Ziconotide Polyacetate
Synonym(s):SNX-111;Ziconotide
- CAS NO.:107452-89-1
- Empirical Formula: C102H172N36O32S7
- Molecular Weight: 2639.13
- MDL number: MFCD00145036
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-10-23 13:36:13
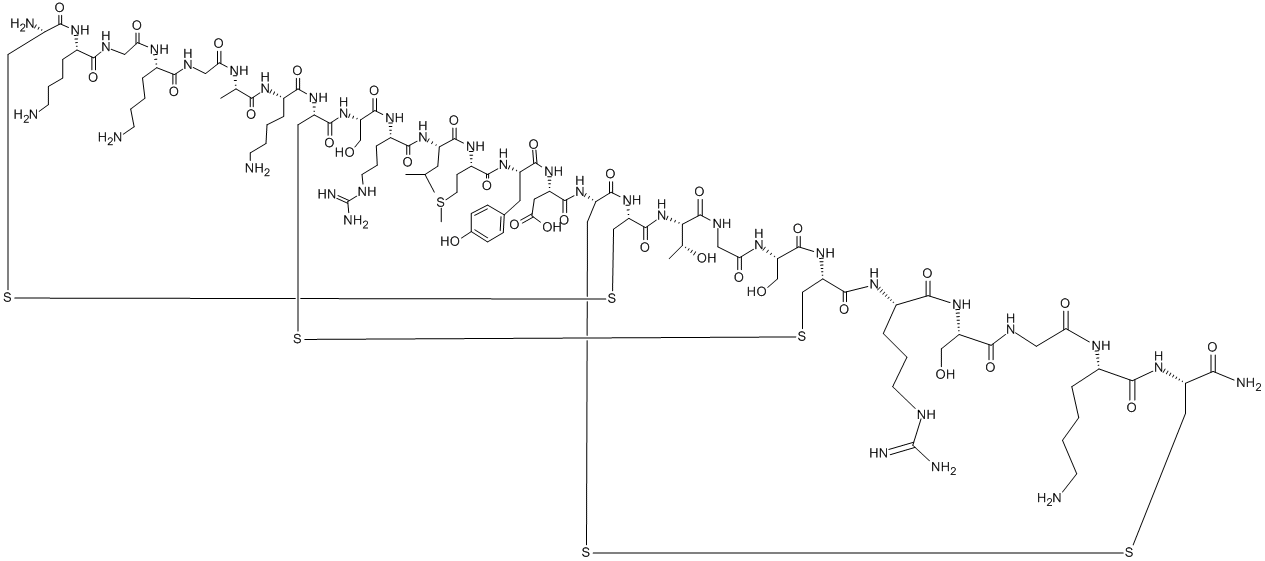
What is Ziconotide Polyacetate?
Absorption
Ziconotide administered intrathecally over one hour in doses between 1 and 10 mcg produced calculated AUC values between 83.6-608 ng*h/mL and Cmax between 16.4-132 ng/mL; these values are approximately dose-proportional. Given the intrathecal administration and low membrane permeability due to its size, ziconotide is expected to remain primarily in the CSF; plasma levels, where detected, remain constant up to nine months following administration.
Toxicity
Symptoms of overdose include neurological effects such as ataxia, nystagmus, stupor, sedation, speech difficulties, dizziness, nausea, and vomiting, and may also cause other effects such as hypotension; overdose is not associated with respiratory depression. In case of overdose, symptom-related supportive care up to and including hospitalization is recommended. Ziconotide has no known antidote, but the withdrawal of ziconotide generally allows patients to clear the drug and recover within 24 hours. As ziconotide does not bind to opiate receptors, opioid antagonists are not effective at ameliorating overdose effects.
Description
ω-conotoxin MVIIA, also knwn as Ziconotide acetate, is a peptide consisting of 25 amino acid. It is a disulfide-bridged polypeptide from the venom of the sea snail Conusmagus that binds to neuronal N-type calcium channels. It forms a compact folded structure, presenting a loop between Cys8 and Cys15 that contains a set of residues critical for its binding. Both ω-conotoxins GVIA and MVIIA could bind to neuronal N-type calcium channels. ω-conotoxin GVIA is rich in hydroxyl groups while ω-conotoxin MVIIA contains a large number of positively charged side chains[1-2].
The Uses of Ziconotide Polyacetate
Ligand for binding studies of voltage sensitive calcium channels.
The Uses of Ziconotide Polyacetate
Ziconotide acetate (ω-Conotoxin MVIIA), the peptide toxin of the Conus magus (cone snail) is a selective antagonist of N-type voltage sensitive calcium channels (VSCC). As a most well-known identified conotoxin so far, it has been used as a effective drug to treat intractable chronic pain in cancer and ADIS patients[2]. Blocks neurotransmitter release by preventing depolarization-induced calcium influx. Used as a ligand for binding studies of voltage sensitive calcium channels. Analgesic; neuroprotective.
Indications
Ziconotide is indicated for the management of severe chronic pain in patients refractory to other treatments, and for whom intrathecal therapy is warranted.
Background
Ziconotide (also known as SNX-111) is a neurotoxic peptide derived from the cone snail Conus magus comprising 25 amino acids with three disulphide bonds. Other such peptides, collectively termed conotoxins, exist, and some have shown efficacy in binding specific subsets of calcium channels; ziconotide is used in part because it can be synthesized without loss of proper bond formation or structural elements. Ziconotide is used to manage severe chronic pain refractory to other methods, through its ability to inhibit N-type calcium channels involved in nociceptive signalling.
Ziconotide was granted FDA approval on December 28, 2004 for marketing by TerSera therapeutics LLC. under the name Prialt. To date, ziconotide is the only calcium channel blocking peptide approved for use by the FDA.
What are the applications of Application
Ziconotide Polyacetate is a selective antagonist of N-type voltage sensitive calcium channels (VSCC)
brand name
Prialt (Elan).
General Description
ω-Conotoxin MVIIA functions as a selective inhibitor of N-type voltage-sensitive calcium channels (VSCCs). It has analgesic and neuroprotective effects. ω-Conotoxin MVIIA is used to treat neuropathic pain.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Neuronal N-type Ca2+ channel blocker in mammalian and amphibian brain; blocks release of GABA and glutamate at neuronal synapses.
Pharmacokinetics
Ziconotide inhibits N-type calcium channels involved in nociceptive signalling, primarily in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord. Although binding is reversible, careful dosing is required to ensure therapeutic effects while minimizing adverse effects, and ziconotide has been described as possessing a narrow therapeutic window. Patients taking ziconontide may experience cognitive and neuropsychiatric symptoms, reduced levels of consciousness, and elevated serum creatine kinase levels. In addition, ziconotide may increase the risk of infection, including serious cases of meningitis. Patients who withdraw from opiates for ziconotide initiation are advised to taper off the dose.
Metabolism
Ziconotide is expected to be processed by various peptidases upon entering systemic circulation; no detailed information on ziconotide metabolism has been reported.
References
[1] Wang R, et al. Development of an ic-ELISA and immunochromatographic strip based on IgG antibody for detection of ω-conotoxin MVIIA. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2019; 378: 120510.
[2] Zhou Y, et al. A Chemoenzymatic Approach To Produce a Cyclic Analogue of the Analgesic Drug MVIIA (Ziconotide). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2023; 62: e202302812.
Properties of Ziconotide Polyacetate
| Density | 1.60±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly, Sonicated), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to Off-White |
Safety information for Ziconotide Polyacetate
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P403+P233:Store in a well-ventilated place. Keep container tightly closed. |
Computed Descriptors for Ziconotide Polyacetate
| InChIKey | BPKIMPVREBSLAJ-QTBYCLKRSA-N |
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1