(s):4-Deoxy-4′-methylpyrido[1′,2′-1,2]imidazo[5,4-c]rifamycin SV;Rifacol;Rifaximin
- CAS NO.:80621-81-4
- Empirical Formula: C43H51N3O11
- Molecular Weight: 785.89
- MDL number: MFCD00864973
- EINECS: 617-130-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-11-13 17:35:57
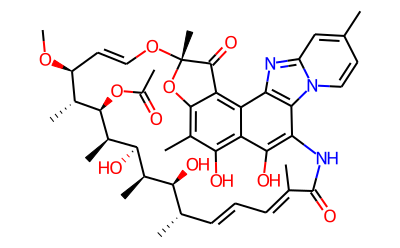
What is Rifaximin?
Absorption
Low absorption in both the fasting state and when administered within 30 minutes of a high-fat breakfast.
Toxicity
LD50 > 2 g/kg (orally, in rats)
Description
Rifaximin is an antibiotic structurally related to rifamycin. It is reported to be efficacious in the treatment of gastrointestinal infections and hepatic encephalopathy, being highly active against Gram-positive and -negative aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. Due to poor systemic absorption, rifaximin is effective in presurgical sterilization of the GI tract.It displays good activity against a wide spectrum of bacteria, including Salmonella spp., S. aureus, and E. coli.
Chemical properties
Red-Orange Crystalline Powder
Originator
Alfa (Italy)
The Uses of Rifaximin
Rifaximin is a non-absorbable semisynthetic Rifamycin antibiotic, antibacterial, RNA synthesis inhibitor, and Muscle Relaxant. It is also a Pregnane X receptor agonist and antibiotic that inhibits RNA synthesis and activates PXR.
Background
Rifaximin is a semisynthetic, rifamycin-based non-systemic antibiotic, meaning that the drug will not pass the gastrointestinal wall into the circulation as is common for other types of orally administered antibiotics. It has multiple indications and is used in treatment of traveller's diarrhea caused by E. coli; reduction in risk of overt hepatic encephalopathy recurrence; as well as diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome (IBS-D) in adult women and men. It is marketed under the brand name Xifaxan by Salix Pharmaceuticals.
Indications
Rifaximin has multiple indications by the FDA: for the treatment of patients (≥12 years of age) with traveller's diarrhea caused by noninvasive strains of Escherichia coli; for the reduction of overt hepatic encephalopathy recurrence in patients ≥18 years of age; and in May 2015 it was approved for irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea (IBS-D) treatment in adult men and women.
Definition
ChEBI: A semisynthetic member of the class of rifamycins and non-systemic gastrointestinal site-specific broad spectrum antibiotic. Used in the treatment of traveller's diarrhoea, hepatic encephalopathy and irritable bowel syndrome.
brand name
Xifaxan (Salix);Normix.
Antimicrobial activity
The in-vitro activity is slightly inferior to that of rifampicin. The MIC90 for Gram-positive cocci is well below 1 mg/L, with the exception of enterococci (MIC 2–8 mg/L). Among intestinal pathogens C. difficile is sensitive (MIC90 0.8 mg/L), Esch. coli, Salmonella spp. and Shigella spp. are inhibited by 4–8 mg/L. Campylobacter jejuni is mostly insensitive.
Pharmaceutical Applications
A semisynthetic derivative of rifamycin S formulated for oral administration. It is poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, where its high concentrations are effective against a variety of gastrointestinal pathogens.
Mechanism of action
Rifaximin is a structural analogue of rifampin and a non-systemic, gastrointestinal site-specific antibiotic. This non-systemic property of the drug is due to the addition of a pyridoimidazole ring, which renders it non-absorbable. Rifaximin inhibits bacterial ribonucleic acid (RNA) synthesis and contributes to restoring intestinal microflora imbalance. Other studies have also shown rifaximin as a pregnane X receptor (PXR) activator. As PXR is responsible for inhibiting the proinflammatory transcription factor NF-kappa B (NF-κB) and is inhibited in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), rifaximin was proven to be effective for the treatment of IBS-D.
Pharmacokinetics
Oral absorption is very low. However, a fraction of the dose may be absorbed and rapidly eliminated through the bile. A 400 mg oral dose produces a maximum plasma concentration of 3.8 mg/L after 1.2 h. The plasma half-life is 5.8 h. Up to 90% of the administered dose is concentrated in the gut, less than 0.2% in the liver and kidney, and less than 0.01% in other tissues.
Clinical Use
It is used for a variety of gastrointestinal diseases, including the treatment of traveler’s diarrhea. Preliminary results suggest clinical efficacy in the therapy of hepatic encephalopathy and of C. difficile infections.
Side Effects
Oral doses up to 100 mg/kg for 6 months produced no significant signs of toxicity to rats. Teratogenic effects in rats and rabbits have been reported (pregnancy category C).
Very few adverse effects were reported during human treatment, mostly gastrointestinal discomfort. Prolonged therapy was associated with infrequent urticarial skin reactions.
in vitro
rifaximin, a gut-specific ligand for the human nuclear receptor pregnane-x receptor (pxr), contributes to the maintenance of the intestinal immune homeostasis. rifaximin abrogates the binding of nf-κb caused by lps. in human colon biopsies from inflammatory bowel diseases patients, exposure of rifaximin (100 μm) reduced mrna levels of il-8, rantes, mip-3α and tnfα induced by lps stimulation [1]. rifaximin acted on the β subunit of the deoxyribonucleic acid (dna)-dependent ribonucleic acid (rna) polymerase enzyme of bacteria to inhibit bacterial rna synthesis. the susceptibility of gram-positive organisms to rifaximin was greater than that of gram-negative organisms [2]. in the dpx2 cell line transfected with stable recombinant human pxr expression, hpxr was significantly activated at rifax concentrations over 1 μm and the ec50 was about 20 μm[3].
in vivo
in the small intestine of hpxr mice treated with rifaximin, several pxr target genes such as cyp3a11, gsta1, mrp2, and oatp2 were up-regulated. rifaximin treatment demonstrated no significant effect on hepatic pxr target genes in wild-type, pxr-null, and hpxr mice [3]. in pxr-humanized mice, long-term administration of rifaximin for 6 months on the liver up-regulated the expression of hepatic genes related to triglyceride synthesis and lipid accumulation [4].
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Ciclosporin: concentration increased by ciclosporin.
Biologiacal activity
In vitro drug interaction studies have shown that rifaximin, at concentrations ranging from 2 to 200 ng/mL, did not inhibit human hepatic cytochrome P450 isoenzymes: 1A2, 2A6, 2B6, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, 2E1, and 3A4. In an in vitro hepatocyte induction model, rifaximin was shown to induce cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4), an isoenzyme that rifampin is known to cause.
Storage
-20°C
References
[1]. mencarelli a, renga b, palladino g, et al. inhibition of nf-κb by a pxr-dependent pathway mediates counter-regulatory activities of rifaximin on innate immunity in intestinal epithelial cells[j]. european journal of pharmacology, 2011, 668(1): 317-324.
[2]. gillis j c, brogden r n. rifaximin[j]. drugs, 1995, 49(3): 467-484.
[3]. ma x, shah y m, guo g l, et al. rifaximin is a gut-specific human pregnane x receptor activator[j]. journal of pharmacology and experimental therapeutics, 2007, 322(1): 391-398.
[4]. cheng j, krausz k, tanaka n, et al. chronic exposure to rifaximin causes hepatic steatosis in pregnane x receptor-humanized mice[j]. toxicological sciences, 2012: kfs211.
[5]. bass n m, mullen k d, sanyal a, et al. rifaximin treatment in hepatic encephalopathy[j]. new england journal of medicine, 2010, 362(12): 1071-1081.
[6]. pimentel m, lembo a, chey w d, et al. rifaximin therapy for patients with irritable bowel syndrome without constipation[j]. new england journal of medicine, 2011, 364(1): 22-32.
[7]. sharara a i, aoun e, abdul-baki h, et al. a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial of rifaximin in patients with abdominal bloating and flatulence[j]. the american journal of gastroenterology, 2006, 101(2): 326-333.
Properties of Rifaximin
| Melting point: | 200-2050C (dec) |
| Density | 1.36±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Store in freezer, under -20°C |
| solubility | ethanol: soluble1mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| pka | 2.83±0.70(Predicted) |
| color | dark orange |
| Merck | 14,8220 |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
Safety information for Rifaximin
Computed Descriptors for Rifaximin
| InChIKey | NZCRJKRKKOLAOJ-XRCRFVBUSA-N |
Rifaximin manufacturer
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 Rifaximin 99%View Details
Rifaximin 99%View Details -
 Rifaximin 98%View Details
Rifaximin 98%View Details -
 Rifaximin 98%View Details
Rifaximin 98%View Details
80621-81-4 -
 Rifaximin 80621-81-4 99%View Details
Rifaximin 80621-81-4 99%View Details
80621-81-4 -
 Rifaximin 96% CAS 80621-81-4View Details
Rifaximin 96% CAS 80621-81-4View Details
80621-81-4 -
 Rifaximin CAS 80621-81-4View Details
Rifaximin CAS 80621-81-4View Details
80621-81-4 -
 Rifaximin CAS 80621-81-4View Details
Rifaximin CAS 80621-81-4View Details
80621-81-4 -
 Rifaximin Api Powder, USPView Details
Rifaximin Api Powder, USPView Details
80621-81-4
